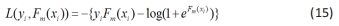[1] 史力民, 马建平.足迹学[M].北京:中国人民公安大学出版社, 2014.
[2] BULDT AK, FORGHANY S, LANDORF KB, et al. Foot posture is associated with plantar pressure during gait: A comparison of normal, planus and cavus feet. Gait Posture. 2018;62:235-240.
[3] ELATAAR FF, ABDELMAJEED SF, ABDELLATIF N, et al. Core muscles’ endurance in flexible flatfeet: A cross -sectional study. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(3):404-410.
[4] FLORES DV, MEJÍA GÓMEZ C, FERNÁNDEZ HERNANDO M, et al. Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity: Anatomy, Biomechanics, Staging, and Imaging Findings. Radiographics. 2019;39(5):1437-1460.
[5] 王新亭,徐聃弟,张峻霞,等.不同足弓结构负重跨障的稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(24):3838-3843.
[6] PHAN CB, LEE KM, KWON SS, et al. Kinematic instability in the joints of flatfoot subjects during walking: A biplanar fluoroscopic study. J Biomech. 2021;127:110681.
[7] 张新语,邢新阳,霍洪峰.矫正鞋垫的设计原理与生物力学功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(23):3744-3750.
[8] 周湘莹,曾庆,廖政文,等.定制型矫形鞋垫在扁平足治疗中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4810-4816.
[9] YAN S, LI R, SHI B, et al. Mixed factors affecting plantar pressures and center of pressure in obese children: Obesity and flatfoot - ScienceDirect. Gait Posture. 2020;80:7-13.
[10] BURNS J, CROSBIE J, HUNT A, et al. The effect of pes cavus on foot pain and plantar pressure. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2005;20(9):877-882.
[11] 王新亭,王琪,徐聃弟,等.基于BP神经网络的高足弓异常程度评价模型的构建[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2021,40(2):252-256.
[12] KOUCHI M, KIMURA M, MOCHIMARU M. Deformation of foot cross-section shapes during walking. Gait Posture. 2009;30(4):482-486.
[13] NAGAHISA T, TAJIRI K, FUNAKOSHI O, et al. Considerations in arch support-development of a pressure device for plantar arch. Kutsu no Igaku (Medical Study of Footwear). 1990;10:51-55 (in Japanese).
[14] HAN K, BAE K, LEVINE N, et al. Biomechanical Effect of Foot Orthoses on Rearfoot Motions and Joint Moment Parameters in Patients with Flexible Flatfoot. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:5920-5928.
[15] KIM JS, LEE MY. The effect of short foot exercise using visual feedback on the balance and accuracy of knee joint movement in subjects with flexible flatfoot. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(13):e19260.
[16] 林锡乾, 董纪文, 傅霆. 幼儿、儿童、少年足弓指数测定及其分析[J]. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版),1994,23(3):101-105.
[17] MURLEY GS, MENZ HB, LANDORF KB. A protocol for classifying normal- and flat-arched foot posture for research studies using clinical and radiographic measurements. J Foot Ankle Res. 2009;2:22.
[18] 陈晓忠,胡丰涵,陆纯明.172例采用横仓氏法测量足弓角的伤残评定[J].中国法医学杂志,2013,28(S1):84-85.
[19] 鲍文霞,梁栋.结合无符号Laplace谱特征的触觉步态识别算法[J].计算机工程与应用,2016,52(1):214-218.
[20] 潘国建.足弓的测量及其分析[J].中国康复医学杂志,2005,20(10): 759-760.
[21] 邱海,熊树平,孙娜,等.人体足弓类型评价参数自动提取、可靠性分析及分类结果一致性研究[J].人类工效学,2012,18(1):21-25+6.
[22] 弓太生,韩珵琨,汤运启,等.扁平足儿童足弓支撑垫的设计与研究[J].中国皮革,2018,47(3):38-41.
[23] WANG CL, LI ZR, NILANJAN D, et al. Histogram of Oriented Gradient Based Plantar Pressure Image Feature Extraction and Classification Employing Fuzzy Support Vector Machine. J Med Imaging Health Inform. 2018;8(4). info:doi/10.1166/jmihi.2018.2310
[24] ZHANG Y, LIANG D, ZHU M, et al. Identity recognition of plantar pressure image based on compressed sensing//International Conference on Mechatronic Sciences, Electric Engineering and Computer: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. 2013: 3128-3131.
[25] 梁栋,高玮玮,张艳,等.基于足底压力图像的静态触觉步态识别[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2013,41(10):25-29.
[26] 王年,樊旭晨,张玉明,等. 基于足迹图像的FtH-Net预测身高方法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(6):106-113,133.
[27] 王军,徐新智,张伟,等. 足底压力动态图像分析系统与临床应用[J]. 中国临床康复,2002,6(6):802-803.
[28] 王军,徐新智.足底压力图像分析系统及骨科应用[J].第四军医大学学报,2001,22(11):990.
[29] LI B, XIANG Q, ZHANG X. The center of pressure progression characterizes the dynamic function of high-arched feet during walking. J Leath Sci Eng. 2020;2(1):1.
[30] ZHANG SL, WANG JY, LI XJ, et al. M6A-GSMS: Computational identification of N6-methyladenosine sites with GBDT and stacking learning in multiple species. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021;30:1-12.
[31] ZHOU LQ, WANG Z, TIAN XF, et al. LPI-deepGBDT: a multiple-layer deep framework based on gradient boosting decision trees for lncRNA-protein interaction identification. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021;22(1):479.
[32] 何泊延. 基于GBDT的数据分类方法的研究及其应用[D].吉林:东北电力大学,2021.
[33] ABHAY SHARMA. Understanding RGB Color Spaces for Monitors, Projectors, and Televisions. Frontline Technology. 2019;35(2):17-43.
[34] LI YT, LIU N, XU J, et al. Detail enhancement of infrared image based on bi-exponential edge preserving smoother. Optik. 2019;199:163300.
[35] 张月芳. 足印法测量足弓与足侧位X光片测量足弓的对比[J]. 解剖学杂志,1985(4):63-65.
[36] CHU WC, LEE SH, CHU W, et al. The use of arch index to characterize arch height: a digital image processing approach. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1995;42(11):1088-1093.
[37] CHUN S, KONG S, MUN KR,et al. A Foot-Arch Parameter Measurement System Using a RGB-D Camera. Sensors (Basel). 2017;17(8):1796.
[38] MENG Y, ZHU H, KWOK CY, et al. Effect of coefficient of friction on arch network in shearing process under low confinement. Powder Technology. 2018;335(15):1-10.
[39] 喻大力. 二维静态足印评价内侧纵弓的效度检验及运动员足印的特点[D].上海:上海体育学院,2016.
[40] 赵碎浪,杨峰,傅陆军,等.足型分类方法研究进展[J].中国皮革, 2020,49(7):7-12.
|

