| [1] Pego AP,Poot AA,Grijpma DW,et al.Copolymers of trimethylene carbonate and ε-caprolactone for porous nerve guides: Synthesis and properties. Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2001;12:35-53.
[2] [Schappacher M,Fabre T,Mingotaud AF,et al.Study of a (trimethylenecarbonate-co-ε-caprolactone) polymer—Part 1: preparation of a new nerve guide through controlled random copolymerization using rare earth catalysts Biomaterials. 2001;22:2849-2855.
[3] Marina SP,Kapil A,Andrew O,et al.Polymer carriers for drug delivery in tissue engineering.Adv Drug Delivery Rev.2007;59:187-206.
[4] Seal BL,Otero TC,Panitch A,et al.Polymeric biomaterials for tissue and organ regeneration Mater Sci Eng R.2001;34:147-230.
[5] Boland ED,Pawlowski KJ,Barnes CP,et al. Electrospinning of bioresorbable polymers for tissue engineering scaffolds.Polymeric Nanofibers. 2006;918: 188-204.
[6] Mathiowitz E,Jacob JS,Jong YS,et al.Biologically erodable microspheres as potential oral drug delivery systems.Nature.1997;386(6623): 410-414.
[7] Zhang Z,Foks MA,Grijpma DW,et al.Synthesis and drug release behavior of poly (trimethylene carbonate)–poly (ethylene glycol)–poly (trimethylene carbonate) nanoparticles.J Controll Release. 2005; 101:392-394.
[8] Zhang Y,Zhuo RX.Synthesis and drug release behavior of poly (trimethylene carbonate)–poly (ethylene glycol)–poly (trimethylene carbonate) nanoparticles.Biomaterials.2005;26:2089-2094.
[9] 王身国.可生物降解的高分子类型、合成和应用[J].化学通报,1997,64(2):45.
[10] 黄发荣,陈涛,沈学宁.高分子材料的循环利用[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2000.
[11] 于丽,冯亚凯,石长灿,等.吗啉-2,5-二酮衍生物及其聚合物的研究进展[J].高分子通报,2015,28(3):18-25.
[12] Xie ZG,Lu TC,Chen XS,et al.Effects of Gel Concentration, Human Fibronectin, and Cation Supplement on the Tissue-Engineered Cartilage. Biomed Mater Res A.2007;(1):238-245.
[13] Fonseca AC,Gil MH,Simoes PN.Biodegradable poly(ester amide)s-A remarkable opportunity for the biomedical area: Review on the synthesis, characterization and applications.Prog Polym Sci. 2014;39(7):1291-1311.
[14] Fonseca AC,Serra AC,Coelho JFJ,et al.Novel poly(ester amide)s from glycine and L-lactic acid by an easy and cost-effective synthesis. Polym Int. 2013; 62(5):736-743.
[15] Glowaky RC,Fung FM.Bioabsorbable polydepsipeptides, their preparation and use. European patent.322154[p].1989-06-28.
[16] Fung FN,Glowaky RC.Bioabsorbable polydepsipeptide, preparation and use thereof.USP, 4916209,1990. 4.10.
[17] In't Veld PJ,Dijkstra PJ,Feijen J.Synthesis of biodegradable polyesteramides with pendant functional groups.Macromol Chem.1992;193:2713.
[18] Wang D,Feng XD.Synthesis of poly(glycolic acid-alt-l-aspartic acid) from a Morpholine-2,5-dione Derivative.Macromolecules.1997;30:5688.
[19] John G,Tsuda S,Morita M.Synthesis and modification of new biodegradable copolymers:Serine/glycolic acid based copolymers.Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem.1997;35:1901.
[20] Hartwig W,Schollkopf U.Asymmetrische Synthesen über heterocyclische Zwischenstufen, XVI. Enantioselektive Synthese von α-Alkyl-α- phenylglycinen durch Alkylieren von an C-6 chiral substituierten 3,6-Dihydro-3- phenyl- 2H-1, 4-oxazin-2-onen.Liebigs Ann Chem.1982:1952.
[21] Nakamura CE,Cosimo RD,Moran JR.Process for the preparation of 3-6-substituted 2,5-morpholinediones, US Patent.5466801,1995-04-10
[22] Nissen D,Gilon C,Goodmann M.Polydepsipeptides, 4 synthesis of thealternating polydepsipeptides poly(Ala-Lac) and poly(Val-Lac).Macromol Chem Phys. 1975;1(1):23-53.
