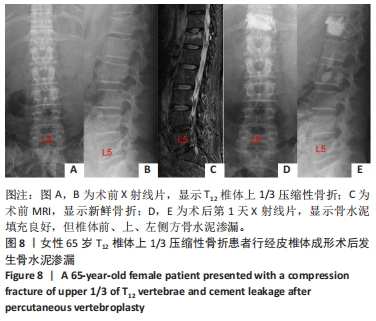
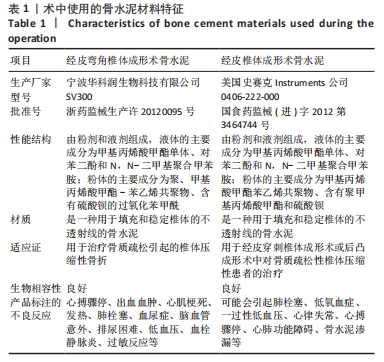
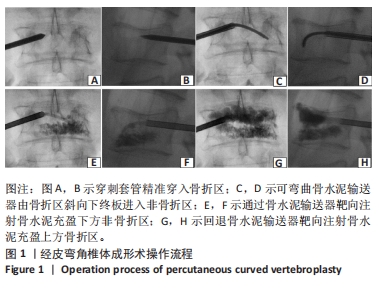
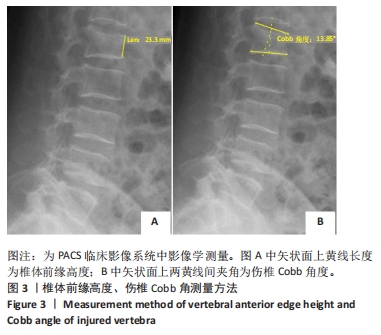
[1] 温勇,杨立进,陈博来,等.骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折手术患者1079例临床特征分析[J]. 广东医学,2019,40(5):680-684.
[2] LIN S, CAI X, CHENG Q, et al. Association between bone turnover markers, BMD and height loss of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):202.
[3] ZHANG H, HU Y, CHEN X, et al. Expert consensus on the bone repair strategy for osteoporotic fractures in China. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:989648.
[4] ROUX C, CORTET B, BOUSSON V, et al. Vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fracture. RMD Open. 2021;7(2):e001655.
[5] HINDE K, MAINGARD J, HIRSCH JA, et al. Mortality Outcomes of Vertebral Augmentation (Vertebroplasty and/or Balloon Kyphoplasty) for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology. 2020;295(1):96-103.
[6] SUN Y, MA H, YANG F, et al. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Zoledronic Acid Combined with PVP/PKP in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021: 6650358-6650358.
[7] 苟永胜,李海波,付柏林,等. 单双侧入路经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗伴伤椎后壁破损的骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折近期疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(10):1281-1287.
[8] LIANG D, YE LQ, JIANG XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis.J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):246-256.
[9] 郝国兵,朱泽兴,刘昆,等. 采用“双侧垂直错位穿刺法”与“双侧水平裂隙穿刺法”行经皮椎体成形术在治疗Ⅰ期Kümmell病的疗效对比[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2022,19(6):30-37.
[10] 胡斌,郑畅,韩晔,等. 弯角椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的有效性及安全性系统评价[J]. 山东医药,2024,64(2):59-63.
[11] LIU J, TANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture in the Midthoracic Vertebrae (T5-8): A Retrospective Study of 101 Patients with 111 Fractured Segments. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:e1381-e1387.
[12] HONG C, CHOI S, PARK M, et al. Body composition and osteoporotic fracture using anthropometric prediction equations to assess muscle and fat masses. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(6):2247-2258.
[13] 张保良,陈允震. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折住院患者的人口学特征及临床特征分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2019,39(24):1523-1535.
[14] 彭亮,俞霞,董刚,等. 一体式胸腰椎骨折充气复位仪的研制与临床应用[J]. 浙江医学,2016,38(12):1015-1018.
[15] ALY MM, AL-SHOAIBI AM, AL-AITHAN A, et al. Can Vertical Laminar Fracture Further Discriminate Fracture Severity Between Thoracolumbar AO Type A3 and A4 Fractures? World Neurosurg. 2021;155:e177-e187.
[16] BASARAN R, EFENDIOGLU M, KAKSI M, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Short- Versus Long-Segment Posterior Fixation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture. World Neurosurg. 2019;128:e1109-e1117.
