中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5897-5906.doi: 10.12307/2025.835
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌改变的相关性及机制
刘家顺1,2,谢鸿儒1,2,孙云凯1,2,李书谨2,3,毛腾飞1,2,安瑶瑶1,2,张 钦1,2
- 1山西医科大学附属运城市中心医院,山西省运城市 044000;2神经医学运城市重点实验室,山西省运城市 044000;3长治医学院,山西省长治市 046000
-
收稿日期:2024-05-24接受日期:2024-08-24出版日期:2025-09-28发布日期:2025-03-07 -
通讯作者:张钦,博士,主任医师,山西医科大学附属运城市中心医院脊柱外科,山西省运城市 044000 -
作者简介:刘家顺,男,1997年生,汉族,山西医科大学骨科学在读硕士,主要从事脊髓损伤的研究。 -
基金资助:山西省教育厅高校科技创新项目(2023L134)
Correlation and mechanism between lumbar disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes
Liu Jiashun1, 2, Xie Hongru1, 2, Sun Yunkai1, 2, Li Shujin2, 3, Mao Tengfei1, 2, An Yaoyao1, 2, Zhang Qin1, 2
- 1Yuncheng City Central Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Yuncheng 044000, Shanxi Province, China; 2Yuncheng Key Laboratory of Neuromedicine, Yuncheng 044000, Shanxi Province, China; 3Changzhi Medical College, Changzhi 046000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-24Accepted:2024-08-24Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-07 -
Contact:Zhang Qin, MD, Chief physician, Yuncheng City Central Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Yuncheng 044000, Shanxi Province, China; Yuncheng Key Laboratory of Neuromedicine, Yuncheng 044000, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Liu Jiashun, Master candidate, Yuncheng City Central Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Yuncheng 044000, Shanxi Province, China; Yuncheng Key Laboratory of Neuromedicine, Yuncheng 044000, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Shanxi Provincial Department of Education College Science and Technology Innovation Project, No. 2023L134
摘要:
文题释义:
腰椎间盘退变:腰椎间盘是位于腰椎骨之间起缓冲和支撑作用的软骨组织。随着年龄的增长,腰椎间盘的水分含量减少,纤维环和软骨组织逐渐退化。在影像学中通常使用Pfirrmann分级来评估腰椎间盘退变,这种退变表现为椎间盘信号减弱、髓核与纤维环的分界不清晰以及椎间盘高度降低。椎旁肌退变:椎旁肌作为脊柱的重要构成部分,包括浅层肌肉如棘肌、最长肌和髂肋肌,以及深层肌肉如多裂肌、回旋肌和横突间肌等。在形态学上,椎旁肌的退变主要表现为肌肉质量的减少和组织的变性。具体而言,肌肉的萎缩和变性意味着肌纤维的数量和体积减少,同时肌肉组织被脂肪组织替代的情况也可能发生。
摘要
背景:椎旁肌退变是腰痛的主要致病因素之一,而椎旁肌的改变则与其发生发展密切相关。现阶段临床工作者关注腰椎退行性疾病中椎旁肌的变化,以预防和治疗腰椎疾病,而忽略了疾病中腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌的联系及相关机制。
目的:对椎旁肌和腰椎间盘的相互作用研究进行全面总结,从而综述腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌的相关性及机制,旨在为临床防治提供
参考。
方法:使用中文关键词“腰椎间盘,椎旁肌,多裂肌,腰痛,退行性变,影像学,磁共振成像”在中国知网、维普、万方等中文数据库中检索相关文献,并使用英文关键词“lumbar disc ,paraspinal muscle ,multifidus muscle,low back pain,degeneration ,imaging ,MRI”在Medline、PubMed、Web of Science等英文数据库中检索。通过初步筛选标题和摘要,按照纳入和排除标准筛选文献,最终选取了68篇文献进行综述分析。
结果与结论:①研究者们利用各种方法来评估椎旁肌的退变程度,同时按照Pfirrmann分级对腰椎间盘退变程度进行评估,发现临床诊疗中应关注性别差异,并重视肥胖等因素对腰椎间盘和肌肉退变的影响,以制定更加个体化的治疗方案。②腰椎间盘退变和椎旁肌肉脂肪浸润之间存在一定关联,但研究结果存在争议。多数研究发现,椎旁肌肉(尤其是多裂肌)的脂肪浸润与腰椎间盘退变程度呈正相关。③目前认为失用性萎缩、去神经机制及炎症因子3种机制可能相互作用,共同导致椎旁肌肉的结构和功能改变,这与腰椎间盘退变和腰痛的发生密切相关。④临床上应关注受累神经根节段以下一级肌肉的变化,有助于诊断和定位腰椎根神经病变。同时,抑制炎症因子可能成为治疗的潜在靶点。⑤临床工作中,首先应通过适当的药物或手术治疗纠正神经根压迫,以控制炎症反应和神经根疼痛,然后再进行针对性的肌肉康复训练。必要时考虑采用干扰电流电刺激等新型治疗方法来改善患者的症状和预后。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘家顺, 谢鸿儒, 孙云凯, 李书谨, 毛腾飞, 安瑶瑶, 张 钦. 腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌改变的相关性及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(27): 5897-5906.
Liu Jiashun, Xie Hongru, Sun Yunkai, Li Shujin, Mao Tengfei, An Yaoyao, Zhang Qin. Correlation and mechanism between lumbar disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5897-5906.