[23] Helder J,Kohn FE,Sato S,et al.Synthesis of poly[oxyethylidene carbonylimino(2-oxoethylene)] [poly(glycine-D,L-lactic acid)] by ring openingpolymerization.Macromol Chem Phys Rapid Comm,1985;6(1):9-14.
[24] Ouchi T,Shiratani M,Jinno M,et al.Synthesis of poly[(glycolic acid)-alt-(L-aspartic acid)] and its biodegradation behavior in vitro. Macromol Rapid Comm.1993;14(12):825-831.
[25] In’t Veld PJA,Dijkstra PJ,van Lochem JH,et al.Synthesis of alternating polydepsipeptides by ring-opening polymerization of morpholine-2,5-dione derivatives Macromol Chem Phys. 1990;191(8):1813-1825.
[26] Zhang HW,Bei JZ,Wang SG.Preparation and drug release behaviors of 5-fluorouracil loaded poly (glycolide-co-lactide-co-caprolactone) nanoparticles. Appl Polym Sci.2007;106(6):3757-3767.
[27] In’t Veld PJA,Dijkstra PJ.Synthesis of biodegradable poly-esteramides with pendant functional groups. Makromolekulare Chemie. 1992;193:2713-2730.
[28] Wang D,Feng XD.Copolymerization of ε-Caprolactone with(3S)-3-[(Benzyloxycarbonyl) methyl] morpholine-2,5-dione and the 13C NMR sequence analysis of the copolymer. Macromolecules. 1998; 31(12):3824-3831.
[29] Batting A,Hiebl B,Feng Y.Biological evaluation of degradable, stimuli-sensitive multiblock copolymers having polydepsipeptide- and poly(?-caprolactone) segments in vitro. Clin Hemorheol Micro. 2011;48(1): 161-172.
[30] 王珍萍,周涛,周科朝.丙交酯制备工艺的研究现状[J].材料导报,2006,20(8):52-54.
[31] Hyon SH,Khosrow J,Yoshito I.Synthesis of polylactides with different molecular weights. Biomaterials. 1997; 18(22):1503-1508.
[32] Anders SE,Mikael S.Properties of lactic acid based polymers and their correlation with composition.Prog Polym Sci.2002;27:1123-1163.
[33] Rasal RM,Janorkarc AV,Hirt DE.Poly(lactic acid) modifications.Prog Polym Sci.2010;35:338-356.
[34] Hiroyuki S,Aki T.Highly biodegradable copolymers composed of chiral depsipeptide and L-lactide units with favorable physical properties.J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem.2002;40(3):302-316.
[35] In´t Veld PJA, Ye W.Copolymerization of ε-caprolactone and morpholine-2 , 5-dionederivatives.Makromol Chem. 1992;193:1927-1942.
[36] Guan H,Xie Z,Zhang P,et al.Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable amphiphilic triblock copolymers containing l-Gluta mic acid units. Biomacromolecules.2005;6(4):1954-1960.
[37] Ouchi T,Nozaki T,Ishikawa A,et al.Synthesis and enzymatic hydrolys is of lactic acid-depsipeptid ecopolymers with functionalized pendangr oups.J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem.1997;35:377-383.
[38] Wang D,Feng XD.Synthesis of Poly(glycolic acid-alt-l-aspartic acid) from a morpholine-2,5-dione derivative.Macromolecules. 1997;30(19):5688.
[39] [Deng X,Yao J,Yuan M,et al.Synthesis of poly[(glycolic acid)-alt-(L-glutamic acid)]and poly{(lactic acid)-co-[(glycolic acid)-alt-(L-glutamic acid)].Macromol Chem Phys.2000;201(17):2371-2376.
[40] Hans RK,Ingrid K.Transesterification of poly (Llactone) with poly (glycolide), poly (β-propiolactone), and poly (ε-caprolactone).Maccromol Sci Chem.1987;24(11):1345.
[41] 王俊凤,张军,张学龙,等.聚乳酸合成的研究进展[J].化工时刊,2007,21(6):51-56.
[42] Feng YK,Klee D, Keul H,et al.Synthesis and characterization of new blockcopolymers with poly(ethyleneoxide) andpoly[3(S)-sec- butylmorpholine- 2,5-dione]sequences. Macromolecular Bioscience. 2001;1(1):30-39.
[43] Krieheldorf HR,Kreiser SI,Boetteher C.Polylactones: 31. Sn(II)octoate-initiated polymerization of L-Lactide: a mechanistic study.Polymer.1995;36(6):1253-1259.
[44] Volker J,Helmut K,Hartwig H.Polylnerization of (3S,6S)-3-isopropyl-6-methyl-2,5-morphoLinedione with tin oetoate and tin acetylaeetonate.Maeromol Chem Phys.1998;199(5):835-843.
