| [1] Huckle J, Dootson G, Medcalf N, et al. Differentiated chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering. Novartis Found Symp.2003;249: 103-112. [2] 安勇,王丹亭,岳宏.基质诱导的自体软骨细胞移植治疗膝关节软骨损伤的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2017,46(7):177-180. [3] Min BH,Choi WH,Lee YS,et al.Effect of different bone marrow stimulation techniques (BSTs) on MSCs mobilization.J Orthop Res. 2013;31(11):1814-1819. [4] Bedi A,Feeley BT,Williams RJ 3rd.Management of articular cartilage defects of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(4): 994-1009. [5] Chiang H,Liao CJ,Wang YH,et al.Comparison of articular cartilage repair by autologous chondrocytes with and without in vitro cultivation.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(2):291-300. [6] Langer R,Vacanti JP.Tissue Engineering.Science. 2000;260(5110): 920-926. [7] 神艳.骺板软骨组织工程支架的研究进展[J].中华小儿外科杂志, 2015, 36(5):397-400. [8] 张柏青,张仲文,孙磊.Ⅱ型胶原修饰脱细胞真皮基质胶原膜修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):871-876. [9] 陈维明.明胶/聚乳酸纳米纤维三维多孔支架的制备及应用于关节软骨组织再生[D].上海:东华大学,2017. [10] 李奇龙.一种光聚合PEGDA-HA水凝胶递送纳米粒药物用于非小细胞肺癌的治疗[D].上海:华东师范大学,2017. [11] 刘环宇,叶静仪,梁佩莹.水凝胶的制备[J].化工时刊, 2014,28(1):11-14. [12] 朱文,段世锋,丁建东.组织工程用水凝胶材料[J].功能高分子学报, 2004, 17(4):689-697. [13] Ninan N,Forget A,Shastri VP,et al.Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory pH-Responsive Tannic Acid-Carboxylated Agarose Composite Hydrogels for Wound Healing.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(42):28511-28521. [14] Singh YP,Bhardwaj N,Mandal BB.Potential of Agarose/Silk Fibroin Blended Hydrogel for in Vitro Cartilage Tissue Engineering.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(33):21236-21249. [15] Zheng L,Sun J,Chen X,et al.In vivo cartilage engineering with collagen hydrogel and allogenous chondrocytes after diffusion chamber implantation in immunocompetent host.Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(8): 2145-2153. [16] Chao PH,Yodmuang S,Wang X,et al.Silk hydrogel for cartliage tissue enginee-ring.J Biomed Mater Res.2010;95(1):84-90. [17] Buwalda SJ,Boere KW,Dijkstra PJ,et al. Hydrogels in a historical perspective: from simple networks to smart materials.J Control Release.2014;190:254-273. [18] Smeets N,Bakaic E,Patenaude M,et al. Injectable poly(oligoethylene glycol methacrylate)-based hydrogels with tunable phase transition behaviours: physicochemical and biological responses. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(10):4143-4155. [19] Elias PZ,Liu GW,Wei H,et al.A functionalized, injectable hydrogel for localized drug delivery with tunable thermosensitivity:synthesis and characterization of physical and toxicological properties.J Control Release. 2015;208:76-84. [20] Lin C,Zhao P,Li F,et al.Thermosensitive in situ-forming dextran- pluronic hydrogels through Michael addition.Mater Sci Eng C. 2010;30(8):1236-1244. [21] Yu L,Ding J.Injectable hydrogels as unique biomedical materials. Chem Soc Rev. 2008;37(8):1473-1481. [22] Ni P, Ding Q, Fan M, et al.Injectable thermosensitive PEG-PCL- PEG hydrogel/acellular bone matrix composite for bone regeneration in cranial defects.Biomaterials. 2014;35(1):236-248. [23] Hudson SP, Langer R, Fink GR, et al. Injectable in situ cross-linking hydrogels for local antifungal therapy. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6): 1444-1452. [24] Li L, Wang N, Jin X, et al. Biodegradable and injectable in situ cross- linking chitosan-hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for postoperative adhesion prevention. Biomaterials. 2014;35(12): 3903-3917. [25] Xie B, Jin L, Luo Z, et al. An injectable thermosensitive polymeric hydrogel for sustained release of Avastin to treat posterior segment disease. Int J Pharm. 