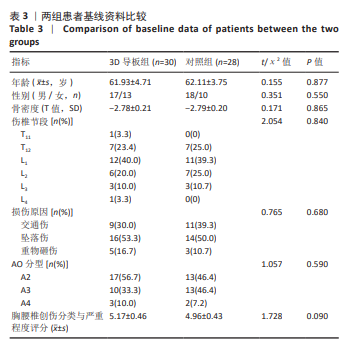
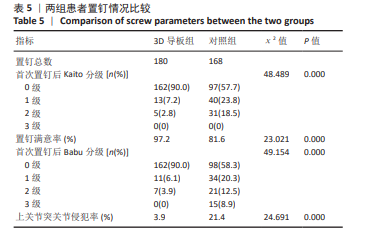
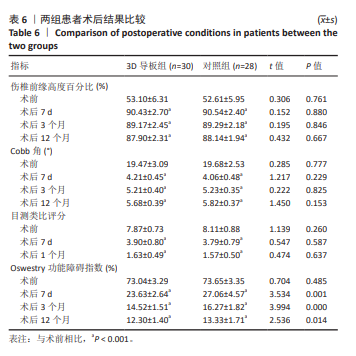
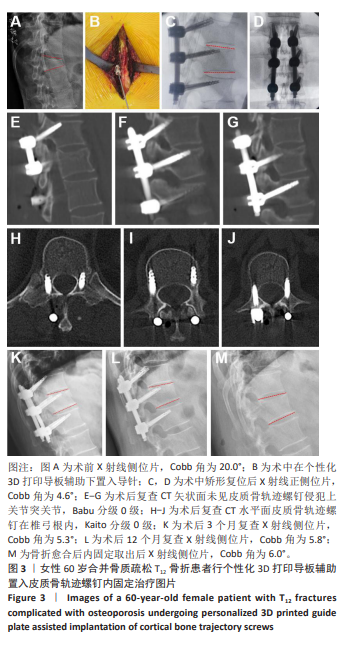
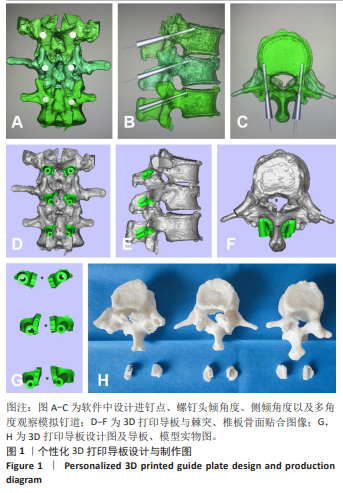
[1] 赵宏涛, 宋霏, 韦祎, 等. 皮质骨轨迹螺钉与传统椎弓根螺钉固定对短节段腰椎融合术患者临床疗效影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022,32(11):1034-1044.
[2] EL SAMAN A, MEIER S, SANDER A, et al. Reduced loosening rate and loss of correction following posterior stabilization with or without PMMA augmentation of pedicle screws in vertebral fractures in the elderly. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2013;39(5): 455-460.
[3] 白璧辉, 谢兴文, 李鼎鹏, 等. 我国近5年来骨质疏松症流行病学研究现状[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(2):253-258.
[4] SKINNER R, MAYBEE J, TRANSFELDT E, et al. Experimental pullout testing and comparison of variables in transpedicular screw fixation. A biomechanical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990;15(3):195-201.
[5] CHANG MC, LIU CL, CHEN TH. Polymethylmethacrylate augmentation of pedicle screw for osteoporotic spinal surgery: a novel technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(10):E317-E324.
[6] LI X, MA Y, DONG J, et al. Retrospective analysis of treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture using mono-segment pedicle instrumentation compared with short-segment pedicle instru mentation. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(10):2034-2042.
[7] SANTONI BG, HYNES RA, MCGILVRAY KC, et al. Cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screws. Spine J. 2009;9(5):366-373.
[8] 穆怀昭, 赵佳佳, 杨朝昕, 等. 3-D打印技术结合经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗中老年胸腰椎爆裂骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2019,25(6):1041-1045.
[9] 蒋维利, 牛国旗, 周功, 等. 3D打印技术辅助成人脊柱侧后凸畸形的术前规划及应用价值[J]. 中国骨伤,2020,33(2):99-105.
[10] SHEHA ED, GANDHI SD, COLMAN MW. 3D printing in spine surgery. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(Suppl 5):S164.
[11] TORTOLANI PJ, STROH DA. Cortical Bone Trajectory Technique for Posterior Spinal Instrumentation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(11): 755-761.
[12] KAITO T, MATSUKAWA K, ABE Y, et al. Cortical pedicle screw placement in lumbar spinal surgery with a patient-matched targeting guide: A cadaveric study. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(6): 865-869.
[13] BABU R, PARK JG, MEHTA AI, et al. Comparison of superior-level facet joint violations during open and percutaneous pedicle screw placement. Neurosurgery. 2012;71(5):962-970.
[14] 张野, 夏辉强, 易威威, 等. 经皮椎体后凸成形术与经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定术对骨量减少型胸腰椎压缩性骨折的疗效对比研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2021,23(6):428-434.
[15] CHEN L, LIU H, HONG Y, et al. Minimally Invasive Decompression and Intracorporeal Bone Grafting Combined with Temporary Percutaneous Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation for Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture with Neurological Deficits. World Neurosurg. 2020;135: e209-e220.
