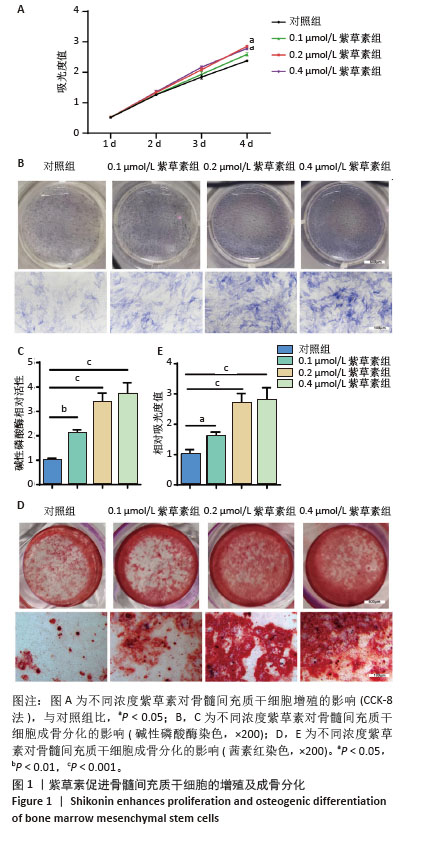
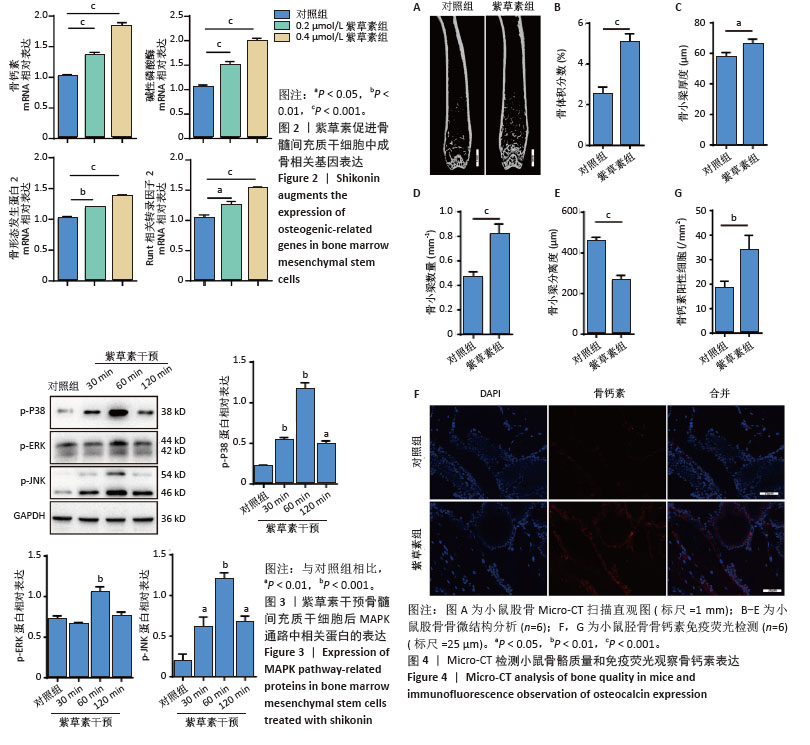
[1] ADEJUYIGBE B, KALLINI J, CHIOU D, et al. Osteoporosis: Molecular Pathology, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19): 14583.
[2] 许嘉木,杨城,李玮民,等. 炎细胞焦亡与炎症因子在骨质疏松症发生中的作用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2026,30(3):691-700.
[3] 刘云,罗晓婷,李崇,等. 雌激素治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].实用临床医学,2020,21(10):91-96.
[4] KOBAYASHI T, MORIMOTO T, ITO K, et al. Denosumab vs. bisphosphonates in primary osteoporosis: a meta-analysis of comparative safety in randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos Int. 2024;35(8):1377-1393.