2015;490(1-2):375-383. [26] 倪培艳,罗静聪,钱志勇.可注射的温度敏感型水凝胶复合材料在骨组织工程中的应用研究[EB/OL]. 北京:中国科技论文在线[2012-02-22]. http://www.paper.edu.cn/releasepaper/content/201202-823. [27] 孙斌.可注射温敏壳聚糖/胶原/甘油磷酸钠水凝胶应用于骨组织工程的初步研究[D].北京:解放军军医进修学院,2011. [28] 赵守军,熊文化,许柯.细胞因子基因转染的骨骺干细胞复合明胶-硫酸软骨素-透明质酸钠支架修复大鼠骨骺生长板缺损的实验研究[J].中医正骨, 2018,30(2):10-15. [29] Tibbitt MW, Anseth KS. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009;103:655–663. [30] Yin HY, Wang Y, Sun Z,et al.Induction of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation and functional cartilage microtissue formation for in vivo cartilage regeneration by cartilage extracellular matrix-derived particles. Acta Biomater.2016;33:96-109. [31] Buckley CT, Kelly DJ. Expansion in the presence of FGF-2 enhances the functional development of cartilaginous tissues engineered using infrapatellar fat pad derived MSCs. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;11:102-111. [32] Pia M,Alexander T, Hagen Schmal,et al.Nanomechanics of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Small GTPases Impact Chondrogenic Differentiation.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(9-10): 1035-1044. [33] Diekman BO,Rowland CR,Lennon DP,et al.Chondrogenesis of adult stem cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow: induction by growth factors and cartilage-derived matrix.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16: 523-533. [34] Almeida HV,Eswaramoorthy R,Cunniffe GM,et al.Fibrin hydrogels functionalized with cartilage extracellular matrix and incorporating freshly isolated stromal cells as an injectable for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:55-62. [35] Masaeli E,Karamali F,Loghmani S,et al.Bio-engineered electrospun nanofibrous membranes using cartilage extracellular matrix particles. Mater Chem B.2017;5:765-776. [36] 张莹莹,宫赫.骨支架材料性能的影响因素及其制备方法[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2015,32(2):480-484. [37] 刘威,于晓巍.天然来源可注射水凝胶修复软骨缺损的研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(2):81-84. [38] 刘杰,周浩,黄郁芳,等.大豆分离蛋白/琼脂糖复合水凝胶[J].高等学校化学学报,2018,39(3):591-597. [39] 朱琳,贺健康,刘亚雄,等.琼脂糖/胶原复合水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J].西安交通大学学报,2013,47(10):121-126. [40] Karim A, Hall AC.Chondrocyte Morphology in Stiff and Soft Agarose Gels and the Influence of Fetal Calf Serum.J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(5): 1041-1052. [41] Li H,Fan J,Sun L,et al.Functional regeneration of ligament-bone interface using a triphasic silk-based graft.Biomaterials. 2016;106: 180-192. [42] Kundu B,Rajkhowa R,Kundu SC,et al. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):457-470. [43] Ng VW,Chan JM,Sardon H,et al.Antimicrobial hydrogels: A new weapon in the arsenal against multidrug-resistant infections. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2014;78:46-62. [44] Ulrich TA,Jain A,Tanner K,et al.Probing cellular mechanobiology in three-dimensional culture with collagen-agarose matrices. Biomaterials. 2010;31(7):1875-1884. [45] 刘威,俞牧雨,于晓巍.可注射RGD功能化的透明质酸果胶水凝胶促进体外成软骨的研究[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2018,39(3):180-186. [46] Huang YX,Zhang XL, Wu AM,et al.An injectable nano-hydroxyapatite (n-HA)/glycol chitosan (G-CS)/hyaluronic acid (HyA) composite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering.RSC Adv. 2016;6:33529-33536. [47] Girotto D,Urbani S,Brun P,et al.Tissue specific gene expression in chondrocytes grown on three-dimensional hyaluronic acid scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2003;24(19):3265-3275. [48] Jakobsen RB,Shahdadfar A,Reinholt FP,et al. Chondrogenesis in a hyaluronic acid scaffold: comparison between chondrocytes and MSC from bone marrow and adipose tissue. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:1407-1416. [49] Liu X,Yang Y,Niu X.An in situ photocrosslinkable platelet rich plasma - Complexed hydrogel glue with growth factor controlled release ability to promote cartilage defect repair. Acta Biomater. 2017; 62:179-187. [50] Mauck RL,Nicoll SB,Seyhan SL,et al.Synergistic action of growth factors and dynamic loading for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng.2003;9(4):597-611. [51] Barry F,Boynton RE,Liu B,et al.Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow:differentiation-dependent gene expression of matrix components.Exp Cell Res. 2001;268(2):189-200. [52] Li WJ,Tuli R,Okafor C,et al.A three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering using human mesenchymal stem cells.Biomaterials.2005;26(6):599-609. [53] Van Susante JL,Buma P,van Beuningen HM,et al. Responsiveness of bovine chondrocytes to growth factors in medium with different serum concentrations.J Orthop Res.2000;18(1):68-77. [54] Schalkwijk J,Joosten LA,van den Berg WB,et al.Insulin-like growth factor stimulation of chondrocyte proteoglycan synthesis by human synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;32(1):66-71. [55] Fortier LA,Nixon AJ,Lust G.Phenotypic expression of equine articular chondrocytes grown in three-dimensional cultures supplemented with supraphysiologic concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-1.Am J Vet Res. 2002;63(2):301-305. [56] Holden P,Meadows RS,Chapman KL,et al.Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein interacts with type IX collagen , and disruptions to these interactions identify a pathogenetic mechanism in a bone dysplasia family.J Biol Chem. 2001;276(8):6046-6055. [57] 毛艳,张西正.软骨组织工程中细胞外基质的研究[J].中国临床康复, 2006, 10(2):152-155. [58] Liu C, Liu D, Wang Y, et al.Glycol chitosan/oxidized hyaluronic acid hydrogels functionalized with cartilage extracellular matrix particles and incorporating BMSCs for cartilage repair. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(1):721-732. [59] Li H,Ghazanfari R,Zacharaki D,et al.Isolation and characterization of primary bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2016;1370(1):109-118. [60] 荣为为,韩明子,金世柱,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在组织工程研究中的应用新进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(5):982-992. [61] 方洪松,周建林,彭昊.组织工程支架材料修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(52):7891-7898. [62] Lv YM,Yu QS. Repair of articular osteochondral defects of the knee joint using a composite lamellar scaffold. Bone Joint Res.2015;4(4): 56-64. [63] Ma X,Sun Y,Cheng X,et al.Repair of osteochondral defects by mosaicplasty and allogeneic BMSCs transplantation.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(4):6053-6059. [64] Yamasaki S,Mera H,Itokazu M,et al.Cartilage Repair With Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation: Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Cartilage.2014;5(4):196-202. [65] Chen WH,Lai MT, Wu AT,et al.In vitro stage-specific chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells committed to chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(2):450-459. [66] Dahlin RL,Ni M,Meretoja VV,et al.TGF-β3 induced chondrogenesis in co-cultures of chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells on biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials.2014;35(1):123-132. |
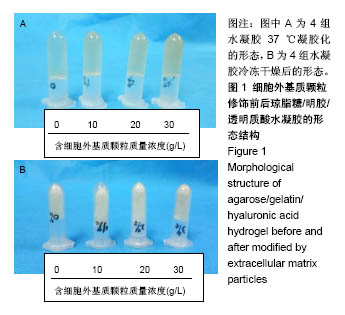
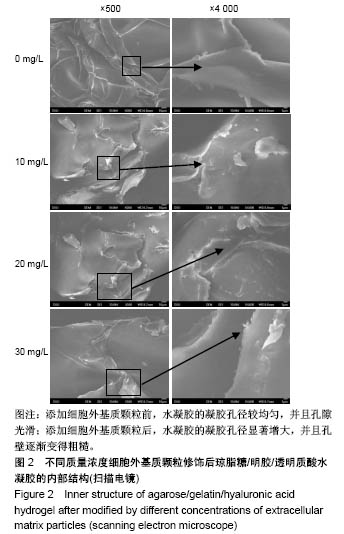
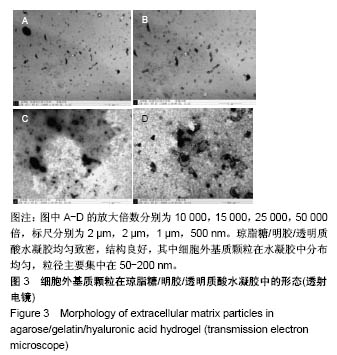
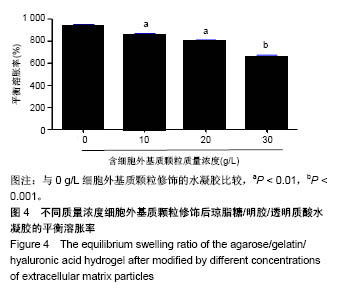
.jpg)
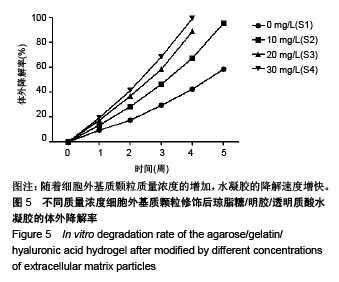
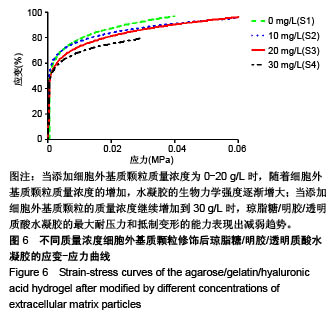
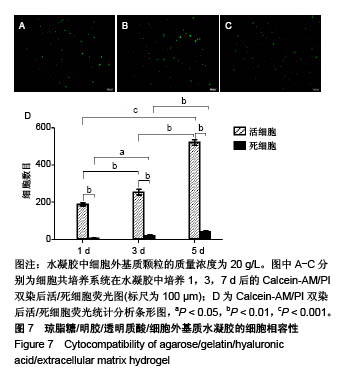
.jpg)