[1] BACKER CL, JACOBS JP. Proceedings of the 8th Scientific Meeting of the World Society for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery (WSPCHS) at the 8th World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery (WCPCCS). World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2024;15(3):263-264.
[2] TSAO CW, ADAY AW, ALMARZOOQ ZI, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation.2022;145(8):e153-e639.
[3] BUŁDAK Ł. Cardiovascular Diseases-A Focus on Atherosclerosis, Its Prophylaxis, Complications and Recent Advancements in Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):4695.
[4] WANG Y, KESHAVARZ M, BARHOUSE P,
et al. Strategies for Regenerative Vascular Tissue Engineering. Advanced Biology. 2023;7(5):e2200050.
[5] CHEN J, ZHANG D, WU LP, et al. Current Strategies for Engineered Vascular Grafts and Vascularized Tissue Engineering. Polymers. 2023;15(9):2015.
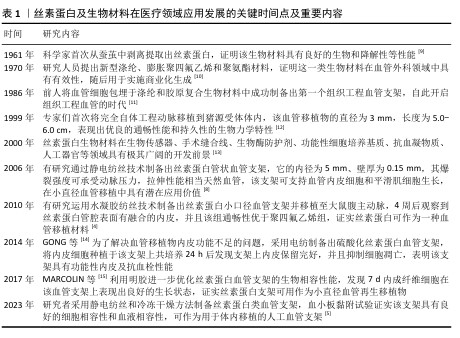
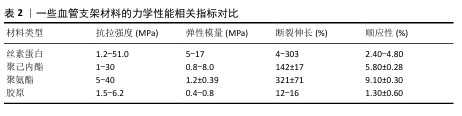
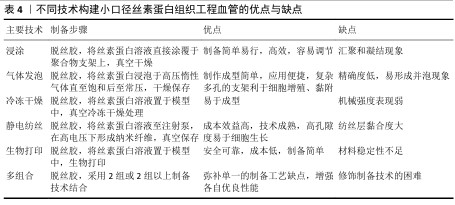
[6] 杨磊,李霞飞,董玉珍,等.小口径组织工程血管支架:如何产生一种具有生理重塑活性的材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(22):3579-3586.
[7] LI MX, WEI QQ, MO HL, et al. Challenges and advances in materials and fabrication technologies of small-diameter vascular grafts. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):91.
[8] LI G, SUN S. Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules. 2022;27(9):2757.
[9] DASTAGIR K, DASTAGIR N, LIMBOURG A,
et al. In vitro construction of artificial blood vessels using spider silk as a supporting matrix. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;101:103436.
[10] BOBADILLA JL. From ebers to EVARs: a historical perspective on aortic surgery. Aorta (Stamford). 2013;1(2):89-95.
[11] HU K, LI Y, KE Z, et al. History, progress and future challenges of artificial blood vessels: a narrative review. Biomater Transl. 2022;3(1):81-98.
[12] THOTTAPPILLIL N, NAI RPD. Scaffolds in vascular regeneration: current status. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2015;11:79-91.
[13] 蔡佳丽,陈菲菲,蒋鸣谦,等.丝素蛋白在生物材料领域的应用[J].广东蚕业, 2021,55(3):5-7.
[14] GONG X, LIU H, DING X, et al. Physiological pulsatile flow culture conditions to generate functional endothelium on a sulfated silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffold. Biomaterials. 2014;35(17):4782-4791.
[15] MARCOLIN C, DRAGHI L, TANZI M, et al. Electrospun silk fibroin-gelatin composite tubular matrices as scaffolds for small diameter blood vessel regeneration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(5):80.
[16] JANANI G, KUMAR M, CHOUHAN D, et al. Insight into Silk-Based Biomaterials: From Physicochemical Attributes to Recent Biomedical Applications. ACS Applied Bio Materials. 2019;2(12):5460-5491.
