| [1] Robertson PA, Tsitsopoulos PP, Voronov LI, et al. Biomechanical investigation of a novel integrated device for intra-articular stabilization of the C1-C2 (atlantoaxial) joint. Spine J. 2012;12: 136-142.[2] Roy AK, Miller BA, Holland CM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of traumatic injury to the craniovertebral junction: a case-based review. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;38: E3.[3] Elliott RE, Tanweer O, Boah A, et al. Atlantoaxial fusion with screw-rod constructs: meta-analysis and review of literature. World Neurosurg. 2014;81: 411-421.[4] Ryang YM, Torok E, Janssen I, et al. Early Morbidity and Mortality in 50 Very Elderly Patients After Posterior Atlantoaxial Fusion for Traumatic Odontoid Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2016;87: 381-391.[5] Du JY, Aichmair A, Kueper J, et al. Biomechanical analysis of screw constructs for atlantoaxial fixation in cadavers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015; 22: 151-161.[6] Bhowmick DA, Benzel EC. Posterior atlantoaxial fixation with screw-rod constructs: safety, advantages, and shortcomings. World Neurosurg. 2014;81: 288-289.[7] Ni B, Guo Q, Lu X, et al. Posterior reduction and temporary fixation for odontoid fracture: a salvage maneuver to anterior screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40: E168-174.[8] Lubelski D, Benzel EC. C1-C2 fusion: promoting stability, reducing morbidity. World Neurosurg. 2014;82: 1052-1054.[9] Lenehan B, Guerin S, Street J, et al. Lateral C1-C2 dislocation complicating a type II odontoid fracture. J Clin Neurosci. 2010;17: 947-949.[10] Bogduk N, Mercer S. Biomechanics of the cervical spine. I: Normal kinematics. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2000;15: 633-648.[11] Kumaresan S, Yoganandan N, Pintar FA. Finite element analysis of anterior cervical spine interbody fusion. Biomed Mater Eng. 1997;7: 221-230.[12] Ng HW, Teo EC. Nonlinear finite-element analysis of the lower cervical spine (C4-C6) under axial loading. J Spinal Disord. 2001;14: 201-210.[13] Zhang QH, Teo EC, Ng HW, et al. Finite element analysis of moment-rotation relationships for human cervical spine. J Biomech. 2006; 39: 189-193.[14] 陈金水,倪斌,陈博,等.寰枢椎脱位三维非线性有限元模型的建立和分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(9):749-753.[15] 郭群峰,陈方经,倪斌,等.带有颅底的全颈椎三维有限元模型的建立及分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(6): 550-554.[16] Hu Y, Dong WX, Hann S, et al. Construction of Finite Element Model for an Artificial Atlanto-Odontoid Joint Replacement and Analysis of Its Biomechanical Properties. Turk Neurosurg. 2016;26: 430-436.[17] Brolin K, Halldin P. Development of a finite element model of the upper cervical spine and a parameter study of ligament characteristics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29: 376-385.[18] El-Rich M, Arnoux PJ, Wagnac E, et al. Finite element investigation of the loading rate effect on the spinal load-sharing changes under impact conditions. J Biomech. 2009;42: 1252-1262.[19] Zhang B, Liu H, Cai X, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Modified TARP Technique Versus Modified Goel Technique for the Treatment of Basilar Invagination: A Finite Element Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41: E459-466.[20] Tan M, Wang H, Wang Y, et al. Morphometric evaluation of screw fixation in atlas via posterior arch and lateral mass. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28: 888-895.[21] Ebraheim N, Rollins JR Jr, Xu R, et al. Anatomic consideration of C2 pedicle screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21: 691-695.