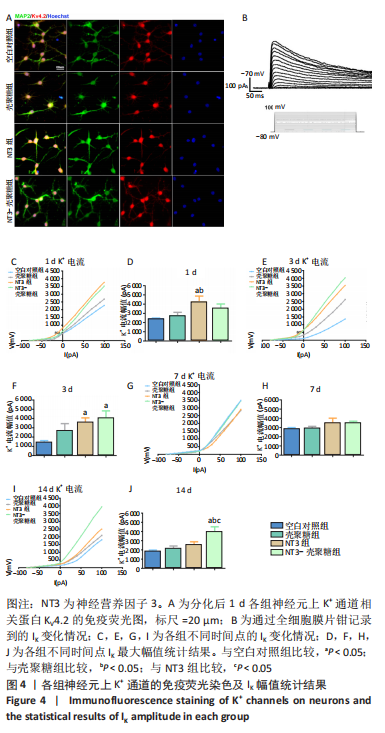
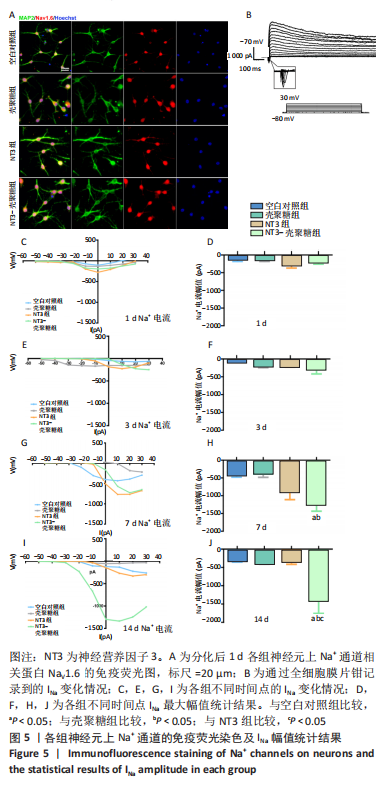
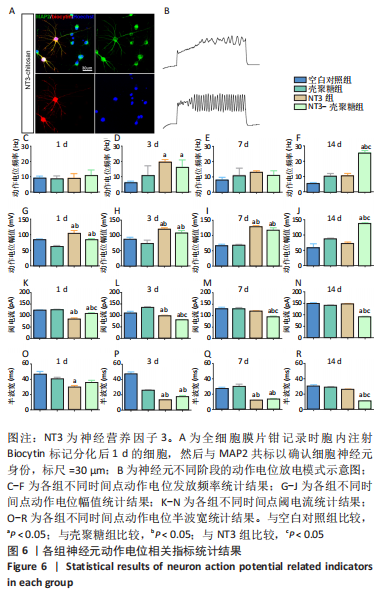
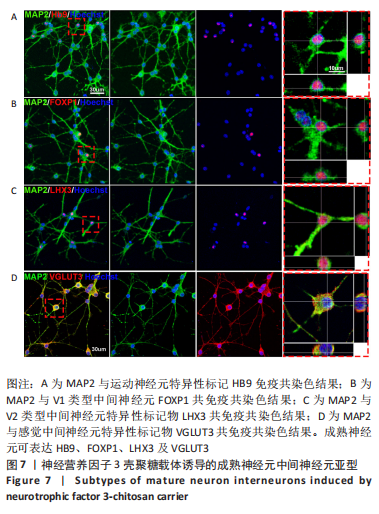
[1] REYNOLDS BA, WEISS S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science (New York, NY). 1992;255(5052):1707-1710.
[2] LI L, CLEVERS H. Coexistence of Quiescent and Active Adult Stem Cells in Mammals. Science. 2010;327(5965):542-545.
[3] NAIK PP, BIRBRAIR A, BHUTIA SK. Mitophagy-driven metabolic switch reprograms stem cell fate. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(1):27-43.
[4] DUAN H, LI X, WANG C, et al. Functional hyaluronate collagen scaffolds induce NSCs differentiation into functional neurons in repairing the traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2016;45:182-195.
[5] ZHU Y, UEZONO N, YASUI T, et al. Neural stem cell therapy aiming at better functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Dev Dyn. 2018; 247(1):75-84.
[6] LIPPERT T, GELINEAU L, NAPOLI E, et al. Harnessing neural stem cells for treating psychiatric symptoms associated to fetal alcohol spectrum disorder and epilepsy. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017;30(Pt A):10-22.
[7] SUZUKI H, AHUJA CS, SALEWSKI RP, et al. Neural stem cell mediated recovery is enhanced by Chondroitinase ABC pretreatment in chronic cervical spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0182339.
[8] KOUTSOUDAKI PN, PAPASTEFANAKI F, STAMATAKIS A, et al. Neural stem/progenitor cells differentiate into oligodendrocytes, reduce inflammation, and ameliorate learning deficits after transplantation in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. Glia. 2016;64(5):763-779.