观测椎旁肌在形态学上的退变最常用的就是影像学工具(表2),MRI具有辐射水平低、分辨率高、无创、方便的优点,MRI可以更好地区分不同的软组织,因为MRI有T1加权(T1W1)和T2加权(T2W1)两种不同的成像特性,而且不涉及辐射处理,这使得MRI能够更清晰地显示脊柱周围脂肪组织的形态和分布。例如:脊柱硬膜外脂肪增生(SEL)是一种由于硬膜外过度脂肪沉积导致脊髓或神经根受压的罕见疾病,成像中硬膜外脂肪厚度没有明确标准,而MRI比电子计算机断层扫描(CT)更能确定神经压迫[17]。尽管MRI是评估椎旁肌变化的金标准,但在临床实践中评估肌肉量(如脂肪浸润)通常需要耗时且需要有经验的技术人员。椎旁肌的横截面积(CSA)和脂肪浸润(FI)常被用作指标评估肌肉功能。SHI等[18]认为去除肌内脂肪后的感兴趣区域的功能横截面积/肌肉横截面积(FCSA/CSA)可以评价椎旁肌的萎缩和肥大程度,同时利用公式FI = 1-FCSA/CSA 评价椎旁肌的脂肪浸润。MANDELLI等[19]指出椎旁肌相对于椎体的横截面积(rCSA),也可以用来描述肌肉的不对称性。随着脊柱稳定性理论的进一步丰富和影像学技术的发展,一些新方法被用来评估椎旁肌的形态和功能,双能X射线骨密度仪与使用MRI进行椎旁肌肉质量3D分析存在强正相关性,在对骨质疏松症和肌肉减少症的诊断有价值[20]。最近,一些研究表明双能电子计算机断层扫描(DECT)量化骨骼肌脂肪分数和 MRI 脂肪分数之间具有极好的相关性,是一种可靠可行的方法[21]。表面肌电图(sEMG)相对于其他影像学检查的特性在于能揭示腰椎旁肌疲劳、躯干肌活动不协调、缺乏屈曲放松现象和椎旁肌肌电活动的不对称性[22],分析椎旁肌可选取时域指标和频域指标,时域指标可反映肌肉收缩过程中的幅值变化情况和肌力平衡性,频域指标反映肌肉疲劳状态和肌力特征,这些特点使表面肌电图可以实时监测人体脊柱两侧椎旁肌的生理状态[23]。

2.2 腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌改变的关系
2.2.1 年龄、性别、体质量对腰椎间盘及椎旁肌的影响 在临床研究中,患者的腰椎间盘和肌肉的退变往往受到多种混合因素的影响,如年龄、性别、体质量指数(BMI)等[14] (表3)。有研究发现,随着年龄的增长椎旁肌质量逐渐减少,腰椎间盘退变等级(Pffirrman分级)逐渐增加[24]。?ZCAN-EK?I等[25]对各50名有腰腿痛症状及年龄相匹配的男女性进行了横断面分析,指出女性相比男性有更大的椎间盘退变风险,女性在L4-5和L5-S1水平的多裂肌和竖脊肌中有更多的脂肪浸润,男性在L5-S1水平的腰大肌中有更多的脂肪浸润。FAUR等[14]回顾性分析16例男性和19例女性慢性下腰痛患者的临床资料,发现男性椎间盘退变更多,女性脂肪浸润更高,但该研究的样本量有限,结果是否可以在更大的研究群体中得到证实存在争议。相反,HOPPE等[26]研究指出年龄和椎间盘退变与椎旁肌肉退变存在独立关联。SHI等[18]发现椎旁肌肉的脂肪浸润不受体质量指数的影响,在L4/5水平女性比男性的脂肪浸润程度更高,但作者并未评估该节段男女椎间盘退变的差异。另一项研究表明,体质量指数较高的患者更多在上腰椎(L2-4)节段出现椎旁肌的脂肪浸润,在L4/5出现椎间盘退变,尤其在女性患者中更为常见[27]。推测与女性和男性的激素状态和脂肪分布模式不同有关,导致女性和男性在承受同等荷载时出现不同的生物力学响应,即在女性患者中,这可能是一种“多米诺骨牌效应”,肥胖导致上腰椎水平椎旁肌质量下降,增加了L4/5椎间盘的剪切力,从而进一步导致下腰椎水平更严重的椎间盘退变,这些变化最终可能导致腰痛的恶化,因此对于女性患者应重视体质量指数/肥胖状态,并密切关注其椎间盘退变和椎旁肌改变的情况,以制定更加针对性的诊疗方案。

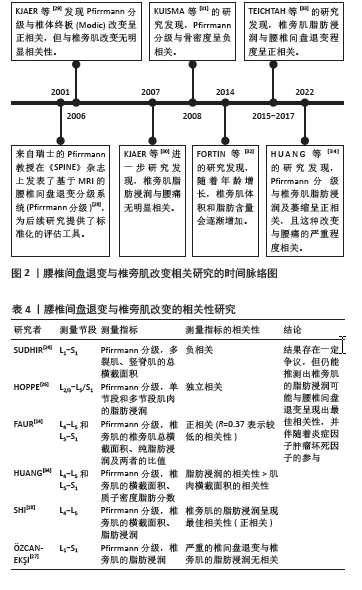
2.2.2 腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌退变的相关性 2001年,Pfirrmann分级首次提出被用于为临床和研究提供一种标准化和可靠的MRI腰椎间盘形态学评估方法[28]。在过去20年中被广泛应用于相关研究(图2) [28-34]。现有证据表明,它与椎体终板改变及骨密度密切相关,但与椎旁肌改变似乎无直接关联[29,31]。该文纳入了近5年的相关文献研究(表4),依据研究者对不同节段腰椎MRI的测量,发现椎旁肌(特别是多裂肌)中的脂肪浸润与下腰痛和腰椎间盘退变有关[18],但并不清楚椎间盘和椎旁肌退变是否为下腰痛发生的独立影响因素。
SUDHIR等[24]收集了504名下腰痛患者的2 520节段(L1-S1)腰椎MRI数据,通过分析腰椎的多裂肌和竖脊肌的总横截面积(GCSA)的数据,以平均值和标准差表示,并测量相应椎间盘的Pfirrmann分级,发现多裂肌的横截面积与腰椎间盘退变之间存在负相关,但该研究未对患者的临床表现、神经学或残疾进行评估,这些因素可能直接或间接地对多裂肌萎缩产生影响;另外,虽然测量了肌肉的横截面积,但未评估肌肉内部脂肪浸润的变化。
HOPPE等[26]对36例下腰痛患者在T2加权MRI图像的椎旁肌进行多节段和单节段肌肉的脂肪浸润分析,单节段肌肉相对于多节段肌肉显示出更高的脂肪浸润,尤其在下腰椎水平(L4/5、L5/S1)显示出比上腰椎水平(L2-4)更高的脂肪浸润程度。
腰椎间盘退变程度和发生率较高的是L4-5和L5-S1节段[35],FAUR等[14]评估了L4-5和L5-S1节段的Pfirrmann分级及椎旁肌总横截面积和纯脂肪浸润的百分比(PFCSA/TMCSA),结果发现L5-S1相对L4-L5的腰椎间盘退变和椎旁肌脂肪浸润程度更高,但由于该研究的患者趋于年轻化,样本数有限不足以代表整体,实验结果可能不具有特异性。HUANG等[34]测量下腰痛患者L4/5和L5/S1水平的椎旁肌横截面积和质子密度脂肪分数(PDFF),发现下腰痛患者的横截面积减少和椎旁肌质子密度脂肪分数增加,且质子密度脂肪分数与腰椎间盘退变变性之间的相关性高于横截面积与腰椎间盘退变变性之间的相关性,提示下腰痛患者椎旁肌存在脂肪替代和肌肉萎缩。
SHI等[18]测量了MRI T2加权下总肌肉横截面积(TCSA)、L4 椎体终板面积和脂肪的横截面积,多裂肌和腰椎间盘标本取自8例因椎间盘突出症(LDH)接受椎间盘切除术的患者,分别通过定量聚合酶链式反应(qPCR) 测定和酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)定量肿瘤坏死因子的基因和蛋白表达水平。线性回归分析表明,Pfirrmann分级与多裂肌的脂肪浸润最相关,与肌肉横截面积无关;与轻度退变组(Ⅱ度退变组)相比,重度退变组(Ⅳ度退变组)多裂肌的脂肪浸润明显增加,同时伴有肿瘤坏死因子信使核糖核酸(TNF mRNA)表达增加;同时,重度退变组椎间盘和多裂肌中肿瘤坏死因子蛋白表达水平分别为(16.62±4.33) pg/g和(13.10±2.76) pg/g,均高于轻度退变组[椎间盘:(9.75±2.18) pg/g;多裂肌:(7.84±2.43) pg/g],
结果显示出多裂肌的脂肪浸润与腰椎间盘退变的最佳相关性,推测机制是腰椎间盘退变通过炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子产生脂肪浸润,但此结论是仅在L4-L5水平评估了椎旁肌的脂肪浸润情况得出的,并不能全面反映整个腰椎段的情况,同时未探讨其他炎症因子的作用。类似的,最近一项在 X 射线透视引导下穿刺L4/5和L5/6 腰椎间盘退变,建立了椎间盘源性腰痛(DLBP)实验大鼠模型[36],组织学检查显示,椎间盘源性腰痛组大鼠的椎间盘出现典型的退变变化,这与腰椎间盘退变变性患者的MRI T2WI结果一致[37-38],包括胶原纤维增加、髓核减少、纤维环增厚、形状扭曲以及肌肉组织的变化,如肌束间隙增加和肌肉组织内脂肪滴增加;此外椎间盘源性腰痛组腰椎间盘退变和椎旁肌中肿瘤坏死因子α的表达明显高于对照组(P < 0.05)。这些结果表明,腰椎间盘退变与椎间盘源性腰痛中的肌肉脂肪浸润之间存在直接联系,可能与肿瘤坏死因子α表达增加有关。
然而,一些研究得出了不同的结论,有研究发现在下腰痛患者中,多裂肌脂肪萎缩的程度与腰椎间盘退变的相关性很差(R=0.37)[14]。有趣的是,另一项研究表明,在患有慢性下腰的女性中,严重腰椎间盘退变和椎旁肌肉的脂肪浸润在任何腰椎水平上都没有显示出统计学显著的关系[16]。
综上所述,目前研究结果存在一定争议,但仍能推测出多裂肌的脂肪浸润可能与腰椎间盘退变呈现出最佳相关性,这可能是因为当肌肉组织发生萎缩时,会出现脂肪浸润进入椎旁肌中。因此,相比于肌肉横截面积的变化,脂肪浸润更能反映肌肉组织的实际变化,脂肪浸润增加表明肌肉质量和功能的下降,这与腰椎间盘退变的关系更为密切。而炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子可能参与了腰椎间盘退变和椎旁肌脂肪浸润的病理过程,需要进一步深入探讨腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌肉变化之间的关系及其潜在的机制,为未来针对性的药物治疗提供了潜在的治疗靶点。
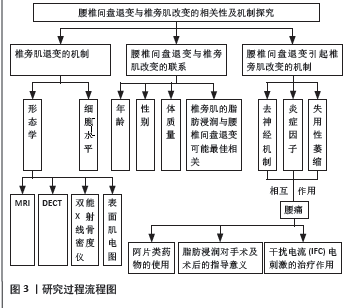
2.3 腰椎间盘退变引起椎旁肌改变的三大机制 尽管腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌改变的相关性是显著的,但并不清楚两者与下腰痛之间的级联反应,需要进一步的纵向研究和病理生理学机制探讨,以更好地理解下腰痛发生的复杂病理过程。目前认为引起椎旁肌结构变化的主要机制有3种[14]:失用性萎缩、肌肉去神经支配(表5[39-41])和炎症反应失调(表6)。
