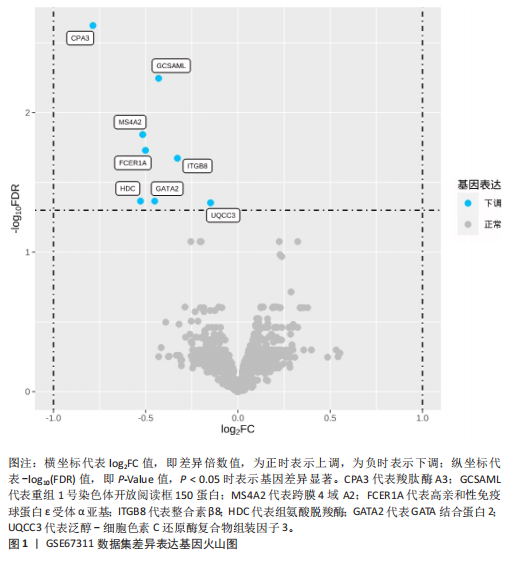
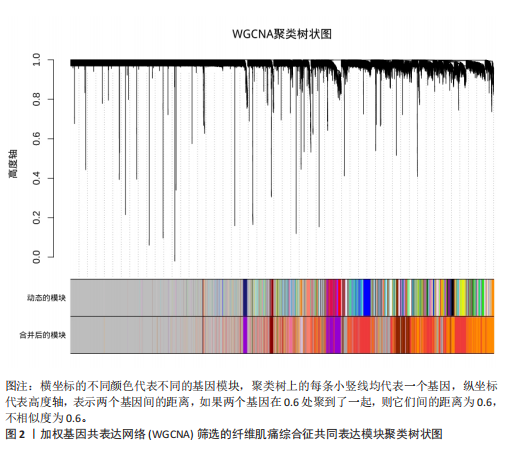
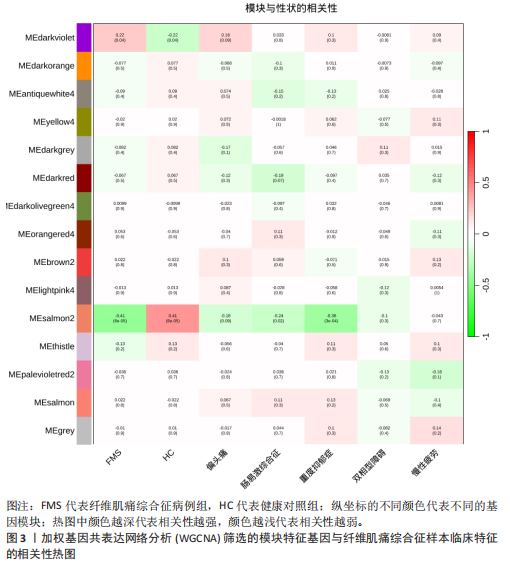
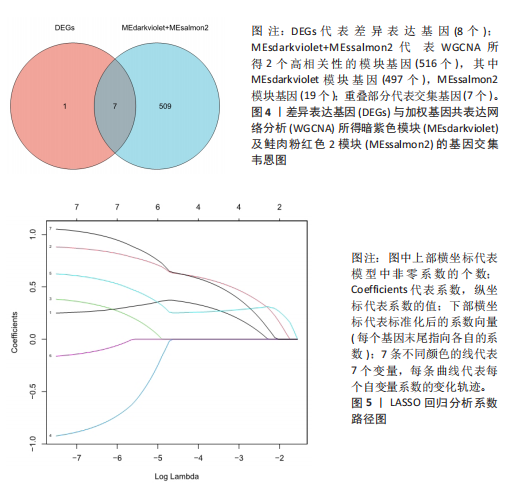
[1] WASTI AZ, MACKAWY AMH, HUSSAIN A, et al. Fibromyalgia interventions, obstacles and prospects: narrative review. Acta Myol. 2023;42(2-3):71-81.
[2] FAVRETTI M, IANNUCCELLI C, DI FRANCO M. Pain biomarkers in fibromyalgia syndrome: current understanding and future directions. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(13):10443.
[3] 刘雅妮,牛红青.25羟基维生素D水平与纤维肌痛综合征关系的Meta分析[J].山西医药杂志,2022,51(2):167-171.
[4] LIU W, LI L, YE H, et al. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis in biomedicine research. Shengwu Gongcheng Xuebao. 2017;33(11):1791-1801.
[5] LE T, ARONOW RA, KIRSHTEIN A, et al. A review of digital cytometry methods: estimating the relative abundance of cell types in a bulk of cells. Brief Bioinform. 2021;22(4):bbaa219.
[6] WANG YY, WANG ZX, HU YD, et al. Current status of pathway analysis in genome-wide association study. Yi Chuan. 2017;39(8): 707-716.
[7] JONES KD, GELBART T, WHISENANT TC, et al. Genome-wide expression profiling in the peripheral blood of patients with fibromyalgia. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016; 34(2 Suppl 96):S89-S98.
[8] MOHAPATRA G, DACHET F, COLEMAN LJ, et al. Identification of unique genomic signatures in patients with fibromyalgia and chronic pain. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):3949.
