[1] MANCHIKANTI L, KOSANOVIC R, CASH KA, et al. Assessment of Prevalence of Cervical Facet Joint Pain with Diagnostic Cervical Medial Branch Blocks: Analysis Based on Chronic Pain Model.Pain Physician. 2020;23(6):531-540.
[2] WILSON JR, VACCARO A, HARROP JS, et al. The impact of facet dislocation on clinical outcomes after cervical spinal cord injury: results of a multicenter North American prospective cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(2):97-103.
[3] WANG HH, WANG K, DENG Z, et al. Effects of facet joint degeneration on stress alterations in cervical spine C5-C6: A finite element analysis. Math Biosci Eng. 2019;16(6):7447-7457.
[4] LEE SH, SON DW, LEE JS, et al. Relationship Between Endplate Defects, Modic Change, Facet Joint Degeneration, and Disc Degeneration of Cervical Spine. Neurospine. 2020;17(2):443-452.
[5] YANG G, BATTIÉ MC, BOYD SK, et al. Cranio-caudal asymmetries in trabecular architecture reflect vertebral fracture patterns. Bone. 2017; 95:102-107
[6] PALEPU V, RAYAPROLU SD, NAGARAJA S. Differences in Trabecular Bone, Cortical Shell, and Endplate Microstructure Across the Lumbar Spine. Int J Spine Surg. 2019;13(4):361-370.
[7] AUGER JD, FRINGS N, WU Y, et al. Trabecular Architecture and Mechanical Heterogeneity Effects on Vertebral Body Strength. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(6):716-726.
[8] GUHA I, KLINTSTRÖM B, KLINTSTRÖM E, et al. A comparative study of trabecular bone micro-structural measurements using different CT modalities. Phys Med Biol. 2020 ,doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/abc367.
[9] ECKSTEIN F, FISCHBECK M, KUHN V, et al. Determinants and heterogeneity of mechanical competence throughout the thoracolumbar spine of elderly women and men. Bone. 2004;35(2): 364-374.
[10] O’LEARY SA, PASCHOS NK, LINK JM, et al. Facet Joints of the Spine: Structure-Function Relationships, Problems and Treatments, and the Potential for Regeneration. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2018;6(20):145-170.
[11] XIAO ZF, HE JB, SU GY, et al. Osteoporosis of the vertebra and osteochondral remodeling of the endplate causes intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1): 207.
[12] WANG HH, WANG K, DENG Z, et al. Effects of facet joint degeneration on stress alterations in cervical spine C5-C6: A finite element analysis. Math Biosci Eng. 2019;16(6):7447-7457.
[13] SABET FA, JIN O, KORIC S, et al. Nonlinear micro-CT based FE modeling of trabecular bone-Sensitivity of apparent response to tissue constitutive law and bone volume fraction. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2018;34(4):e2941.
[14] YAMADA S, CHIBA K, OKAZAKI N, et al. Correlation between vertebral bone microstructure and estimated strength in elderly women: An ex-vivo HR-pQCT study of cadaveric spine. Bone. 2019;120:459-464.
[15] RIEGER R, AUREGAN JC, HOC T. Micro-finite-element method to assess elastic properties of trabecular bone at micro- and macroscopic level. Morphologie. 2018;102(336):12-20.
[16] BARRETT JM, MCKINNON C, CALLAGHAN JP. Cervical spine joint loading with neck flexion. Ergonomics. 2020;63(1):101-108.
[17] GAUTHIER R, LANGER M, FOLLET H,et al. 3D micro structural analysis of human cortical bone in paired femoral diaphysis, femoral neck and radial diaphysis. J Struct Biol. 2018;204(2):182-190.
[18] POPIELUSZKO P, HENRY BM, SANNA B,et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of variations in branching patterns of the adult aortic arch. J Vasc Surg. 2018;68(1):298-306.
[19] VURAL A, DERIN ÇIÇEK EE. Is the asymmetry between the vertebral arteries related to cerebral dominance? Turk J Med Sci. 2019;49(6): 1721-1726.
[20] VITOSEVIC F, RASULIC L, MEDENICA SM. Morphological Characteristics of the Posterior Cerebral Circulation:An Analysis Based on Non-Invasive Imaging. Turk Neurosurg. 2019;29(5):625-630.
[21] GONG H, ZHANG M, YEUNG HY, et al. Regional variations in microstructural properties of vertebral trabeculae with aging. J Bone Miner Metab. 2005;23(2):174-180.
[22] REINA N, CAVAIGNAC E, PAILHE R, et al. BMI-related microstructural changes in the tibial subchondral trabecular bone of patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2017;5(8):1653-1660.
[23] GREENWOOD C, CLEMENT JG, DICKEN AJ, et al. The micro-architecture of human cancellous bone from fracture neck of femur patients in relation to the structural integrity and fracture toughness of the tissue. Bone Rep. 2015;3:67-75.
[24] LI S, WANG C, SHAN Z, et al. Trabecular Microstructure and Damage Affect Cement Leakage From the Basivertebral Foramen During Vertebral Augmentation. Spine. 2017;42(16):939-948.
[25] BARON EM, YOUNG WF. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a brief review of its pathophysiology, clinical course, and diagnosis. Neurosurgery. 2007;60(11):35-41.
