中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (35): 5614-5619.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1007
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印技术辅助上颈椎肿瘤模型的术前规划及手术模拟
陈雍君1,钟 华2,华 强1,林永祥1,李 华1,胡治平1,段少银2,赵慧毅1
- 厦门大学附属中山医院,1脊柱外科,2影像科,福建省厦门市 361004
Preoperative planning and operative simulation of three-dimensional printing-assisted upper cervical spine tumor model
Chen Yongjun1, Zhong Hua2, Hua Qiang1, Lin Yongxiang1, Li Hua1, Hu Zhiping1, Duan Shaoyin2, Zhao Huiyi1
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, 2Department of Radiography, Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361004, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
3D打印:又称增材制造技术,基于材料累加、叠层制造方法,通过计算机辅助建模,用粉末状金属或塑料等可黏合材料精确堆积制造原形的一种数字化成型技术。随着3D打印技术在医学领域的深入应用,将此技术应用于上颈椎肿瘤精准治疗成为可能。
上颈椎肿瘤有限元模型:目前上颈椎肿瘤有限元模型大多采用CT平扫结合增强图像数据,3D打印仿真模型与术中实际肿瘤存在一定误差,采取CT结合MR的数据来建模,发挥各自的优势,得到的模型更加符合真实。
摘要
背景:目前上颈椎肿瘤有限元模型大多采用CT平扫结合增强图像数据,3D打印仿真模型与术中实际肿瘤存在一定误差,采取CT结合MR的数据来建模,发挥各自的优势,得到的模型更加符合真实。
目的:探讨3D打印上颈椎肿瘤模型在术前规划、模拟手术中的应用。
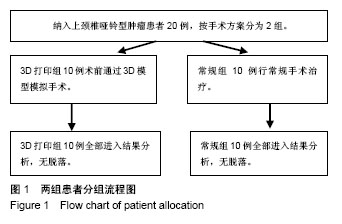
方法:纳入厦门大学附属中山医院2015至2017年收治的上颈椎哑铃型肿瘤(ToyamaⅡa、Ⅲa、Ⅴ型)患者20例,根据手术方案分为2组,每组10例。3D打印组应用3D打印技术辅助上颈椎哑铃型肿瘤精准手术治疗,术前获取患者头颅CT/MR资料,建立患者上颈椎肿瘤个体化模型,通过3D模型模拟手术,采取一期颈后路肿瘤切除+寰枢椎椎弓根内固定治疗;常规组进行常规手术。对比2组手术时间、出血量、住院天数及术后1年日本骨科协会评分改善率。
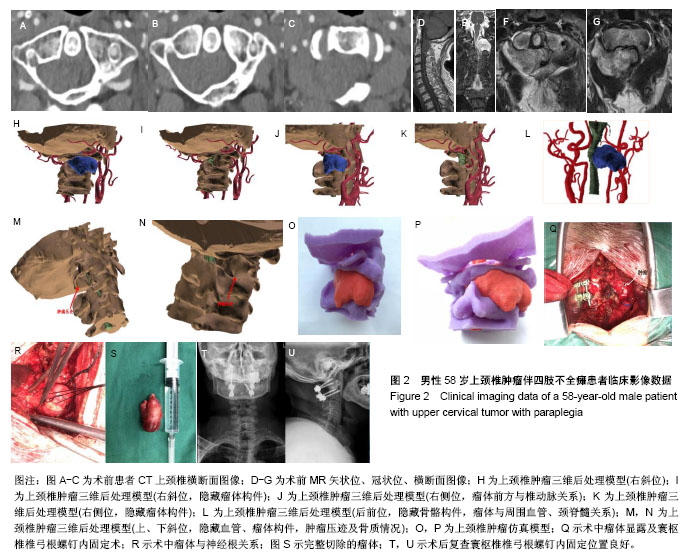
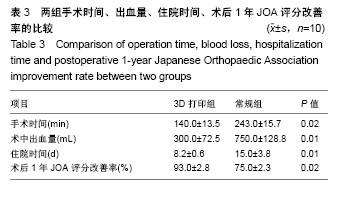
结果与结论:①三维模型能清楚显示肿瘤的形态及其与邻近血管、上颈椎的空间关系,并在体外进行仿真模型的模拟手术;术中借助3D模型能指导肿瘤切除并重建上颈椎稳定性;②与常规组相比,3D打印组手术时间、出血量、住院时间均明显减少(P < 0.05);③3D打印组术后1年日本骨科协会评分改善率为(93.0±2.8)%,常规组为(75.0±2.3)%,差异有显著性意义(t=5.634,P < 0.05);④所有患者随访期间无内固定松动和后凸畸形的发生;⑤结果表明,3D打印上颈椎肿瘤模型技术上可行,能够有效辅助复杂上颈椎疾病手术方案的制定及模拟手术,提高手术效率和安全性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-8206-0853(段少银)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)