[9] GERRA MC, CARNEVALI D, PEDERSEN IS, et al. DNA methylation changes in genes involved in inflammation and depression in fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Scand J Pain. 2021;21(2):372-383.
[10] GERRA MC, CARNEVALI D, OSSOLA P,
et al. DNA methylation changes in fibromyalgia suggest the role of the immune-inflammatory response and central sensitization. J Clin Med. 2021;10(21):4992.
[11] FITZCHARLES MA, COHEN SP, CLAUW DJ, et al. Nociplastic pain: towards an understanding of prevalent pain conditions. Lancet. 2021;397(10289):2098-2110.
[12] DE TOMMASO M, VECCHIO E, NOLANO M. The puzzle of fibromyalgia between central sensitization syndrome and small fiber neuropathy: a narrative review on neurophysiological and morphological evidence. Neurol Sci. 2022;43(3):1667-1684.
[13] JI RR, NACKLEY A, HUH Y, et al. Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic and widespread pain. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(2):343-366.
[14] TSILIONI I, PIPIS H, FREITAG M, et al. Effects of an extract of salmon milt on symptoms and serum TNF and substance p in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Clin Ther. 2019;41(8):1564-1574.
[15] Al SS, VARGA SJ, Al-HUSINAT L, et al. Unraveling the complex web of fibromyalgia: a narrative review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(2):272.
[16] HELLMAN L, AKULA S, FU Z, et al. Mast cell and basophil granule proteases - in vivo targets and function. Front Immunol. 2022;13:918305.
[17] BRUM E, FIALHO M, BECKER G, et al. Involvement of peripheral mast cells in a fibromyalgia model in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024;967:176385.
[18] MOKHEMER SA, DESOUKY MK, ABDELGHANY AK, et al. Stem cells therapeutic effect in a reserpine-induced fibromyalgia rat model: a possible NLRP3 inflammasome modulation with neurogenesis promotion in the cerebral cortex. Life Sci. 2023;325:121784.
[19] KRUPA AJ, CHROBAK AA, SOLTYS Z, et al. Psychopathological symptoms in fibromyalgia and their associations with resistance to pharmacotherapy with SNRI. Psychiatr Pol. 2024. doi: 10.12740/PP/OnlineFirst/176000.
[20] ZABIHIYEGANEH M, AMINI KA, AKBARI A, et al. Association of serum vitamin D status with serum pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and clinical severity of fibromyalgia patients. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023;55:71-75.
[21] ELLERGEZEN P, ALP A, ÇAVUN S, et al. Pregabalin inhibits proinflammatory cytokine release in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Arch Rheumatol. 2023;38(2):307-314.
[22] HALILI A. Temporal model for central sensitization: a hypothesis for mechanism and treatment using systemic manual therapy, a focused review. MethodsX. 2023; 10:101942.
[23] BANFI G, DIANI M, PIGATTO PD, et al. T Cell Subpopulations in the physiopathology of fibromyalgia: evidence and perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1186.
[24] CONTI P, GALLENGA CE, CARAFFA A, et al. Impact of mast cells in fibromyalgia and low-grade chronic inflammation: can IL-37 play a role? Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(1):e13191.
[25] THEOHARIDES TC, TSILIONI I, BAWAZEER M. Mast cells, neuroinflammation and pain in fibromyalgia syndrome. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:353.
[26] LENERT ME, SZABO-PARDI TA, BURTON MD. Regulatory T-cells and IL-5 mediate pain outcomes in a preclinical model of chronic muscle pain. Mol Pain. 2023;19:804311971.
[27] EGE F, ISIK R. A comparative assessment of the inflammatory markers in patients with fibromyalgia under duloxetine treatment. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023;28(8):161.
[28] VALENCIA C, FATIMA H, NWANKWO I, et al. A correlation between the pathogenic processes of fibromyalgia and irritable bowel syndrome in the middle-aged population: a systematic review. Cureus. 2022;14(10):e29923.
[29] VERMA V, DRURY GL, PARISIEN M, et al. Unbiased immune profiling reveals a natural killer cell-peripheral nerve axis in fibromyalgia. Pain. 2022;163(7):e821-e836.
[30] BLANCO S, SANROMAN L, PEREZ-CALVO S, et al. Olfactory and cognitive functioning in patients with fibromyalgia. Psychol Health Med. 2019;24(5):530-541.
[31] SAYILIRS S, ÇULLU N. Decreased olfactory bulb volumes in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2017;36(12): 2821-2824.
[32] ÖZSOY-ÜNÜBOL T, KULLAKÇI H, ILHAN İ, et al. Evaluation of olfactory and gustatory functions in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: its relationship with anxiety, depression, and alexithymia. Arch Rheumatol. 2020;35(4):584-591.
[33] DORRIS ER, MACCARTHY J, SIMPSON K, et al. Sensory perception quotient reveals visual, scent and touch sensory hypersensitivity in people with fibromyalgia syndrome. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022;3:926331.
[34] CLAUW D, SARZI-PUTTINI P, PELLEGRINO G, et al. Is fibromyalgia an autoimmune disorder? Autoimmun Rev. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103424.
|