[26] LIU XS, SAJDA P, SAHA PK, et al. Quantification of the roles of trabecular microarchitecture and trabecular type in determining the elastic modulus of human trabecular bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21(10):1608-1617.
[27] LIU XS, STEIN EM, ZHOU B, et al. Individual trabecula segmentation (ITS)-based morphological analyses and microfinite element analysis of HR-pQCT images discriminate postmenopausal fragility fractures independent of DXA measurements. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(2): 263-272.
[28] LIU XS, SAJDA P, SAHA PK, et al. Complete volumetric decomposition of individual trabecular plates and rods and its morphological correlations with anisotropic elastic moduli in human trabecular bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(2):223-235.
[29] LIU XS, COHEN A, SHANE E, et al. Individual trabeculae segmentation (ITS)-based morphological analysis of high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography images detects abnormal trabecular plate and rod microarchitecture in premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(7):1496-1505.
[30] RIEGER R, AUREGAN JC, HOC T. Micro-finite-element method to assess elastic properties of trabecular bone at micro- and macroscopic level. Morphologie. 2018;102(336):12-20.
[31] FUGGLE NR, CURTIS EM, WARD KA, et al. Fracture prediction, imaging and screening in osteoporosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(9): 535-547.
[32] HULME PA, BOYD SK, FERGUSON SJ. Regional variation in vertebral bone morphology and its contribution to vertebral fracture strength. Bone. 2007;41(6):946-957.
(责任编辑:GD,ZN,ZH)
|
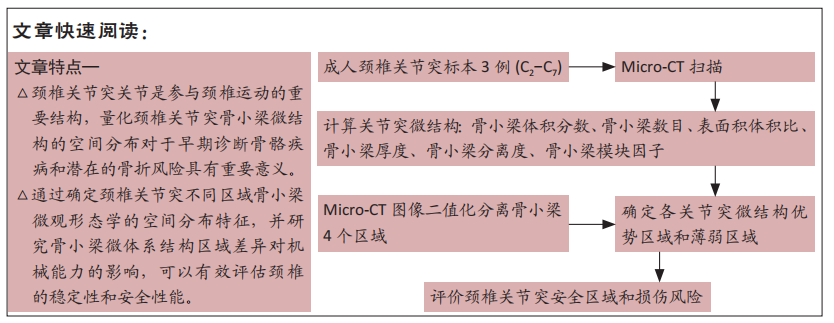
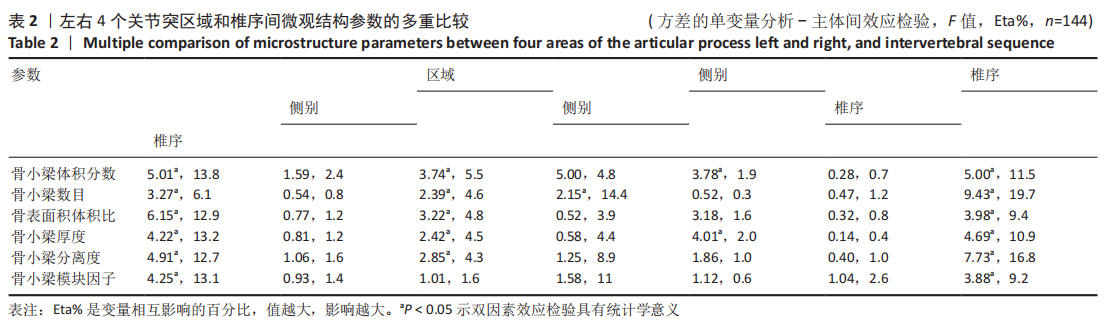


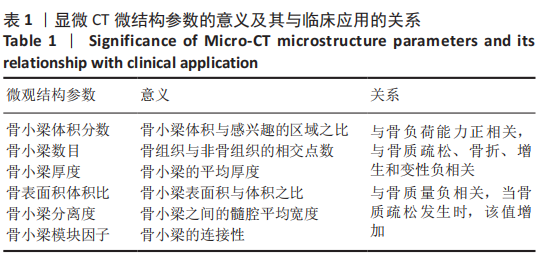
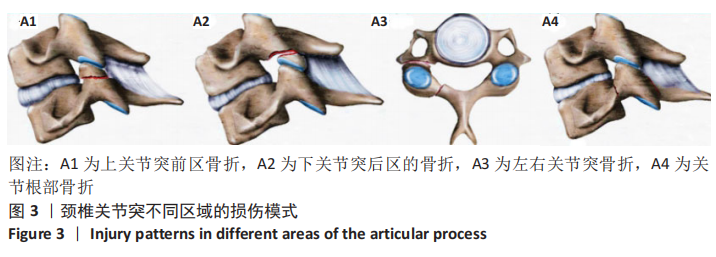 不同椎序及左右关节突对整个颈椎生理活动的贡献不同,C2-C7关节突和各区域骨小梁体积分数最大和最小值分别为C5和C7的上前和上后区域;对于骨小梁数目和骨小梁厚
不同椎序及左右关节突对整个颈椎生理活动的贡献不同,C2-C7关节突和各区域骨小梁体积分数最大和最小值分别为C5和C7的上前和上后区域;对于骨小梁数目和骨小梁厚