[45] Krleheldorf HR,Hauser K.Polylaetones,45. Homo-and CoPolymerizatio-nsof 3-Methylporpholine-2,5-dione Initiated with a Cyclic Tin Alkoxide.Maeromol Chem Phys.2001;202(7):1219-1226.
[46] Feng YK,Klee D,Keul H,et al.Synthesis and characterization of new block copolymers with poly(ethylene oxide) and poly[3(S)-sec- butylmorpholine-2,5-dione]sequences, Macromolecular. Bioscience.2001;1(1):30-39.
[47] Feng YK,Klee D,Hocker H.Synthesis of poly[(lactic acid)-alt-or co-((S)-aspartic acid)] from(3S,6R,S)-3-[(benzyloxycarbonyl)methyl]-6-methylmorpholine-2,5-dione.Macromol Chem Phys. 2002; 203:819-824.
[48] Liu Y,Yuan M,Deng X.Study on biodegradable polymers: synthesis and characterization of poly(DL-lactic acid-co-l-lysine) random copolymer.Eur Polym J.2003;39(5):977-983.
[49] Yakai F,Jens K,Doris K,et al.Enzyme-catalyzed ring-opening polymerization of 3(S)-isopro- Pylmorpholine-2,5-dione.Maeromol Rapid Comm. 1999;20(2):88-90.
[50] Yakai F,Doris K,Helmut K,et al.Lipase-catalyzed ring-opening polymerization of morholine-2,5-dione derivatives:Anovel route to the synthesis of poly(ester-amide)s.MacromoleeularChemistry and Physies.2000;201(18):2670-2675.
[51] Ouchi T,Shiratani M,Jinno M,et al.Synthesis of poly[(glycolic acid)-alt-(L-aspartic acid)] and its biodegradation behavior in vitro.Macromol Rapid Comm.1993;14(12):825-831.
[52] Feng Y,Klee D,Höcker H.Lipase catalyzed copolymerization of 3(S)-isopropylmorpholine- 2,5-dione and D,L-lactide.Macromol Biosci.2004; 4(6):587-590.
[53] Ouchi T,Hamada A,Ohya Y.Biodegradable microspheres having reactive groups prepared from L-lactic acid-depsipeptide copolymers.Chem Phys. 1999;200:436.
[54] [Hoffman JD,Miller RL.Kinetic of crystallization from the melt and chain folding in polyethylene fractions revisited: theory and experiment.Polymer. 1997;38(13): 3151-3212. |
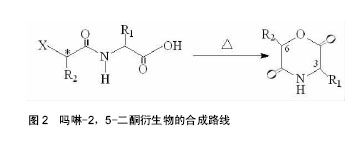
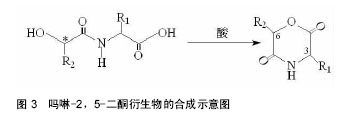
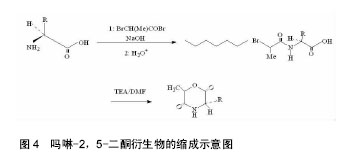
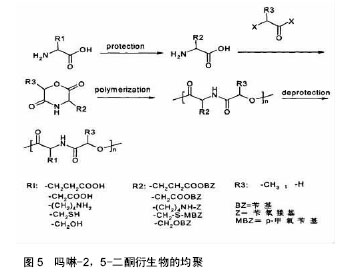
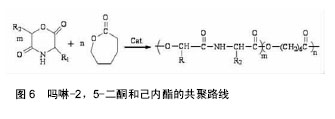
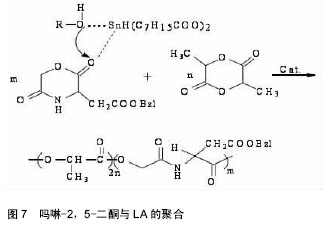

.jpg) 文章总结了吗啉-2,5-二酮及其衍生物单体与聚合物的合成方法,讨论了其优缺点。论述了催化聚合吗啉二酮时常用的催化剂的特征,并介绍了吗啉-2,5-二酮聚合物的应用,最后提出了吗啉-2,5-二酮及其衍生物单体与聚合物的研究趋势。
文章总结了吗啉-2,5-二酮及其衍生物单体与聚合物的合成方法,讨论了其优缺点。论述了催化聚合吗啉二酮时常用的催化剂的特征,并介绍了吗啉-2,5-二酮聚合物的应用,最后提出了吗啉-2,5-二酮及其衍生物单体与聚合物的研究趋势。