2.3.1 失用性萎缩 失用性肌肉萎缩是由于长期缺乏活动或使用而导致的一种常见的肌肉退行性变化,腰椎间盘退变通常会导致腰背肌群的长期失用和活动受限,从而引发相应的肌肉萎缩。既往研究发现,椎间盘突出症等病变会压迫脊神经,造成腰背肌群的神经支配障碍以及炎症因子的上调,这种神经功能紊乱会导致肌肉纤维的失活和萎缩[42-43]。当腰椎间盘退变引起下腰痛导致腰背部肌肉的功能性锻炼丧失,毛细血管反应性降低,肌肉供血不足,长期缺氧、糖原利用率低、代谢产物的积累导致肌肉水肿,由于肌肉的失用和退化,肌肉组织逐渐被脂肪组织所取代,所以失用性萎缩往往会影响椎旁肌的整体,因椎旁肌的退变往往是局部的,所以失用机制往往被拒绝,该文不做重点讨论,而椎旁肌的变化导致的神经支配是常见的局部或节段性。
2.3.2 去神经机制 根据去神经机制,腰椎间盘(包括髓核、纤维环和软骨板)在不同程度的退变后,受到外力因素的影响,椎间盘的纤维环可能会破裂,导致髓核从破裂处突出(或脱出),这会导致相邻的神经根或马尾神经受到刺激或压迫,长期的神经去支配可能会引起周围神经的阶段性脱髓鞘和轴突变性,最终导致肌肉的神经支配和肌核数量逐渐减少[44]。随着失神经时间的延长肌纤维萎缩,肌细胞无法维持基本功能,最终分化成纤维细胞。此外,成纤维细胞的增殖导致去神经肌肉中结缔组织的增殖。肌肉中的毛细血管和其他小血管被密集的胶原蛋白层包围,将它们与相邻的肌纤维分隔开来,它可能影响血管床和肌纤维之间的物质交换,也影响轴突的插入和延伸,肌肉纤维化是不可避免的。
(1)去神经机制导致椎旁肌横截面积改变:既往研究表明腰椎间盘退变导致髓核向外突出,压迫神经根,引起椎旁肌痉挛、萎缩等改变[45]。PLOUMIS等[39]评估了40例单节段退行性椎间盘疾病引起的单侧下腰痛患者椎旁肌的横截面积,其中32例患者存在与椎间盘病变相符的腰椎根性疼痛,发现患侧肌肉的横截面积显著小于无症状侧,多裂肌在病变节段上方的横截面积减少最多,其他肌肉在病变节段下方的横截面积减少最多,推测持续性单侧下腰痛会导致相应肌肉群的单侧性萎缩,这可能是由于神经反射抑制机制造成的。除多裂肌外,其他肌肉在病变节段下方的萎缩更严重,可能是由于这些肌肉受到了来自病变节段上方和下方的双重影响,导致了更大程度的萎缩,这提示临床医生在评估和治疗时应关注病变节段以及其下方的肌肉状态。不同于PLOUMIS等[39]的研究结果,KANG等[40]通过将37例单侧L4或L5神经根病患者分为2组,在3个水平上测量多裂肌的总肌肉横截面积和纯肌肉横截面积:L4棘突中部、L5棘突中部和S1骶骨中嵴,通过使用T1加权快速自旋回波序列的MRI扫描获取轴位图像,以检测右侧和左侧椎旁肌的横截面积并使用Rapidia分析程序手动勾画多裂肌的感兴趣区域(ROI)为总肌肉横截面积,采用基于像素信号强度差异的阈值技术,从总肌肉横截面积中去除脂肪成分,得到纯肌肉横截面积,计算纯肌肉横截面积与总肌肉横截面积的比率(PMCSA/TMCSA)以估计萎缩的严重程度,结果发现该比率的最低值出现在L4神经根病组的L5棘突中部以及L5神经根病组的S1骶骨中嵴(S1椎体中央裂水平),推测这可能与多裂肌的解剖和神经支配特点有关:多裂肌由不同节段的肌束组成,每个肌束由相应节段的背支神经支配,多裂肌的肌束从上位椎体的棘突起始,沿着椎板和棘突的背侧表面向下延伸,因此上位椎体起始的肌束位置是较浅和外侧的,而下位椎体起始的肌束位置是较深和内侧的,L4肌束附着在L5椎体的棘突上,L5肌束附着在S1椎体的中央裂上,这表明多裂肌的最严重萎缩发生在受累神经根节段数以下的一级。所以临床医生在评估多裂肌萎缩的严重程度和位置时,应关注受累神经根节段数以下一级的变化,这有助于诊断和确定腰椎根神经病变的水平。
(2)去神经机制导致椎旁肌脂肪浸润程度改变:在人类研究中,COOLEY等[46]发现神经根的持续压迫不仅导致肌纤维萎缩,并伴有脂肪浸润,而且脂肪浸润增加与肌肉横截面积的一致减少有关。一项猪的模型研究中,实验性造成椎间盘和神经根损伤后,数天内观察到椎间盘损伤引起的多裂肌面积减小仅局限于损伤节段(L4),而神经根损伤引起的横断面积减小则分布在更广泛的区域(L4-L6) [41],推测椎间盘病变后的椎旁肌快速水平特异性变化可能是由反射抑制机制引起的。这表明,多裂肌不对称可能是急性疼痛性椎间盘病变的早期指标,多裂肌萎缩的水平侧特异性可以帮助定位疼痛性腰椎间盘相关的病理。该研究还发现,椎间盘损伤导致双侧多裂肌水含量和乳酸浓度降低,而神经根损伤仅影响损伤侧;同时组织学检查显示,椎间盘损伤和神经根损伤都会导致多裂肌内脂肪细胞增大和肌纤维集聚,但分布不同,椎间盘损伤的变化仅局限于损伤节段。因此临床上,评估多裂肌的变化可以帮助区分椎间盘和神经根损伤的病因,为诊断提供依据,需要根据具体损伤情况进行个体化评估和干预。HYUN等[47]通过肌电图检查发现神经根病患者的多裂肌不对称性显著增加,但没有研究特定节段的不对称性。然而,KOTTLORS等[48]提出特定节段的神经支配椎旁肌的效应降低了肌肉起源的水平,该节段神经背支内侧分支支配椎旁肌,因此,任何神经根病变对多裂肌的原发性改变在受影响神经根背支内侧分支供应的水平上最深刻,在更远的肌肉中发生的变化逐渐变小。这可能有助于解释偶尔发现受影响神经根上方肌肉的椎旁肌功能横截面积降低(尽管不显著),但主要由受压神经根供应肌肉的功能横截面积显著降低的可能性更大。有研究报告指出总肌肉横截面积的腰椎节段侧间差异不如功能横截面积的一致性[49],肌肉萎缩最简单地通过成像评估为总肌肉横截面积的整体尺寸减小,忽略了单个肌束可能萎缩并被脂肪浸润取代而导致整体肌肉横截面积没有明显变化的可能性,这同样可以解释脂肪浸润是腰椎间盘退变中一个重要因素。
2.3.3 炎症学说 已有动物研究表明,局部炎症活性的失调是与腰椎间盘退变病变/损伤相关的椎旁肌中脂肪和结缔组织积聚的主要潜在因素[50](例如,腰椎间盘退变自发变性[51-52]、实验性腰椎间盘退变损伤[49]),包括急性期抑制椎旁肌激活[41]、亚急性和慢性期椎旁肌萎缩导致慢缩肌纤维丢失、结缔组织积聚和脂肪浸润。CHEN等[53]研究发现腰椎间盘退变的患者中肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素1β、转化生长因子β1等炎症基因与多裂肌的脂肪浸润和横截面积减少相关。
(1)肿瘤坏死因子:既往研究认为,炎症因子是腰椎间盘退变的重要因素,尤其是肿瘤坏死因子α,慢性低水平肿瘤坏死因子α可能是促进骨骼肌脂肪因子形成的重要因素[54-55]。在动物实验中,JAMES等[51]建立了一个可控的腰椎间盘退变绵羊模型,发现在腰椎间盘退变病变后3个月和6个月,多裂肌和脂肪组织中存在更大比例的促炎性M1巨噬细胞,而巨噬细胞总数保持不变;6个月时,肿瘤坏死因子在脂肪和结缔组织中的表达增加,M1巨噬细胞表达的肿瘤坏死因子比例也增加;结果表明,巨噬细胞和促炎细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子在腰椎间盘退变变性期间多裂肌、脂肪和结缔组织的亚急性/早期慢性重塑阶段中发挥积极作用,推测实验性腰椎间盘退变后,多裂肌中M1巨噬细胞的增加导致了肿瘤坏死因子表达的升高,从而诱导脂肪浸润。类似的,一项对于椎间盘突出症患者的多裂肌研究中发现,高程度的脂肪浸润与肿瘤坏死因子表达升高有关[53],这为解释脂肪和肿瘤坏死因子之间的双向关系提供了证据。
(2)白细胞介素1β:JAMES等[51]指出白细胞介素1β的更高表达促进肌肉分化,并在肌生成的早期阶段和纤维化的减少中发挥作用,这可能导致肌肉横截面积的减少。类似的,一项关于腰椎间盘退变病变的小鼠模型研究表明,通过运动阻断白细胞介素1β的表达可能导致不同的纤维化/脂肪浸润,间充质干细胞治疗后椎旁肌中白细胞介素1β的减少与椎旁肌中存在的结构重塑成分的减弱/延迟发展相关[52]。而WANG等[56]研究发现肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β在腰椎间盘退变中的表达水平明显升高,且与腰椎间盘退变程度呈正相关,肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β可通过激活多种信号通路,如核因子κB、AP-1等,参与腰椎间盘退变的多个病理过程,包括炎症反应、基质破坏、细胞衰老、凋亡、焦亡以及增殖等。因此抑制肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β有望缓解腰椎间盘退变和下腰痛,促进正常腰椎结构功能组织恢复的再生特性,并因此成为潜在的治疗靶点。
(3)转化生长因子β1:转化生长因子β1在椎间盘突出症患者椎旁肌中的确切表达方式及其确切意义目前尚不清楚。但有研究表明,转化生长因子β1能够激活肌源性干细胞,改变它们的生物学活性,促使它们大量合成和分泌胶原纤维,增强细胞外基质的沉积和重塑,从而促进失神经骨骼肌的纤维化过程[57]。LIU等 [58]研究发现在纤维化过程中,骨骼肌中转化生长因子β1的表达显著增加并持续高水平表达,同时Ⅰ型胶原纤维的沉积与转化生长因子β1的表达密切相关。因此,转化生长因子β1在失神经骨骼肌纤维化中起重要作用,是探索失神经肌萎缩防治的重要突破点。但临床治疗的主要挑战是了解如何改善肌肉再生,减少肌肉纤维化和萎缩,改善患者的疼痛症状,并在不改变转化生长因子β1在其他组织中的正常功能的情况下做到这一点,这是现阶段临床治疗中面对的难点。