[22] Panjabi M, Dvorak J, Crisco JJ 3rd, et al. Effects of alar ligament transection on upper cervical spine rotation. J Orthop Res. 1991;9: 584-593.[23] Zhang H, Bai J. Development and validation of a finite element model of the occipito-atlantoaxial complex under physiologic loads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32: 968-974.[24] Goel A, Nadkarni T, Shah A, et al. Radiologic Evaluation of Basilar Invagination Without Obvious Atlantoaxial Instability (Group B Basilar Invagination): Analysis Based on a Study of 75 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2016;95: 375-382.[25] Huang DG, Hao DJ, He BR, et al. Posterior atlantoaxial fixation: a review of all techniques. Spine J. 2015;15: 2271-2281.[26] Lopez AJ, Scheer JK, Leibl KE, et al. Anatomy and biomechanics of the craniovertebral junction. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;38: E2.[27] Huang DG, Hao DJ, Li GL, et al. C2 nerve dysfunction associated with C1 lateral mass screw fixation. Orthop Surg. 2014;6: 269-273.[28] 马向阳,杨进城,尹庆水,等.后路寰枢椎钉棒固定非融合治疗新鲜Ⅱ型齿状突骨折保留寰枢椎旋转功能的临床初探[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013, 23(5): 411-415.[29] 周风金,倪斌,刘洪超,等.一种后路寰枢椎动态内固定系统的研制及其解剖学研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2011,9(3): 183-187.[30] Cai X, He X, Li H, et al. Total atlanto-odontoid joint arthroplasty system: a novel motion preservation device for atlantoaxial instability after odontoidectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2013;38: E451-457.[31] Kato K, Yokoyama T, Ono A, et al. Novel motion preservation device for atlantoaxial instability. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26: E107-111.[32] Chen J, Zhou F, Ni B, et al. New Posterior Atlantoaxial Restricted Non-Fusion Fixation for Atlantoaxial Instability: A Biomechanical Study. Neurosurgery. 2016;78: 735-741.[33] Ji W, Zheng M, Kong G, et al. Computed Tomographic Morphometric Analysis of Pediatric C1 Posterior Arch Crossing Screw Fixation for Atlantoaxial Instability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41: 91-96.[34] Yu HM, Malhotra K, Butler JS, et al. Anterior and posterior fixation for delayed treatment of posterior atlantoaxial dislocation without fracture. BMJ Case Rep. 2015;2015. pii: bcr2015212436.[35] Srivastava SK, Aggarwal RA, Nemade PS, et al. Single-stage anterior release and posterior instrumented fusion for irreducible atlantoaxial dislocation with basilar invagination. Spine J. 2016;16: 1-9.[36] Platzer P, Thalhammer G, Krumboeck A, et al. Plate fixation of odontoid fractures without C1-C2 arthrodesis: practice of a novel surgical technique for stabilization of odontoid fractures, including the opportunity to extend the fixation to C3. Neurosurgery. 2009;64: 726-733; discussion 733.[37] Lu B, He X, Zhao CG, et al. Biomechanical study of artificial atlanto-odontoid joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34: 1893-1899.[38] Ma X, Peng X, Xiang H, et al. A finite element modeling of posterior atlantoaxial fixation and biomechanical analysis of C2 intralaminar screw fixation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127: 1266-1271.[39] Cai X, Yu Y, Liu Z, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of occipitocervical fixation using an anterior occiput-to-axis locking plate system: a pilot study. Spine J. 2014;14: 1399-1409.[40] Zhang BC, Liu HB, Cai XH, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a novel transoral atlantoaxial anchored cage with established fixation technique - a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16: 261. |
.jpg)

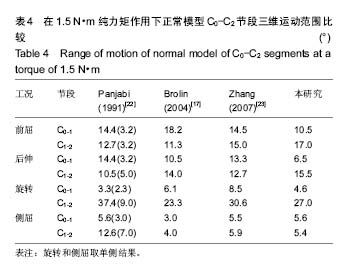
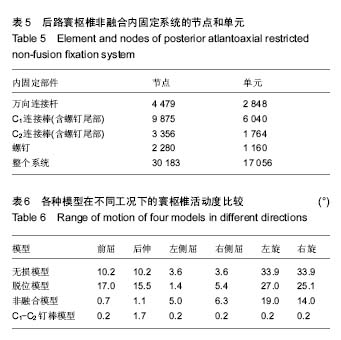
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)