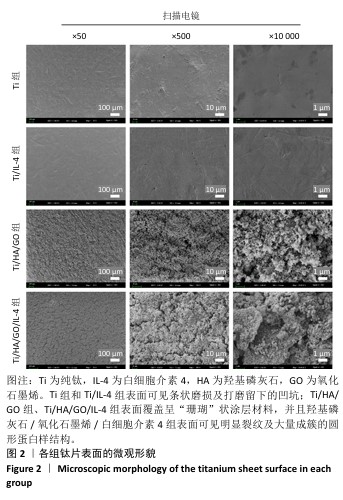
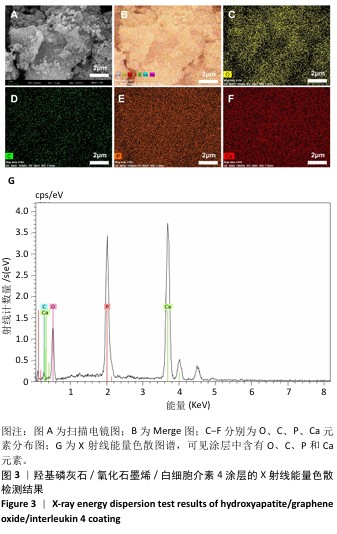
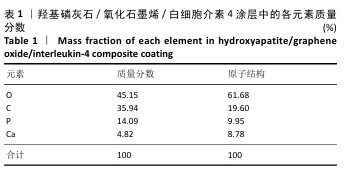
[1] SCHWENDICKE F, NITSCHKE I, STARK H, et al. Epidemiological trends, predictive factors, and projection of tooth loss in Germany 1997-2030: part II. Edentulism in seniors. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(11): 3997-4003.
[2] ZHANG J, ZHUANG Y, SHENG R, et al. Smart stimuli-responsive strategies for titanium implant functionalization in bone regeneration and therapeutics. Mater Horiz. 2024;11(1):12-36.
[3] STICH T, ALAGBOSO F, KRENEK T, et al. Implant-bone-interface: Reviewing the impact of titanium surface modifications on osteogenic processes in vitro and in vivo. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022;7(1):e10239.
[4] ALBREKTSSON T, TENGVALL P, AMENGUAL L, et al. Osteoimmune regulation underlies oral implant osseointegration and its perturbation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1056914.
[5] MUNIR MU, SALMAN S, JAVED I, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite as a delivery system: overview and advancements. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2021;49(1):717-727.
[6] ZHANG D, LIU H, XUE X, et al. Enhancing immune modulation and bone regeneration on titanium implants by alleviating the hypoxic microenvironment and releasing bioactive ions. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;236:113805.
[7] MONDAL S, PARK S, CHOI J, et al. Hydroxyapatite: A journey from biomaterials to advanced functional materials. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;321:103013.
[8] GUNGORDU ER S, EDIRISINGHE M, TABISH TA. Graphene-Based Nanocomposites as Antibacterial, Antiviral and Antifungal Agents. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(6):e2201523.
[9] PAPI M. Graphene-Based Materials: Biological and Biomedical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):672.
[10] HUNG HS, KUNG ML, CHEN FC, et al. Nanogold-Carried Graphene Oxide: Anti-Inflammation and Increased Differentiation Capacity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(8):2046.
[11] YUAN B, CHEN H, ZHAO R, et al. Construction of a magnesium hydroxide/graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite composite coating on Mg-Ca-Zn-Ag alloy to inhibit bacterial infection and promote bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:354-367.
[12] BAHETI W, LV S, MILA, et al. Graphene/hydroxyapatite coating deposit on titanium alloys for implant application. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2023;21:22808000221148104.
[13] BAHETI W, CHEN X, LA M, et al. Biomimetic HA-GO implant coating for enhanced osseointegration via macrophage M2 polarization-induced osteo-immunomodulation. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2024;22:22808000241266665.
[14] GAAFAR MS, YAKOUT SM, BARAKAT YF, et al. Electrophoretic deposition of hydroxyapatite/chitosan nanocomposites: the effect of dispersing agents on the coating properties. RSC Adv. 2022;12(42): 27564-27581.
[15] SARPAL S, SINGH AK, BHARDWAJ H, et al. Graphene oxide-Mn3O4 nanocomposites for advanced electrochemical biosensor for fumonisin B1 detection. Nanotechnology. 2023;34(46).doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aceaff.
[16] AKRAM W, ZAHID R, USAMA RM, et al. Enhancement of Antibacterial Properties, Surface Morphology and In Vitro Bioactivity of Hydroxyapatite-Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite Coating by Electrophoretic Deposition Technique. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(6):693.
[17] WU S, LAI Y, ZHENG X, et al. Facile fabrication of linezolid/strontium coated hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide nanocomposite for osteoporotic bone defect. Heliyon. 2024;10(11): e31638.