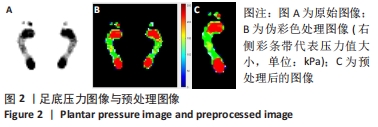


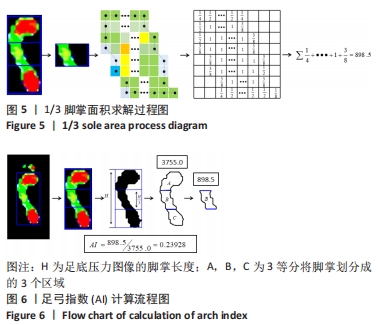
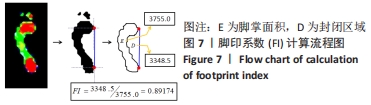
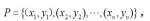 找到这些像素点的最小外接四边形,并获取矩形左上角点的坐标(x,y),矩形的高H和宽W,以及倾斜角度θ,旋转至矩形成竖直方向,同时足底图像的内容也得到摆正,实现去脚趾操作。脚掌分区采用划分矩形的方法,对矩形沿H三等分将脚掌划分成3个区域。分别提取脚掌轮廓和脚掌中间1/3的轮廓,并计算两部分的轮廓面积,轮廓线由N个顶点组成,也即像素点集P,这些顶点的位置是对应像素点的中心值,图5所示为中间1/3脚掌轮廓面积的求解过程,脚掌面积同理。最后计算足弓指数,并根据足弓指数的取值区间输出足型,见图6。
找到这些像素点的最小外接四边形,并获取矩形左上角点的坐标(x,y),矩形的高H和宽W,以及倾斜角度θ,旋转至矩形成竖直方向,同时足底图像的内容也得到摆正,实现去脚趾操作。脚掌分区采用划分矩形的方法,对矩形沿H三等分将脚掌划分成3个区域。分别提取脚掌轮廓和脚掌中间1/3的轮廓,并计算两部分的轮廓面积,轮廓线由N个顶点组成,也即像素点集P,这些顶点的位置是对应像素点的中心值,图5所示为中间1/3脚掌轮廓面积的求解过程,脚掌面积同理。最后计算足弓指数,并根据足弓指数的取值区间输出足型,见图6。

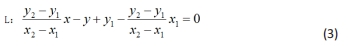


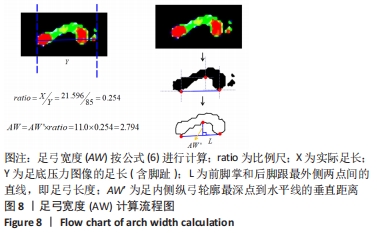

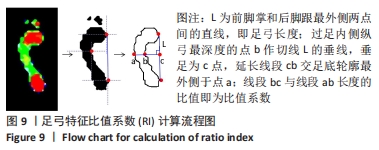


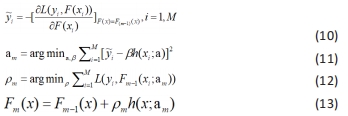
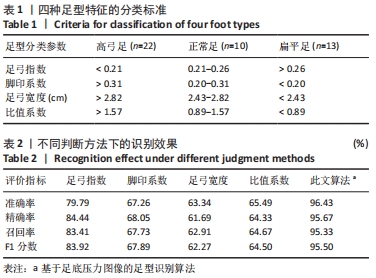
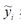 指损失函数的负梯度在当前模型的值,每颗回归树需要拟合的目标;am为最优的基分类器;ρm为最优的学习率;Fm(x)为加法模型更新m次后的模型。
指损失函数的负梯度在当前模型的值,每颗回归树需要拟合的目标;am为最优的基分类器;ρm为最优的学习率;Fm(x)为加法模型更新m次后的模型。
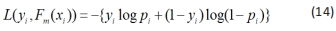
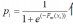 代入上式可得简化后的损失函数如(15)式。
代入上式可得简化后的损失函数如(15)式。