[5] WU H, LIN XQ, LONG Y, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is potential therapeutic target of osteoporosis. Heliyon. 2022;8(12): e12288.
[6] CHEN LR, KO NY, CHEN KH. Medical Treatment for Osteoporosis: From Molecular to Clinical Opinions. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2213.
[7] KOBAYAKAWA T, MIYAZAKI A, SAITO M, et al. Denosumab versus romosozumab for postmenopausal osteoporosis treatment. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1): 11801.
[8] ENSRUD KE, CRANDALL CJ. Osteoporosis. Ann Intern Med. 2024;177(1): ITC1-ITC6.
[9] REID IR, BILLINGTON EO. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet. 2022;399(10329):1080-1092.
[10] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014; 507(7492):323-328.
[11] FU R, LV WC, XU Y, et al. Endothelial ZEB1 promotes angiogenesis-dependent bone formation and reverses osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):460.
[12] YANG SH, SHARROCKS AD, WHITMARSH AJ. Transcriptional regulation by the MAP kinase signaling cascades. Gene. 2003;320:3-21.
[13] LIU L, ZHENG J, YANG Y, et al. Hesperetin alleviated glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs through regulating the ERK signaling pathway. Med Mol Morphol. 2021;54(1):1-7.
[14] LIU Q, ZHUANG Y, OUYANG N, et al. Cytochalasin D Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of MC3T3-E1 Cells via p38-MAPK Signaling Pathway. Curr Mol Med. 2019;20(1):79-88.
[15] LIU L, MIAO Y, SHI X, et al. Phosphorylated Chitosan Hydrogels Inducing Osteogenic Differentiation of Osteoblasts via JNK and p38 Signaling Pathways. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(3):1500-1509.
[16] PRASADAM I, ZHOU Y, DU Z, et al. Osteocyte-induced angiogenesis via VEGF-MAPK-dependent pathways in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;386(1-2):15-25.
[17] ZHANG Y, HAN H, QIU H, et al. Antiviral activity of a synthesized shikonin ester against influenza A (H1N1) virus and insights into its mechanism. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;93:636-645.
[18] WANG J, CHEN Z, FENG X, et al. Shikonin ameliorates injury and inflammatory response of LPS-stimulated WI-38 cells via modulating the miR-489-3p/MAP2K1 axis. Environ Toxicol. 2021;36(9):1775-1784.
[19] HE Y, LUO K, HU X, et al. Antibacterial Mechanism of Shikonin Against Vibrio vulnificus and Its Healing Potential on Infected Mice with Full-Thickness Excised Skin. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2023;20(2):67-79.
[20] YAN C, LI Q, SUN Q, et al. Promising Nanomedicines of Shikonin for Cancer Therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:1195-1218.
[21] FANG T, WU Q, MU S, et al. Shikonin stimulates MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation and differentiation via the BMP-2/Smad5 signal transduction pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(2):1269-1274.
[22] LI F, LIU X, LI M, et al. Inhibition of PKM2 suppresses osteoclastogenesis and alleviates bone loss in mouse periodontitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;129:111658.
[23] LU C, ZHANG Z, FAN Y, et al. Shikonin induces ferroptosis in osteosarcomas through the mitochondrial ROS-regulated HIF-1α/HO-1 axis. Phytomedicine. 2024;135:156139.
[24] CHEN Z, WU FF, LI J, et al. Investigating the synergy of Shikonin and Valproic acid in inducing apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells via ROS-mediated EGR1 expression. Phytomedicine. 2024;126:155459.
[25] LOHBERGER B, KALTENEGGER H, ECK N, et al. Shikonin Derivatives Inhibit Inflammation Processes and Modulate MAPK Signaling in Human Healthy and Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(6):3396.
[26] LI F, YIN Z, ZHOU B, et al. Shikonin inhibits inflammatory responses in rabbit chondrocytes and shows chondroprotection in osteoarthritic rabbit knee. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015;29(2):656-662.
