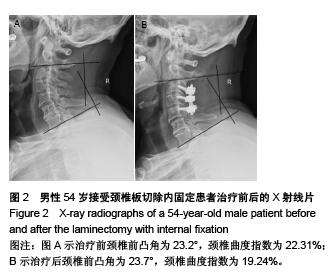
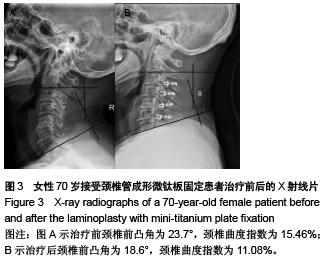
| [1] Rhee JM, Basra S. Posterior surgery for cervical myelopathy: laminectomy, laminectomy with fusion, and laminoplasty. Asian Spine J. 2008; 2(2): 114-126.
[2] Sekhon LH. Posterior cervical decompression and fusion for circumferential spondylotic cervical stenosis: review of 50 consecutive cases. J Clin Neurosci. 2006;13(1): 23-30.
[3] Chiba K, Toyama Y, Matsumoto M, et al. Segmental motor paralysis after expansive open?door laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(19): 2108-2115.
[4] Sakanra H,Hosono N, Mukai Y, et al. C5 palsy after decompression surgery for cerviealmyelopathy. Spine. 2003; 21(1):2447-2451.
[5] Hashimoto M, Mochizuki M,Aiba A,et al. C5 palsy following anterior decompression and spinal fusion for cervical degenerative diseases.Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10):1702-1710.
[6] Cabraja M, Abbushi A, Koeppen D, et al. Comparison between anterior and posterior decompression with instrumentation for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: sagittal alignment and clinical outcome. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28(3):E15.
[7] Kanchiku T,Imajo Y,Suzuki H,et al. Results of surgical treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy in patients aged 75 years or more: a comparative study of operative methods. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(8):1045-1050.
[8] Heller JG, Edwards CC 2nd, Murakami H, et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy:an independent matched cohort analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(12):1330-1336.
[9] Uchida K, Nakajima H, Sato R, et al. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy associated with kyphosis or sagittal sigmoid alignment: outcome after anterior or posterior decompression. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(5):521-528.
[10] Suda K, Abumi K, Ito M, et al. Local kyphosis reduces surgical outcomes of expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(12): 1258-1262.
[11] Petraglia AL, Srinivasan V, Coriddi M, et al. Cervical lamino-plasty as a management option for patients with cervical spondy-lotic myelopathy: a series of 40 patients. Neurosurgery. 2010;67(2):272-277.
[12] Dimar JR 2nd, Bratcher KR, Brock DC, et al. Instrumented open-door laminoplasty as treatment for cervical myelopathy in 104 patients. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2009;38(7): E123-128.
[13] Woods BI, Hohl J, Lee J, et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3): 688-695.
[14] Kang SH, Rhim SC, Roh SW, et al. Postlaminoplasty cervical range of motion: early results. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(5): 386-390.
[15] Yeh KT,Yu TC,Chen IH,et al. Expansive open-door laminoplasty secured with titanium miniplates is a good surgical method for multiple-level cervical stenosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;21;9:49.
[16] Miller JA,Lubelski D,Alvin MD,et al. C5 palsy after posterior cervical decompression and fusion: cost and quality-of-life implications. Spine J. 2014;14 (12):2854-2860.
[17] Epstein NE,Hollingsworth R.C5 Nerve root palsies following cervical spine surgery: A review. Surg Neurol Int. 2015; 6(Suppl 4):S154-163.
[18] Guzman JZ,Baird EO,Fields AC,et al. C5 nerve root palsy following decompression of the cervical spine: a systematic evaluation of the literature. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(7): 950-955.
[19] Satomi K, Nishu Y, Kohno T, et al. Long-term follow-up studies of open-door expansive laminoplasty for cervical stenotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(5): 507-510.
[20] Imagama S, Matsuyama Y, Yukawa Y, et al. C5 palsy after cervical laminoplasty: a multicentre study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(3):393-400.
[21] Meng H,Fang X, Hao D, et al. Incidences of C5 nerve palsy after multi-segmental cervical decompression through different approaches.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015;35(3):315-318.
[22] Gu Y, Cao P, Gao R, et al. Incidence and risk factors of C5 palsy following posterior cervical decompression: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2014;27;9(8):e101933.
[23] Sasai K, Saito T, Akagi S, et al. Preventing C5 palsy after laminoplasty. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(17):1972-1977.
[24] Hojo Y, Ito M, Abumi K, et al. A late neurological complication following posterior correction surgery of severe cervical kyphosis. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(6): 890-898.
[25] Nakashima H, Imagama S, Yukawa Y, et al. Multivariate analysis of C5 palsy incidence after cervical posterior fusion with instrumentation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(2): 103-110.
[26] Heller JG, Silcox DH 3rd, Sutterlin CE 3rd. Complications of posterior cervical plating. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(22): 2442-2448.
[27] Nobuyuki T, Li ZH, Ryoji A, et al. Paralysis of the arm after posterior decomp ression of the cervical sp inal cord: I. Anatomical investigation of the mechanism of paralysis. Eur Spine J. 1993;2 (4):191-196.
[28] Yamashita T, Yokogusu K, Yokozawa H,et al. C5 nerve palsyafter cervical laminoplasty: an analysis of three cases.Seikei Geka. 1996;47(3):1365-1369.
[29] Sodeyama T, Goto S, Mochizuki M,et al. Efect of deeompression enlargement laminoplasty for posterior shifting of the spinaleordSpine. 1999;24(2):1527-1531.
[30] Radcliff KE,Limthongkul W,Kepler CK,et al. Cervical laminectomy width and spinal cord drift are risk factors for postoperative C5 palsy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(2): 86-92.
[31] Tsuzuki N, Abe R, Saiki K, et al. Extradural tethering effect as one mechanism of radiculopathy complicating posterior decompression of the cervical spinal cord. Spine. 1996;21(2): 203-211.
[32] Katsumi K,Yamazaki A,Watanabe K,et al.Analysis of C5 palsy after cervical open-door laminoplasty: relationship between C5 palsy and foraminal stenosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013; 26(4):177-182.
|

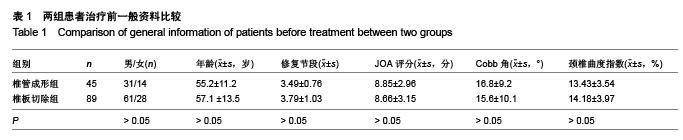
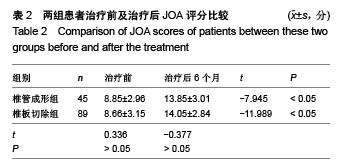
.jpg)