[17] SAHOO JK, HASTURK O, FALCUCCI T, et al. Silk chemistry and biomedical material designs. Nat Rev Chem. 2023;7(5):
302-318.
[18] AHSAN F, ANSARI TM, USMANI S, et al. An Insight on Silk Protein Sericin: From Processing to Biomedical Application. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2018;68(6):317-327.
[19] GUPTA P, MANDAL BB. Silk biomaterials for vascular tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2021;134:79-106.
[20] 匙峰,梁帅,王倩,等.丝素蛋白在骨组织工程领域的应用研究进展[J].西华师范大学学报(自然科学版),2022, 43(2):137-143.
[21] BUCCIARELLI A, MOTTA A. Use of Bombyx mori silk fibroin in tissue engineering: From cocoons to medical devices, challenges, and future perspectives. Biomater Adv. 2022;139:212982.
[22] ALKAZEMI H, CHAI J, ALLARDYCE BJ, et al. Glycerol-plasticized silk fibroin vascular grafts mimic key mechanical properties of native blood vessels. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2025;113(1):e37802.
[23] MICHELI L, PARISIO C, LUCARINI E, et al. Restorative and pain-relieving effects of fibroin in preclinical models of tendinopathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;148:112693.
[24] ZOU S, YAO X, SHAO H, et al. Nonmulberry silk fibroin-based biomaterials: Impact on cell behavior regulation and tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022;153: 68-84.
[25] CHEN Y, JIA Z, SHAFIQ M, et al. Gas foaming of electrospun poly(L-lactide-co-caprolactone)/silk fibroin nanofiber scaffolds to promote cellular infiltration and tissue regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;201:111637.
[26] BOJEDLA SSR, CHAMEETTACHAL S, YELESWARAPU S, et al. Silk fibroin microfiber-reinforced polycaprolactone composites with enhanced biodegradation and biological characteristics. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(7):1386-1400.
[27] LU Y, HUANG X, YUTING L, et al. Silk Fibroin-Based Tough Hydrogels with Strong Underwater Adhesion for Fast Hemostasis and Wound Sealing. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(1):319-331.
[28] LI Z, TAN G, XIE H, et al. The Application of Regenerated Silk Fibroin in Tissue Repair. Materials (Basel). 2024;17(16):3924.
[29] GRANEY PL, BEN-SHAUL S, LANDAU S, et al. Macrophages of diverse phenotypes drive vascularization of engineered tissues. Sci Adv. 2020;6(18):eaay6391.
[30] MA L, DONG W, LAI E, et al. Silk fibroin-based scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1381838.
[31] LI H, WANGY, SUN X, et al. Steady-State Behavior and Endothelialization of a Silk-Based Small-Caliber Scaffold In Vivo Transplantation. Polymers (Basel). 2019; 11(8):1303.
[32] ZHAO L, LI X, YANG L, et al. Evaluation of remodeling and regeneration of electrospun PCL/fibrin vascular grafts in vivo. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111441.
[33] JIA W, LI M, LIU L, et al. Fabrication and assessment of chondroitin sulfate-modified collagen nanofibers for small-diameter vascular tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;257:117573.
[34] BUSCEMI S, PALUMBO VD, MAFFONGELLI A, et al. Electrospun PHEA-PLA/PCL Scaffold for Vascular Regeneration: A Preliminary in Vivo Evaluation. Transplant Proc. 2017; 49(4):716-721.
[35] ROCKWOOD DN, PREDA RC, YÜCEL T, et al. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat Protoc. 2011;6(10): 1612-1631.
[36] ANAND P, PANDEY JP, PANDEY DM. Study on cocoonase, sericin, and degumming of silk cocoon: computational and experimental. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021;19(1):32.
[37] LIU X, HUANG Q, PAN P, et al. Comparative Study of the Preparation of High-Molecular-Weight Fibroin by Degumming Silk with Several Neutral Proteases. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(16):3383.