2.4 临床防治 综上所述,腰椎间盘退变导致的神经根损伤通过引发局部炎症反应和炎症因子的作用,导致相应椎旁肌的萎缩和功能障碍,并逐步产生失用性萎缩,最终导致下腰痛的产生。先前的动物和人类研究表明,肌电活动增加和肌肉结构重塑(例如肌肉萎缩、脂肪浸润和纤维类型变化)与下腰痛相关[59-60]。根据北美脊柱协会(NASS)的定义,下腰痛是指源于肌肉骨骼系统的疼痛或不适感,发生在背部区域,从最低肋骨到臀部,有时甚至延伸到大腿[61]。下腰痛的早期研究主要集中在腰椎间盘退变和过度负荷等因素。在正常人中,腰椎旁肌肉的肌肉负荷处于平衡状态,然而,当腰椎间盘退变使腰椎变得不稳定时,脊柱旁肌肉的张力负荷会增加以维持脊柱平衡,在严重不稳定或长期肌肉超负荷的情况下,脊柱旁肌肉可能会萎缩和脂肪变性[62],从而导致脊柱不稳和下腰痛的产生。同样,椎旁肌的退变会加速腰椎的退变。椎旁肌在加强椎间关节和稳定身体和脊柱,肌肉的横截面积与产生力量的能力有关,减少了肌肉的横截面积区域会导致肌肉力量不平衡,进而导致脊柱运动不稳定,脊柱的这种不稳定性导致了载荷在整个椎间盘中的不合理分配,并可能导致腰椎间盘退变和下腰痛。因此应该重视强化椎旁肌肉形态上的改变,以预防下腰痛并遏制退行性变的级联效应。
HAN等[63]对461例接受腰椎椎间融合术治疗的腰椎椎管狭窄(DLSS)患者进行了为期1年的病例对照研究,将160对患者分为脂肪浸润< 25%组和脂肪浸润≥25%组,根据L4水平多裂肌的脂肪浸润情况发现脂肪浸润≥25%组发生骨不连的风险显著增高,高脂肪浸润会影响螺钉松动患者的骨愈合,而如果患者没有出现螺钉松动,脂肪浸润则不会产生这种影响,提示高脂肪浸润在骨不连中可能起次要作用;在螺钉固定不满意的患者中,低多裂肌的脂肪浸润可能是骨不连的保护因素。而CARVALHO等[64]调查了患有椎间盘突出症并行腰椎间盘切除术的患者后发现,椎旁肌脂肪浸润< 15%与术后预后更好相关,而脂肪浸润> 30%与术后状况更差相关,这表明椎旁肌的康复训练是有用的,提升了患者术后的预后质量并减低了骨不愈合的发生率。
最新的一项研究指出,短期使用阿片类药物治疗慢性下腰痛可能会增加不良事件的发生,包括胃肠道不良事件(恶心、呕吐等)和神经系统不良事件(头晕、嗜睡
等) [65-66],因此在权衡利弊后,需要根据患者的具体情况谨慎使用阿片类药物,并密切监测不良事件的发生,与患者充分沟通利弊,以达到最佳的治疗效果。而神经性疼痛是由炎症、刺激或过度压迫神经组织引起的,根据KAMATH等[67]关于MRI上肌肉去神经支配的外观的综述,去神经支配后几天内或几周内可能发生水肿样信号变化;此外,在去神经支配几周后,可以看到进行性肌肉萎缩和脂肪浸润,并描述了肌肉假性肥大的情况,其可在去神经支配后数周内发生,此时肌肉短暂增大,整个肌肉中可见过量脂肪浸润,并且存在增加的细胞外液;这种现象可以解释肌肉中出现更多的脂肪成分。而YANG等[17]指出脊柱硬膜外脂肪增生是一种罕见疾病,其相对传统的神经抑制不同,是由于硬膜外过度脂肪沉积导致脊髓或神经根受压。因此,在椎间盘突出症合并神经根病的患者中,可以预见要制止和纠正严重的脂肪浸润和肌肉变性,首先应通过适当的药物或手术治疗纠正神经根压迫,以控制炎症反应和神经根疼痛。
最新的一项研究指出,干扰电流(IFC)电刺激治疗腰椎间盘退变、肌肉萎缩或骨骼肌功能障碍患者有良好的效果[68],作为一种应用于肌肉骨骼疾病治疗的电刺激,它可以降低到达深部肌肉组织的皮肤阻抗,而不会增加患者的不适感,并且在增加神经肌肉的兴奋性、缓解炎症、消除浮肿、减轻神经或肌肉疼痛、促进神经再生、增强肌肉力量和改善身体活动方面有效。

| [1] WANG F, CAI F, SHI R, et al. Aging and age related stresses: a senescence mechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):398-408. [2] SILAGI ES, SHAPIRO IM, RISBUD MV. Glycosaminoglycan synthesis in the nucleus pulposus: Dysregulation and the pathogenesis of disc degeneration. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:368-379. [3] BOOS N, WEISSBACH S, ROHRBACH H, et al. Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(23):2631-2644. [4] THOMPSON JP, PEARCE RH, SCHECHTER MT, et al. Preliminary evaluation of a scheme for grading the gross morphology of the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990;15(5):411-415. [5] MIMURA M, PANJABI MM, OXLAND TR, et al. Disc degeneration affects the multidirectional flexibility of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(12):1371-1380. [6] LANE NE, NEVITT MC, GENANT HK, et al. Reliability of new indices of radiographic osteoarthritis of the hand and hip and lumbar disc degeneration. J Rheumatol. 1993;20(11):1911-1918. [7] 刘珍珍,陈建宇,蔡兆熙,等.腰椎间盘退变MRI: T1rho值与Pfirrmnn分级及T2值的相关性[J].中国医学影像技术,2014(2): 260-264. [8] KETTLER A, WILKE HJ. Review of existing grading systems for cervical or lumbar disc and facet joint degeneration. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(6): 705-718. [9] AGHA O, MUELLER-IMMERGLUCK A, LIU M, et al. Intervertebral disc herniation effects on multifidus muscle composition and resident stem cell populations. JOR Spine. 2020;3(2):e1091. [10] SHAHIDI B, FISCH KM, GIBBONS MC, et al. Increased Fibrogenic Gene Expression in Multifidus Muscles of Patients With Chronic Versus Acute Lumbar Spine Pathology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(4):E189-E195. [11] CHEN X, HODGES PW, JAMES G, et al. Do Markers of Inflammation and/or Muscle Regeneration in Lumbar Multifidus Muscle and Fat Differ Between Individuals with Good or Poor Outcome Following Microdiscectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(10):678-686. [12] HODGES PW, DANNEELS L. Changes in Structure and Function of the Back Muscles in Low Back Pain: Different Time Points, Observations, and Mechanisms. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2019;49(6):464-476. [13] KALICHMAN L, CARMELI E, BEEN E. The Association between Imaging Parameters of the Paraspinal Muscles, Spinal Degeneration, and Low Back Pain. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:2562957. [14] FAUR C, PATRASCU JM, HARAGUS H, et al. Correlation between multifidus fatty atrophy and lumbar disc degeneration in low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):414. [15] HIYAMA A, KATOH H, SAKAI D, et al. The correlation analysis between sagittal alignment and cross-sectional area of paraspinal muscle in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):352. [16] ÖZCAN-EKŞI EE, EKŞI MŞ, TURGUT VU, et al. Reciprocal relationship between multifidus and psoas at L4-L5 level in women with low back pain. Br J Neurosurg. 