[16] 赵加庆, 赵子豪, 于先凯, 等. 复合骨水泥椎体成形治疗骨量减少胸腰椎骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(16):1457-1461.
[17] WANG H, ZHANG L, DU H, et al. Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Bilateral Pedicle Approach Combined with Positional Reduction for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023;29(6):176-181.
[18] DU SY, DAI J, ZHOU ZT, et al. Size selection and placement of pedicle screws using robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-guided techniques for thoracolumbar fractures: possible implications for the screw loosening rate. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):365.
[19] 周昌俊, 龙胜利, 邹伟, 等. 经皮椎弓根螺钉技术治疗胸腰椎骨折共平面置钉导向器设计与临床应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(4):534-538.
[20] 钱立雄, 郝定均, 孙宏慧, 等. 骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定与皮质骨轨迹螺钉固定治疗腰椎退变性疾病合并骨质疏松的效果比较[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2019,4(13):87-90.
[21] 赵世新, 席海洋, 王朕, 等. 皮质骨轨迹螺钉在脊柱外科中的应用进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(12):1124-1128.
[22] BOKOV A, BULKIN A, ALEYNIK A, et al. Pedicle Screws Loosening in Patients With Degenerative Diseases of the Lumbar Spine: Potential Risk Factors and Relative Contribution. Global Spine J. 2019;9(1): 55-61.
[23] SILVA F, SILVA PS, VAZ R, et al. Midline lumbar interbody fusion (MIDLIF) with cortical screws: initial experience and learning curve. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2019;161(12):2415-2420.
[24] MATSUKAWA K, KATO T, YANAI Y, et al. Influence of facetectomy, cross-link augmentation, and interbody procedure on progression of bone fusion in single-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion using the long cortical bone trajectory technique. J Neurosurg Spine. 2024;41(4):483-488.
[25] ZHANG RJ, LI HM, CAO H, et al. Cortical bone trajectory screws used to save failed traditional trajectory screws in the osteoporotic lumbar spine and vice versa: a human cadaveric biomechanical study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;30(6):759-766.
[26] WANG Y, LIU H, LI B, et al. Three different screw trajectories in single segment fixation: a finite element analysis and biomechanical study. Spine J. 2025;30:S1529-9430(25)00077-4.
[27] TSAGKARIS C, FASSER MR, FARSHAD M, et al. Stability of medially and laterally malpositioned screws: a biomechanical study on cadavers. Spine J. 2025;25(2):380-388.
[28] 韦继刚, 益小平. 皮质骨螺钉与椎弓根螺钉内固定在创伤性胸腰椎骨折手术中的临床应用对比[J]. 临床与病理杂志,2023,43(6):1234-1241.
[29] 周志豪, 阿拉法特·卡哈尔, 王轶希, 等. 传统椎弓根螺钉与改良皮质骨轨迹置钉技术的生物力学性能有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2789-2794.
[30] 丁红涛, 海涌, 刘玉增, 等. 皮质骨轨迹螺钉固定在合并骨质疏松腰椎退行性疾病手术中应用的效果[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022, 32(12):1058-1066.
[31] LI JC, YANG ZQ, XIE TH, et al. Deterioration of the fixation segment’s stress distribution and the strength reduction of screw holding position together cause screw loosening in ALSR fixed OLIF patients with poor BMD. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:922848.
[32] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, NEMOTO O, et al. Morphometric measurement of cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screw insertion using computed tomography. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013; 26(6):248-253.
[33] IWATSUKI K, YOSHIMINE T, OHNISHI Y, et al. Isthmus-guided cortical bone trajectory for pedicle screw insertion. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(3): 244-248.
[34] 苏林涛, 江剑峰,马俊, 等. O臂导航在椎弓根发育性狭窄胸腰椎骨折中的精准应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(9): 1855-1862.
[35] 张希诺, 刘玉增, 李越, 等. 骨科手术机器人辅助与X线透视辅助下徒手皮质骨轨迹螺钉置入治疗单节段退行性腰椎疾病的临床对比研究[J]. 首都医科大学学报,2023,44(5):836-844.
[36] WU C, DENG J, LI T, et al. Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement Aided by a New Drill Guide Template Combined with Fluoroscopy: An Accuracy Study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):471-479.
[37] GALVEZ M, MONTOYA CE, FUENTES J, et al. Error Measurement Between Anatomical Porcine Spine, CT Images, and 3D Printing. Acad Radiol. 2020;27(5):651-660.
[38] ALAN N, DENG H, MUTHIAH N, et al. Graft subsidence and reoperation after lateral lumbar interbody fusion: a propensity score-matched and cost analysis of polyetheretherketone versus 3D-printed porous titanium interbodies. J Neurosurg Spine. 2023; 39(2):187-195.
[39] JEONG S, YANG A, DHODAPKAR MM, et al. 3D printed pedicle screw guides reduce the rate of intraoperative screw revision in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery. Spine J. 2023;23(12):1894-1899.
[40] KIM J, RAJADURAI J, CHOY WJ, et al. Three-Dimensional Patient-Specific Guides for Intraoperative Navigation for Cortical Screw Trajectory Pedicle Fixation. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:674-679.
[41] 丁祥, 李超, 牛国旗, 等. 个体化3D打印导向模板辅助强直性脊柱炎颈椎椎弓根螺钉置入的实验研究[J]. 实用医学杂志,2020,36(8): 1072-1076.
[42] 连学辉, 肖红利, 卢涛, 等. 3D打印体外导板辅助经皮椎弓根螺钉固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效观察[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2022,32(8):704-712. |