[18] CHIANG CC, XIA X, CRACIUN V, et al. Enhancing the Hydrophobicity and Antibacterial Properties of SiCN-Coated Surfaces with Quaternization to Address Peri-Implantitis. Materials (Basel). 2023; 16(17):5751.
[19] KWON D, CHA BG, CHO Y, et al. Extra-Large Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Directing in Vivo M2 Macrophage Polarization by Delivering IL-4. Nano Lett. 2017;17(5):2747-2756.
[20] SCHLUNDT C, FISCHER H, BUCHER CH, et al. The multifaceted roles of macrophages in bone regeneration: A story of polarization, activation and time. Acta Biomater. 2021;133:46-57.
[21] IWASZKO M, BIALY S, BOGUNIA-KUBIK K. Significance of Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 in Inflammatory Arthritis. Cells. 2021;10(11):3000.
[22] ZHOU T, YANG Z, NI B, et al. IL-4 induces reparative phenotype of RPE cells and protects against retinal neurodegeneration via Nrf2 activation. Cell Death Dis. 2022; 13(12):1056.
[23] LI Q, LIANG B, WANG F, et al. Delivery of Interleukin 4 from a Titanium Substrate Coated with Graphene Oxide for Enhanced Osseointegration by Regulating Macrophage Polarization. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020; 6(9):5215-5229.
[24] XU J, ZHANG J, SHI Y, et al. Surface Modification of Biomedical Ti and Ti Alloys: A Review on Current Advances. Materials (Basel). 2022; 15(5):1749.
[25] GALINDO-MORENO P, CATENA A, PEREZ-SAYANS M, et al. Early marginal bone loss around dental implants to define success in implant dentistry: A retrospective study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2022;24(5):630-642.
[26] JIA Z, SHI Y, XIONG P, et al. From Solution to Biointerface: Graphene Self-Assemblies of Varying Lateral Sizes and Surface Properties for Biofilm Control and Osteodifferentiation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(27):17151-17165.
[27] MAJUMDER P, GANGOPADHYAY R. Evolution of graphene oxide (GO)-based nanohybrid materials with diverse compositions: an overview. RSC Adv. 2022;12(9):5686-5719.
[28] 吾凡别克·巴合提.羟基磷灰石-氧化石墨烯纳米涂层促进成骨分化及调节巨噬细胞极化的研究 [D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2023.
[29] YAO D, ZHAO Z, WU Z, et al. Characterization of PA12/HA composite scaffolds based on selective laser sintering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023;145:106000.
[30] OZTURK GUNDUZ E, TASASIZ B, GEDIK ME, et al. NI-BODIPY-GO Nanocomposites for Targeted PDT. ACS Omega. 2023;8(9):8320-8331.
[31] ZHOU M, GRAVES DT. Impact of the host response and osteoblast lineage cells on periodontal disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:998244.
[32] LIU H, CHENG J, CHEN F, et al. Biomimetic and cell-mediated mineralization of hydroxyapatite by carrageenan functionalized graphene oxide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(5):3132-3140.
[33] SOUZA AP, NEVES JG, NAVARRO DA ROCHA D, et al. Chitosan/Xanthan/Hydroxyapatite-graphene oxide porous scaffold associated with mesenchymal stem cells for dentin-pulp complex regeneration. J Biomater Appl. 2023;37(9):1605-1616.
[34] 吕尚毅,何惠宇,吾凡别克·巴合提,等.氧化石墨烯-羟基磷灰石复合涂层材料的理化性质及生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(10):1477-1483.
[35] 马丽莎,何惠宇,吾凡别克·巴合提,等.氧化石墨烯/羟基磷灰石复合涂层对RAW264.7巨噬细胞免疫活性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(10):2023-2029.
[36] ALLEN JE. IL-4 and IL-13: Regulators and Effectors of Wound Repair. Annu Rev Immunol. 2023;41:229-254.
[37] 都曼别克·阿曼台,何惠宇,韩祥祯.羟基磷灰石-氧化石墨烯复合涂层促进大鼠骨缺损的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(10):2030-2037.
[38] ASLAM KHAN MU, ABD RAZAK SI, AL ARJAN WS, et al. Recent Advances in Biopolymeric Composite Materials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicines: A Review. Molecules. 2021;26(3):619.
[39] LI M, LIU J, CUI X, et al. Osteogenesis effects of magnetic nanoparticles modified-porous scaffolds for the reconstruction of bone defect after bone tumor resection. Regen Biomater. 2019;6(6):373-381.
[40] SHI C, GAO J, WANG M, et al. Functional hydroxyapatite bioceramics with excellent osteoconductivity and stern-interface induced antibacterial ability. Biomater Sci. 2016;4(4):699-710. |