2021;35(2):220-228. [17] YANG F, LIU Z, ZHU Y, et al. Imaging of muscle and adipose tissue in the spine: A narrative review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(49): e32051. [18] SHI L, YAN B, JIAO Y, et al. Correlation between the fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscles and disc degeneration and the underlying mechanism. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):509. [19] MANDELLI F, NÜESCH C, ZHANG Y, et al. Assessing Fatty Infiltration of Paraspinal Muscles in Patients With Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Goutallier Classification and Quantitative MRI Measurements. Front Neurol. 2021;12:656487. [20] LEE SY, KIM DH, PARK SJ, et al. Novel lateral whole-body dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry of lumbar paraspinal muscle mass: results from the SarcoSpine study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(4): 913-920. [21] LIU Z, ZHANG Y, HUANG D, et al. Quantitative Study of Vertebral Body and Paravertebral Muscle Degeneration Based on Dual-Energy Computed Tomography: Correlation With Bone Mineral Density. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2023;47(1):86-92. [22] LI P, NIE Y, CHEN J, et al. [Application progress of surface electromyography and surface electromygraphic biofeedback in low back pain]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017;31(4): 504-507. [23] YE K, XING L, LU J, et al. [Design of Paravertebral Muscle Monitoring System Based on Surface Electromyography]. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2019;43(5):318-321. [24] SUDHIR G, JAYABALAN V, SELLAYEE S, et al. Is there an interdependence between paraspinal muscle mass and lumbar disc degeneration? A MRI based study at 2520 levels in 504 patients. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;22:101576. [25] ÖZCAN-EKŞI EE, EKŞI MŞ, AKÇAL MA. Severe Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Is Associated with Modic Changes and Fatty Infiltration in the Paraspinal Muscles at all Lumbar Levels, Except for L1-L2: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of 50 Symptomatic Women and 50 Age-Matched Symptomatic Men. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:e1069-e1077. [26] HOPPE S, MAURER D, VALENZUELA W, et al. 3D analysis of fatty infiltration of the paravertebral lumbar muscles using T2 images-a new approach. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(9):2570-2576. [27] ÖZCAN-EKŞI EE, TURGUT VU, KÜÇÜKSÜLEYMANOĞLU D, et al. Obesity could be associated with poor paraspinal muscle quality at upper lumbar levels and degenerated spine at lower lumbar levels: Is this a domino effect? J Clin Neurosci. 2021;94:120-127. [28] PFIRRMANN CW, METZDORF A, ZANETTI M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(17):1873-1878. [29] KJAER P, KORSHOLM L, BENDIX T, et al. Modic changes and their associations with clinical findings. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(9):1312-1319. [30] KJAER P, BENDIX T, SORENSEN JS, et al. Are MRI-defined fat infiltrations in the multifidus muscles associated with low back pain? BMC Med. 2007;5:2. [31] KUISMA M, KARPPINEN J, NIINIMÄKI J, et al. Modic changes in endplates of lumbar vertebral bodies: prevalence and association with low back and sciatic pain among middle-aged male workers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(10):1116-1122. [32] FORTIN M, VIDEMAN T, GIBBONS LE, et al. Paraspinal muscle morphology and composition: a 15-yr longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;46(5):893-901. [33] TEICHTAHL AJ, URQUHART DM, WANG Y, et al. Fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles is associated with low back pain, disability, and structural abnormalities in community-based adults. Spine J. 2015; 15(7):1593-1601. [34] HUANG Y, WANG L, ZENG X, et al. Association of Paraspinal Muscle CSA and PDFF Measurements With Lumbar Intervertebral Disk Degeneration in Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:792819. [35] LEE SK, JUNG JY, KANG YR, et al. Fat quantification of multifidus muscle using T2-weighted Dixon: which measurement methods are best suited for revealing the relationship between fat infiltration and herniated nucleus pulposus. Skeletal Radiol. 