[9] SHETTY AK. Hippocampal injury-induced cognitive and mood dysfunction, altered neurogenesis, and epilepsy: Can early neural stem cell grafting intervention provide protection? Epilepsy Behav. 2014;38:117-124.
[10] ZHANG ML, ZHANG XJ, KANG J, et al. Matrine promotes NT3 expression in CNS cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurosci Lett. 2017;649:100-106.
[11] YANG Z, ZHANG A, DUAN H, et al. NT3-chitosan elicits robust endogenous neurogenesis to enable functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(43):13354-13359.
[12] YANG Z, DUAN H, MO L, et al. The effect of the dosage of NT-3/chitosan carriers on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(18):4846-5448.
[13] LI X, YANG Z, ZHANG A. The effect of neurotrophin-3/chitosan carriers on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials. 2009;30(28):4978-4985.
[14] CALDEIRA V, DOUGHERTY KJ, BORGIUS L, et al. Spinal Hb9::Cre-derived excitatory interneurons contribute to rhythm generation in the mouse. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41369.
[15] MORIKAWA Y, KOMORI T, HISAOKA T, et al. Detailed Expression Pattern of Foxp1 and Its Possible Roles in Neurons of the Spinal Cord during Embryogenesis. Dev Neurosci. 2009;31(6):511-522.
[16] MORIKAWA Y, HISAOKA T, SENBA E. Characterization of Foxp2-expressing cells in the developing spinal cord. Neuroscience. 2009; 162(4):1150-1162.
[17] LEE B, LEE S, AGULNICK AD, et al. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins are required for LIM complexes to induce transcriptionally active chromatin and specify spinal neuronal identities. Development. 2016;143(10):1721-1731.
[18] FRANCIUS C, HIDALGO-FIGUEROA M, DEBRULLE S, et al. Vsx1 Transiently Defines an Early Intermediate V2 Interneuron Precursor Compartment in the Mouse Developing Spinal Cord. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016;9:145.
[19] SHARMA K, SHENG HZ, LETTIERI K, et al. LIM homeodomain factors Lhx3 and Lhx4 assign subtype identities for motor neurons. Cell. 1998; 95(6):817-828.
[20] SAKAI K, SANDERS KM, LIN SH, et al. Low-Threshold Mechanosensitive VGLUT3-Lineage Sensory Neurons Mediate Spinal Inhibition of Itch by Touch. J Neurosci. 2020;40(40):7688-7701.
[21] LU H, LI M, SONG T, et al. Retrovirus delivered neurotrophin-3 promotes survival, proliferation and neuronal differentiation of human fetal neural stem cells in vitro. Brain Res Bull. 2008;77(4):158-164.
[22] YUAN SH, MARTIN J, ELIA J, et al. Cell-Surface Marker Signatures for the Isolation of Neural Stem Cells, Glia and Neurons Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. PloS One. 2011;6(3):e17540.
[23] ZHANG J, JIAO J. Molecular Biomarkers for Embryonic and Adult Neural Stem Cell and Neurogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2015:727542.
[24] FRIOCOURT G, KOULAKOFF A, CHAFEY P, et al. Doublecortin Functions at the Extremities of Growing Neuronal Processes. Cerebral Cortex. 2003;13(6):620-626.
[25] GUPTE RP, KADUNGANATTIL S, SHEPHERD AJ, et al. Convergent Phosphomodulation of the Major Neuronal Dendritic Potassium Channel Kv4.2 by Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-activating Polypeptide. Neuropharmacology. 2016;101:291-308.
[26] KIM DM, NIMIGEAN CM. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels: A Structural Examination of Selectivity and Gating. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8(5):a029231.
[27] XIAO F, ZHANG X, NI P, et al. Voltage-dependent potassium channel Kv 4.2 alleviates the ischemic stroke impairments through activating neurogenesis. Neurochem Int. 2021;150:105155.
[28] O’BRIEN JE, MEISLER MH. Sodium channel SCN8A (Nav1.6): properties and de novo mutations in epileptic encephalopathy and intellectual disability. Front in Genet. 2013;4:213.
[29] WANG X, ZHANG XG, ZHOU TT, et al. Elevated Neuronal Excitability Due to Modulation of the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Nav1.6 by Aβ1−42. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:94.
[30] ZYBURA AS, BAUCUM AJ 2ND, RUSH AM, et al. CaMKII enhances voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.6 activity and neuronal excitability. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(33):11845-11865.
[31] BEAN BP. The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(6):451-465.
[32] KIEHN O. Decoding the organization of spinal circuits that control locomotion. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016;17(4):224-238.
[33] ZHOLUDEVA LV, ABRAIRA VE, SATKUNENDRARAJAH K, et al. Spinal Interneurons as Gatekeepers to Neuroplasticity after Injury or Disease. J Neurosci. 2021;41(5):845-854.
[34] KUMAMARU H, LU P, ROSENZWEIG ES, et al. Regenerating Corticospinal Axons Innervate Phenotypically Appropriate Neurons within Neural Stem Cell Grafts. Cell Rep. 2019;26(9):2329-2339.e4.
|