[27] CHEN LR, KO NY, CHEN KH. Medical Treatment for Osteoporosis: From Molecular to Clinical Opinions. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2213.
[28] GONG W, ZHANG N, CHENG G, et al. Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch Extracts Prevent Bone Loss and Architectural Deterioration and Enhance Osteoblastic Bone Formation by Regulating the IGF-1/PI3K/mTOR Pathway in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16):3964.
[29] WANG F, QIAN H, KONG L, et al. Accelerated Bone Regeneration by Astragaloside IV through Stimulating the Coupling of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(7):1821-1836.
[30] JANG SY, LEE JK, JANG EH, et al. Shikonin blocks migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells through inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(6):2827-2833.
[31] HAN X, KANG KA, PIAO MJ, et al. Shikonin Exerts Cytotoxic Effects in Human Colon Cancers by Inducing Apoptotic Cell Death via the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria-Mediated Pathways. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019;27(1):41-47.
[32] KO H, KIM SJ, SHIM SH, et al. Shikonin induces apoptotic cell death via regulation of p53 and Nrf2 in AGS human stomach carcinoma cells. Biomol Ther. 2016;24(5):501-509.
[33] DUAN D, ZHANG B, YAO J, et al. Shikonin targets cytosolic thioredoxin reductase to induce ROS-mediated apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;70:182-193.
[34] GUPTA B, CHAKRABORTY S, SAHA S, et al. Antinociceptive properties of shikonin: in vitro and in vivo studies. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016; 94(7):788-796.
[35] LEE JH, HAN SH, KIM YM, et al. Shikonin inhibits proliferation of melanoma cells by MAPK pathway-mediated induction of apoptosis. Biosci Rep. 2021;41(1):BSR20203834.
[36] MAJIDINIA M, SADEGHPOUR A, YOURSEFI B. The roles of signaling pathways in bone repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(4): 2937-2948.
[37] SONG Y, WU H, GAO Y, et al. Zinc Silicate/Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Collagen Scaffolds Promote Angiogenesis and Bone Regeneration via the p38 MAPK Pathway in Activated Monocytes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(14):16058-16075.
[38] GUO J, CHEN Z, XIAO Y, et al. SATB1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of diabetic rat BMSCs through MAPK signalling activation. Oral Dis. 2023;29(8):3610-3619.
[39] QIN W, SHANG Q, SHEN G, et al. Restoring bone-fat equilibrium: Baicalin’s impact on P38 MAPK pathway for treating diabetic osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;175:116571.
[40] WANG J, FANG CL, NOLLER K, et al. Bone-derived PDGF-BB drives brain vascular calcification in male mice. J Clin Invest. 2023;133(23): e168447.
[41] BAI W, CHENG M, JIN J, et al. KAP1 modulates osteogenic differentiation via the ERK/Runx2 cascade in vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(4):3217-3228.
[42] ZHAO Y, XU Y, ZHENG H, et al. QingYan formula extracts protect against postmenopausal osteoporosis in ovariectomized rat model via active ER-dependent MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signal pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;268:113644.
[43] KIM H, OH N, KWON M, et al. Exopolysaccharide of Enterococcus faecium L15 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via p38 MAPK pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1): 446.
[44] NOTH U, TULI R, SEGHATOLESLAMI R, et al. Activation of p38 and Smads mediates BMP-2 effects on human trabecular bone-derived osteoblasts. Exp Cell Res. 2003;291(1):201-211.
[45] LV J, WANG Q, LIU D, et al. Calcium phytate reverses high glucose-inhibited osteogenesis of BMSCs via the MAPK/JNK pathway. Oral Dis. 2024;30(3):1379-1391.
[46] LI M, XING X, HUANG H, et al. BMSC-Derived ApoEVs Promote Craniofacial Bone Repair via ROS/JNK Signaling. J Dent Res. 2022;101(6): 714-723.
|