2020;49(2):263-271. [36] HUANG Y, WANG L, LUO B, et al. Associations of Lumber Disc Degeneration With Paraspinal Muscles Myosteatosis in Discogenic Low Back Pain. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:891088. [37] CAO Y, GUO QW, WAN YD. Significant Association between the T2 Values of Vertebral Cartilage Endplates and Pfirrmann Grading. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(4):1164-1172. [38] LIANG X, XIE R, HOU B, et al. Feasibility study for evaluating lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration using histogram analysis of T2* values. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(10):2600-2608. [39] PLOUMIS A, MICHAILIDIS N, CHRISTODOULOU P, et al. Ipsilateral atrophy of paraspinal and psoas muscle in unilateral back pain patients with monosegmental degenerative disc disease. Br J Radiol. 2011;84(1004):709-713. [40] KANG JI, KIM SY, KIM JH, et al. The location of multifidus atrophy in patients with a single level, unilateral lumbar radiculopathy. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013;37(4):498-504. [41] HODGES P, HOLM AK, HANSSON T, et al. Rapid atrophy of the lumbar multifidus follows experimental disc or nerve root injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(25):2926-2933. [42] ZHAI WJ, WANG ZK, LIU HL, et al. Comparison between minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of multi‑segmental lumbar degenerative disease: A systematic evaluation and meta‑analysis. Exp Ther Med. 2024; 27(4):162. [43] JI LL, YEO D, KANG C. Muscle Disuse Atrophy Caused by Discord of Intracellular Signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020 Apr 28. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8072. [44] REBOLLEDO DL, GONZÁLEZ D, FAUNDEZ-CONTRERAS J, et al. Denervation-induced skeletal muscle fibrosis is mediated by CTGF/CCN2 independently of TGF-β. Matrix Biol. 2019;82:20-37. [45] YALTIRIK K, GÜDÜ BO, IŞIK Y, et al. Volumetric Muscle Measurements Indicate Significant Muscle Degeneration in Single-Level Disc Herniation Patients. World Neurosurg. 2018;116:e500-e504. [46] COOLEY JR, JENSEN TS, KJAER P, et al. Spinal degeneration and lumbar multifidus muscle quality may independently affect clinical outcomes in patients conservatively managed for low back or leg pain. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):9777. [47] HYUN JK, LEE JY, LEE SJ, et al. Asymmetric atrophy of multifidus muscle in patients with unilateral lumbosacral radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(21):E598-602. [48] KOTTLORS M, GLOCKER FX. Polysegmental innervation of the medial paraspinal lumbar muscles. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(2):300-306. [49] HODGES PW, JAMES G, BLOMSTER L, et al. Multifidus Muscle Changes After Back Injury Are Characterized by Structural Remodeling of Muscle, Adipose and Connective Tissue, but Not Muscle Atrophy: Molecular and Morphological Evidence. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(14):1057-1071. [50] JAMES G, CHEN X, DIWAN A, et al. Fat infiltration in the multifidus muscle is related to inflammatory cytokine expression in the muscle and epidural adipose tissue in individuals undergoing surgery for intervertebral disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(4):837-845. [51] JAMES G, SLUKA KA, BLOMSTER L, et al. Macrophage polarization contributes to local inflammation and structural change in the multifidus muscle after intervertebral disc injury. Eur Spine J. 2018; 27(8):1744-1756. [52] JAMES G, MILLECAMPS M, STONE LS, et al. Dysregulation of the Inflammatory Mediators in the Multifidus Muscle After Spontaneous Intervertebral Disc Degeneration SPARC-null Mice is Ameliorated by Physical Activity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(20):E1184-E1194. [53] CHEN X, LI Y, WANG W, et al. Correlation between inflammatory cytokine expression in paraspinal tissues and severity of disc degeneration in individuals with lumbar disc herniation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):193. [54] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):47-60. [55] RUIZ-FERNÁNDEZ C, FRANCISCO V, PINO J, et al. Molecular Relationships among Obesity, Inflammation and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Are Adipokines the Common Link? Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(8):2030. [56] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110660. [57] FANBIN M, JIANGHAI C, JUAN L, et al. Role of transforming growth factor-β1 in the process of fibrosis of denervated skeletal muscle. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011;31(1):77-82. [58] LIU F, TANG W, CHEN D, et al. Expression of TGF-β1 and CTGF Is Associated with Fibrosis of Denervated Sternocleidomastoid Muscles in Mice. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2016;238(1):49-56. [59] RANGER TA, CICUTTINI FM, JENSEN TS, et al. Paraspinalmuscle cross-sectional area predicts low back disability but not pain intensity. Spine J. 2019;19(5):862-868. [60] AGTEN A, STEVENS S, VERBRUGGHE J, et al. Biopsy samples from the erector spinae of persons with nonspecific chronic low back pain display a decrease in glycolytic muscle fibers. Spine J. 2020;20(2): 199-206. [61] KREINER DS, MATZ P, BONO CM, et al. Guideline summary review: an evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. Spine J. 2020;20(7):998-1024. [62] FREEMAN MD, WOODHAM MA, WOODHAM AW. The role of the lumbar multifidus in chronic low back pain: a review. PM R. 2010;2(2):142-146; quiz 1 p following 167. [63] HAN G, ZOU D, LI X, et al. Can fat infiltration in the multifidus muscle be a predictor of postoperative symptoms and complications in patients undergoing lumbar fusion for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis? A case-control study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):289. [64] CARVALHO V, SANTOS J, SANTOS SILVA P, et al. Relationship between fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscles and clinical outcome after lumbar discectomy. Brain Spine. 2022;2:101697. [65] JONES CM, LIN CC, DAY RO, et al. OPAL: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial of opioid analgesia for the reduction of pain severity in people with acute spinal pain-a statistical analysis plan. Trials. 2022; 23(1):212. [66] NURY E, SCHMUCKER C, NAGAVCI B, et al. Efficacy and safety of strong opioids for chronic noncancer pain and chronic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Pain. 2022;163(4):610-636. [67] KAMATH S, VENKATANARASIMHA N, WALSH MA, et al. MRI appearance of muscle denervation. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37(5):397-404. [68] YUAN H, DONG L, ZHANG O, et al. A comparison of interferential current efficacy in elderly intervertebral disc degeneration patients with or without sarcopenia: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):214. |
| [1] | 曾 轩, 翁 汭, 叶仕成, 唐佳栋, 莫 凌, 李文超. 两种腰椎旋扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症:生物力学差异的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [2] | 王亚磊, 王学志, 周 涛, 沈鑫鑫, 方 丁, 陈宏亮. 骶髂关节强直对L5/S1节段椎间孔入路椎间融合效果及腰椎矢状位参数的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 634-641. |
| [3] | 廖广滔, 冯梓誉, 傅小勇, 赵清兰, 陈 超, 洪劲松. 距下关节制动治疗儿童柔性扁平足:影像学指标与临床疗效的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 661-670. |
| [4] | 王志鹏, 张晓刚, 张宏伟, 赵希云, 李元贞, 郭成龙, 秦大平, 任 真. 机器学习在腰椎间盘突出症患者预后预测模型中应用价值的系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 740-748. |
| [5] | 余伟杰, 曹东东, 郭天赐, 牛朴钰, 杨家麟, 王思敏, 刘爱峰. 经皮内镜腰椎间盘切除后复发风险预测模型的系统评价和Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 749-759. |
| [6] | 周 峰, 符鹏飞, 钱宇帆, 许平成, 郭炯炯, 张 磊. 全身骨骼三维建模成像系统检测脊柱矢状位失衡与膝关节参数的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 596-603. |
| [7] | 杜彦利, 汪 屹, 王振宇, 王煊晖, 李新业, 熊喜峰, 缪海雄, . p53在肌肉骨骼疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(10): 2503-2514. |
| [8] | 苗嘉航, 马 胜, 李渠蓬, 余会林, 胡天宇, 高 啸, 冯 虎. 颈椎前凸比率可作为多节段脊髓型颈椎病后路术式选择的决策指标[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1796-1802. |
| [9] | 张春霖, 侯曌华, 严 旭, 姜 岩, 付 苏, 宁永明, 李东哲, 董 超, 刘小康, 王永魁, 曹争明, 杨腾跃. 腰椎“内聚式”对称减压人工诱导突出椎间盘自然回缩的减压机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1810-1819. |