[38] WANG HY, WEI ZG, ZHANG YQ. Dissolution and regeneration of silk from silkworm Bombyx mori in ionic liquids and its application to medical biomaterials. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;143:594-601.
[39] DE GIORGIO G, MATERA B, VURRO D, et al. Silk Fibroin Materials: Biomedical Applications and Perspectives. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024;11(2):167.
[40] FUEST S, SMEETS R, GOSAU M, et al. Layer-by-Layer Deposition of Regenerated Silk Fibroin horizontal line An Approach to the Surface Coating of Biomedical Implant Materials. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(12):6644-6657.
[41] ZHAN C, XIA C, WANG P, et al. Modulation of neo-endothelialization of vascular graft materials by silk fibroin. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2021;66(6):573-580.
[42] KIRITANI S, KANEKO J, ITO D, et al. Silk fibroin vascular graft: a promising tissue-engineered scaffold material for abdominal venous system replacement. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):21041.
[43] MANIGLIO D, BONANI W, MIGLIARESI C, et al. Silk fibroin porous scaffolds by N(2)O foaming. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(5):491-506.
[44] LEE S, LEE J, BAEK J, et al. Design of Volumetric Nanolayers via Rapid Proteolysis of Silk Fibroin for Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2022;23(12):4995-5006.
[45] ZHU M, WANG K, MEI J, et al. Fabrication of highly interconnected porous silk fibroin scaffolds for potential use as vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):2014-2023.
[46] WANG M, WANG Y, PAN P, et al. A high molecular weight silk fibroin scaffold that resists degradation and promotes cell proliferation. Biopolymers. 2023;114(7):e23554.
[47] MALEKI S, SHAMLOO A, KALANTARNIA F. Tubular TPU/SF nanofibers covered with chitosan-based hydrogels as small-diameter vascular grafts with enhanced mechanical properties. Scientific Reports. 2022;12(1):6179.
[48] CHEN N, JIN W, GAO H, et al. Sequential intervention of anti-inflammatory and osteogenesis with silk fibroin coated polyethylene terephthalate artificial ligaments for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Mater Chem B. 2023; 11(34):8281-8290.
[49] HODGE J G, QUINT C. Improved porosity of electrospun poly (Lactic-Co-Glycolic) scaffolds by sacrificial microparticles enhances cellular infiltration compared to sacrificial microfiber. J Biomater Appl. 2022;37(1):77-88.
[50] YANG L, WANG X, XIONG M, et al. Electrospun silk fibroin/fibrin vascular scaffold with superior mechanical properties and biocompatibility for applications in tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):3942.
[51] DURÁN-REY D, BRITO-PEREIRA R, RIBEIRO C, et al. Development of Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Vascular Repair. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(3):1121-1130.
[52] ALESSANDRINO A, CHIARINI A, BIAGIOTTI M, et al. Three-Layered Silk Fibroin Tubular Scaffold for the Repair and Regeneration of Small Caliber Blood Vessels: From Design to in vivo Pilot Tests. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:356.
[53] 刘月,蒋紫仪,李晶晶,等.聚左旋乳酸己内酯/丝素蛋白小口径人工血管细胞共培养及体内生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(22):3505-3513.
[54] ALKAZEMI H, CHAI J, ALLARDYCE BJ, et al. Glycerol-plasticized silk fibroin vascular grafts mimic key mechanical properties of native blood vessels. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2025;113(1):e37802.
[55] FILIPE EC, SANTOS M, HUNG J, et al. Rapid Endothelialization of Off-the-Shelf Small Diameter Silk Vascular Grafts. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2018;3(1):38-53.
[56] LIU J, CHEN D, ZHU X, et al. Development of a decellularized human amniotic membrane-based electrospun vascular graft capable of rapid remodeling for small-diameter vascular applications. Acta Biomater. 2022;152:144-156.
[57] XU Y, WANG C, YANG Y, et al. A Multifunctional 3D Bioprinting System for Construction of Complex Tissue Structure Scaffolds: Design and Application. Int J Bioprint. 2022;8(4): 617.