[17] 谢胜荣,董迎春,王艳,等. 不同穿刺入路经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的疗效对比[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2020, 18(4):227-231.
[18] YANG W, YANG J, LIANG M. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Does Not Increase the Incidence of New Fractures in Adjacent and Nonadjacent Vertebral Bodies. Clin Spine Surg. 2019;32(2): E99-E106.
[19] 管华清,郭炯炯,姜为民,等. 椎体强化术治疗脊柱骨质疏松性三明治骨折术后夹心椎再骨折的影响因素分析[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2018,34(9):793-798.
[20] 张子龙,杨俊松,井齐明,等. 椎体成形术与后凸成形术治疗累及椎体中1/3急性骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效对比[J]. 骨科, 2022,13(1):34-40.
[21] ORTIZ AO, BORDIA R. Injury to the vertebral endplate-disk complex associated with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(1):115-120.
[22] ZHAO FD, POLLINTINE P, HOLE BD, et al. Vertebral fractures usually affect the cranial endplate because it is thinner and supported by less-dense trabecular bone. Bone. 2009;44(2):372-379.
[23] CHE-NORDIN N, DENG M, GRIFFITH JF, et al. Prevalent osteoporotic vertebral fractures more likely involve the upper endplate than the lower endplate and even more so in males. Ann Transl Med. 2018; 6(22):442.
[24] SHIN DE, LEE Y, AN HJ, et al. Trabecular structural difference between the superior and inferior regions of the vertebral body: a cadaveric and clinical study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1238654.
[25] 郝定均,张嘉男,杨俊松,等. 急性症状性骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折分型及其可信度检验和临床应用效果评价[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2021,37(3):250-260.
[26] 孙宏琪,赵健军,姜铁斌,等. 不同骨水泥弥散程度下骨水泥分布类型对经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折疗效的影响[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2024,22(2):87-93.
[27] 阿卜杜吾普尔·海比尔,库提鲁克·守克尔,阿里木江·玉素甫,等.单侧经皮椎体成形骨水泥分布对椎体压缩性骨折修复疗效的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(10):2015-2022.
[28] 阿卜杜吾普尔·海比尔,阿里木江·玉素甫,林航,等. 经皮椎体成形术中骨水泥分布对手术及邻近椎体再发骨折的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(29):4657-4662.
[29] ZHOU C, LIAO Y, HUANG S, et al. Effect of cement distribution type on clinical outcome after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the aging population. Front Surg. 2022;9:975832.
[30] 张益山,武壮壮,吕智. 椎体强化术后骨水泥分布情况对临床预后的影响[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2023,44(5):279-283.
[31] 肖建林,朱新林,谭屏,等. 椎体骨质疏松性骨折椎体成形术后骨水泥弥散分布与疗效的关系[J]. 中国现代手术学杂志,2023,27(4): 300-306.
[32] 吕泽斌,白尚君,宋江润,等. 骨水泥分布形态对经皮椎体成形术疗效的影响[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2023,26(4):480-484.
[33] PAN Z, ZHOU Q, YANG M, et al. Effects of distribution of bone cement on clinical efficacy and secondary fracture after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Front Surg. 2023;9:1054995.
[34] 刘芳,肖志宏,黄兰香. 两种不同入路PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者的效果比较[J]. 中外医学研究,2023,21(5):30-33.
[35] 钟睿,姜威,熊森,等. 单侧弯角与直行入路椎体成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折疗效的对照研究[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2018, 34(2):102-108.
[36] 张大鹏,毛克亚,强晓军,等. 弯角经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折术后的骨水泥分布[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2022, 20(2):121-124.
[37] MA X, XING D, MA J, et al. Risk factors for new vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: qualitative evidence synthesized from a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(12):E713-E722.
[38] HONG SJ, LEE S, YOON JS, et al. Analysis of intradiscal cement leakage during percutaneous vertebroplasty: multivariate study of risk factors emphasizing preoperative MR findings. J Neuroradiol. 2014;41(3):195-201.
[39] 王继,夏子茗,薛鸿,等. 弯角与单侧PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2023,25(2):103-110.
[40] 黄汇宇,胡海刚,林旭,等. 弯角弥散导针在单侧穿刺经皮椎体成形术中的应用研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(12):1587-1594.
[41] 李晖,孟祥翔,张超远. 三种穿刺经皮椎体成形术的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(15):1363-1367.
[42] HUANG H, HU H, LIN X, et al. Application of Curved Diffusion Needle in unilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(12):1587-1594.
|