| [10] | 鹿 麒, 孙玛骥, 王学志, 宋 婷, 马一鸣, 袁 峰, 陈宏亮. 两种可视化关节突成型技术治疗L5-S1椎间盘突出症:临床结局半年随访评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1841-1847. |
| [11] | 冯志萌, 孙 宁, 孙兆忠, 李岳飞, 刘昌震, 李 洒. 影像三维重建安全辅助单孔分体内镜治疗L5/S1极外侧腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1876-1882. |
| [12] | 支 芳, 朱满华, 熊 伟, 林星镇. 腰椎间盘突出症模型大鼠疼痛的针刺干预[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [13] | 杨 煜, 李英豪, 多壮志, 周定容. 整体功能性体育锻炼对腰椎间盘突出症术后患者腰椎生物力学的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(33): 7096-7101. |
| [14] | 张博淳, 李 威, 李广政, 丁浩秦, 李 刚, 梁学振, . 神经影像学变化与骨坏死的关联:UK Biobank及FinnGen数据库的大样本分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(30): 6574-6582. |
| [15] | 郑 翔, 张明兴, 黄 雅, 单莎瑞. 生物反馈助力电刺激对慢性非特异性腰痛患者下肢步行功能的改善[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(3): 547-553. |
椎间盘退变是各种临床脊柱疾病的基础,例如环撕裂、脊柱不稳定、小关节退变、椎间盘突出、椎管狭窄和慢性下腰痛 [1-2]。退行性椎间盘疾病被认为是一种常见的脊柱疾病,流行病学研究已经使用不同的措施来定义疾病。在组织学研究中包括颗粒变化、撕裂和裂隙形成、软骨细胞增殖、黏液变性和细胞死亡[3],而宏观分级系统包括终板和椎体以及核和环的变化[4]。影像学研究通过不同程度的关节间隙狭窄分类椎间盘退变、终板硬化和骨赘[5-6],而磁共振成像(MRI)研究集中于个体特征,包括纤维环撕裂、突出的髓核和椎间盘高度。目前,在临床实践中,椎间盘退变程度的评估广泛采用Pfirrmann分级系统[7-8],根据椎间盘结构的外观、信号强度、椎间盘高度以及髓核和纤维环之间的区别分配5个分级(表1),但 Pfirrmann分级主要依据评估者的主观评价,缺乏客观的定量评价指标。
椎旁肌作为脊柱的重要构成部分,其解剖结构复杂而精细,包括浅层纵向长纤维竖脊肌和深层斜向短纤维横突棘肌。竖脊肌包括棘肌、最长肌和髂肋肌,横突棘肌则包括半棘肌、多裂肌和回旋肌。椎旁肌主要由多裂肌、竖脊肌和腰大肌组成。在生理功能方面,椎旁肌承担着伸展脊柱、参与脊柱旋转以及维持稳定性的任务。椎间盘退变会导致椎旁肌的变化,这些变化包括肌肉中脂肪和结缔组织的增加、纤维类型的变化、扭曲的细胞群、改变的基因表达、低肌肉阻力、低肌肉强度和肌肉萎缩[9-14]。既往文献多集中于探讨退行性腰椎疾病中椎旁肌的变化,而忽略了疾病中腰椎间盘退变程度对椎旁肌的影响,该文对测量评估“Pfirrmann分级”和“椎旁肌退变”数据的文献进行系统全面的归纳总结,对两者的相关性及机制进行综述,旨在为临床预防和疾病诊治提供指导。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2023年7月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时间范围设置为1984-2024年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 在中国知网、维普、万方、Medline、PubMed、Web of Science等中英文数据库进行检索。
1.1.4 检索词 中文关键词为“腰椎间盘,椎旁肌,多裂肌,腰痛,退行性变”,英文关键词为“lumbar disc ,paraspinal muscle ,multifidus muscle,low back pain,
degeneration,imaging,MRI ”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究性论文与著作、综述性论文等。
1.1.6 检 索 策 略 以在PubMed数据库中的检索式为例:((((lumbar disc[MeSH Terms]) OR Paraspinal Muscle[MeSH Terms]) OR lumbar disc[Title/Abstract]) OR Paraspinal Muscle
[Title/Abstract]) OR lumbar disc AND Paraspinal Muscle。
1.2 纳入与排除标准
纳入标准:①与关键词相关的临床或基础研究;②文献类型包括专著、论文、综述;③文章描述腰椎间盘退变;④文章描述椎旁肌退变;⑤文章描述腰痛及相关治疗手段。
排除标准:①重复的文章;②未能找到相应全文;③非重点研究椎旁肌退变的文章;④非重点研究腰椎间盘退变的文章;⑤未详细描述两者机制的文章;⑥中文文章与外文研究重复。
1.3 数据提取 共检索得到文献3 072篇,包括英文文献2 996篇、中文文献76篇。根据上述的纳入及排除标准筛选文献,并排除与该文研究内容相关性差、质量不高和重复的文献3 004篇,符合标准的文献共68篇,其中中文文献1篇、英文文献67篇。文献筛选流程图见图1。
研究发现,学者们多采用MRI、DECT、表面肌电图等影像学检查对腰椎间盘退变患者的椎旁肌进行定量评估,通过对比不同退变程度下椎旁肌的形态、结构以及功能变化,发现腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌的改变存在密切的相关性,两者受年龄、体质量、性别等混合因素的影响,尤其是女性肥胖患者,需要针对性的诊疗。随着腰椎间盘的退变,椎旁肌的形态、结构和功能均会发生相应的变化,这种变化表现在肌肉纤维的萎缩、脂肪浸润等形态学层面,现阶段国内外研究者们测量了一些指标如横截面积(CSA)、脂肪浸润、横截面积比(FCSA/CSA)、相对横截面积(rCSA)等被用来评价椎旁肌的状态,文章论述了不同的学者选取不同的节段并测量相应的Pfirrmann分级和椎旁肌退变参数,发现腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌改变具有密切的相关性,并在腰痛的进展中产生一定的作用,但并不清楚三者之间的级联反应。 通过既往5年内文献的研究推测多裂肌的脂肪浸润与腰椎间盘的退变有最佳相关性,但此结论是建立在腰椎间盘退变好发的L4/5节段研究的,并不能全面反映整个腰椎节段,并且研究样本取自8例因椎间盘突出症接受椎间盘切除术的患者,研究样本量小,难以充分反映整体情况,需要进一步扩大样本量,提高研究的代表性。同时此次研究忽略了其他炎症因子的影响,所以结论仍存争议,这是该文在论述两者相关性时的局限性。接着探究了腰椎退变导致椎旁肌改变的机制,其中失用性萎缩导致的肌肉功能锻炼的丧失,导致肌肉逐步被脂肪组织所替代,这些变化进一步加剧了腰椎间盘退变的进程,形成了恶性循环。
此外,该研究还发现了一些新的影响因素和机制。例如,神经支配的抑制、炎症因子的释放等都可能在腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌改变的过程中发挥重要作用,神经支配受抑制会导致肌纤维的变化以及脂肪的替代,并发现了多裂肌受单神经单节段支配的特殊性,这种特殊性使多裂肌的萎缩发生在腰椎间盘退变的相应节段及下一级,为临床上通过肌肉萎缩诊断神经根病变的位置提供参考,同时指导患者进行合理的康复锻炼。另一方面,腰椎间盘退变所释放的炎症因子也会对椎旁肌产生影响,肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素1β、转化生长因子β1等炎症基因与多裂肌的脂肪浸润和横截面积减少相关,临床的难点在于抑制炎症因子的释放并缓解疼痛的症状,但目前对机制研究不够深入,大部分研究集中在炎症因子水平与椎旁肌形态改变的变化,对其具体作用机制了解不足,需要进一步开展细胞和动物实验,深入探讨炎症因子在椎旁肌改变中的作用。
最后,总结了二者互相作用发展产生腰痛的力学机制,认为临床工作中应谨慎使用阿片类药物治疗慢性腰痛,及时纠正神经根压迫引起的肌肉萎缩和脂肪浸润,同时考虑采用干扰电流电刺激等新型治疗方法来改善患者的症状和预后,并重视椎旁肌脂肪浸润的情况对手术预后的影响。文章提出了一些值得关注的治疗方向,但在具体的临床应用中还存在一些局限性,如:药物和非药物治疗之间寻求最佳平衡还需进一步研究;虽然提到了干扰电流(IFC)电刺激在治疗中的作用,但具体的适应证、治疗方案和长期疗效还需进一步研究验证。
综上所述,未来的研究应该注重扩大样本量、深入探讨机制,并开展更多干预研究,需要更多的临床研究和实践来完善相关的诊疗方案,以进一步完善腰椎间盘退变导致椎旁肌改变的认知,为未来的研究和治疗提供了新的方向和思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
研究发现,学者们多采用MRI,DECT,表面肌电图等影像学检查对腰椎间盘退变患者的椎旁肌进行定量评估,通过对比不同退变程度下椎旁肌的形态、结构以及功能变化,发现腰椎间盘退变与椎旁肌的改变存在密切的相关性,两者受年龄、体重、性别等混合因素的影响,尤其是女性肥胖患者需要针对性的诊疗。#br# #br# #br# 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||