[58] XIAO M, YAO J, SHAO Z, et al. Silk-Based 3D Porous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024; 10(5):2827-2840.
[59] LI X, LI N, FAN Q, et al. Silk fibroin scaffolds with stable silk I crystal and tunable properties. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;248: 125910.
[60] LI H, LI N, ZHANG H, et al. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Perfusable Hierarchical Microchannels with Alginate and Silk Fibroin Double Cross-linked Network. 3D Print Addit Manuf. 2020; 7(2):78-84.
[61] WANG H, ZHOU X, WANG J, et al. Fabrication of channeled scaffolds through polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) printed sacrificial templates for tissue formation. Bioact Mater. 2022;17: 261-275.
[62] GUPTA P, LORENTZ KL, HASKETT DG,
et al. Bioresorbable silk grafts for small diameter vascular tissue engineering applications: In vitro and in vivo functional analysis. Acta Biomater. 2020;105:146-158.
[63] HAJIABBAS M, ALEMZADEH I, VOSSOUGHI M. A porous hydrogel-electrospun composite scaffold made of oxidized alginate/gelatin/silk fibroin for tissue engineering application. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;245:116465.
[64] SONG J, CHEN Z, MURILLO LL, et al. Hierarchical porous silk fibroin/poly(L-lactic acid) fibrous membranes towards vascular scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;166: 1111-1120.
[65] KUANG H, WANG Y, SHI Y, et al. Construction and performance evaluation of Hep/silk-PLCL composite nanofiber small-caliber artificial blood vessel graft. Biomaterials. 2020;259:120288.
[66] CORDELLE J, MANTERO S. Insight on the endothelialization of small silk-based tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;43(10):631-644.
[67] RODRIGUEZ M, KLUGE JA, SMOOT D, et al.
Fabricating mechanically improved silk-based vascular grafts by solution control of the gel-spinning process. Biomaterials. 2020;230:119567.
[68] LIU X, OUYANG Q, YAO X, et al. A facile nanopattern modification of silk fibroin electrospun scaffold and the corresponding impact on cell proliferation and osteogenesis. Regen Biomater. 2024; 11:rbae117.
[69] CALDIROLI A, PEDERZANI E, PEZZOTTA M, et al. Hybrid fibroin/polyurethane small-diameter vascular grafts: from fabrication toin vivopreliminary assessment. Biomed Mater.2022;17(5).doi:10.1088/1748-605X/ac885a.
[70] GUPTA P, MANDAL BB. Fabrication of Small-Diameter Tubular Grafts for Vascular Tissue Engineering Applications Using Mulberry and Non-mulberry Silk Proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 2022; 2375:125-139.
[71] ALMASI-JAF A, SHAMLOO A, SHAYGANI H, et al. Fabrication of heparinized bi-layered vascular graft with PCL/PU/gelatin co-electrospun and chitosan/silk fibroin/gelatin freeze-dried hydrogel for improved endothelialization and enhanced mechanical properties. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt2):126807.
[72] CHAN AHP, FILIPE EC, TAN RP, et al. Altered processing enhances the efficacy of small-diameter silk fibroin vascular grafts. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):17461.
[73] FUKUDA K, KANEKO J, KIRITANI S, et al.
Thick silk fibroin vascular graft: A promising tissue-engineered scaffold material for abdominal vein grafts in middle-sized mammals. Int J Artif Organs. 2024;47(3):190-197.
[74] RIZZI S, MANTERO S, BOSCHETTI F, et al. Luminal endothelialization of small caliber silk tubular graft for vascular constructs engineering. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022; 9:1013183.
[75] FUKAYAMA T, OZAI Y, SHIMOKAWATOKO H, et al. Evaluation of endothelialization in the center part of graft using 3 cm vascular grafts implanted in the abdominal aortae of the rat. J Artif Organs. 2017;20(3):221-229. |