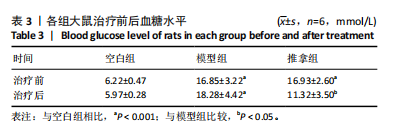
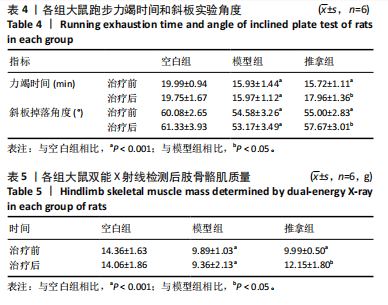
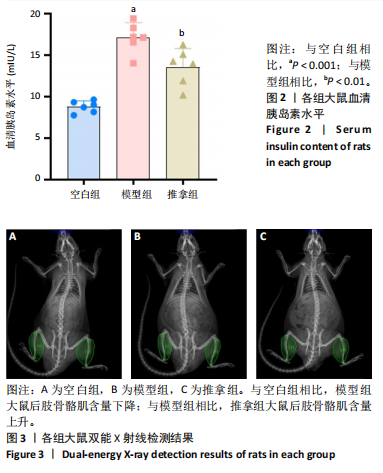
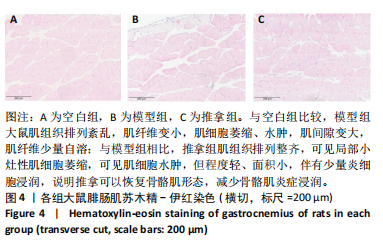
[1] SHAW JE, SICREE RA, ZIMMET PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87(1):4-14.
[2] IZZO A, MASSIMINO E, RICCARDI G, et al. A Narrative Review on Sarcopenia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence and Associated Factors. Nutrients. 2021; 13(1):183.
[3] SATAKE S, ARAI H. Chapter 1 Frailty: Definition, diagnosis, epidemiology. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2020;20 Suppl 1:7-13.
[4] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31.
[5] ZUGASTI MURILLO A, PETRINA-JÁUREGUI ME, RIPA-CIÁURRIZ C, et al. SeDREno study - prevalence of hospital malnutrition according to GLIM criteria, ten years after the PREDyCES study. Nutr Hosp. 2021;38(5):1016-1025.
[6] AHMAD K, SHAIKH S, AHMAD SS, et al. Cross-Talk Between Extracellular Matrix and Skeletal Muscle: Implications for Myopathies. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:142.
[7] MCCALL-CULBREATH KD, ZUTTER MM. Collagen receptor integrins: rising to the challenge. Curr Drug Targets. 2008;9(2):139-149.
[8] CSAPO R, GUMPENBERGER M, WESSNER B. Skeletal Muscle Extracellular Matrix - What Do We Know About Its Composition, Regulation, and Physiological Roles? A Narrative Review. Front Physiol. 2020;11:253.
[9] KANG L, LANTIER L, KENNEDY A, et al. Hyaluronan accumulates with high-fat feeding and contributes to insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2013;62(6):1888-1896.
[10] HUANG S, XIANG C, SONG Y. Identification of the shared gene signatures and pathways between sarcopenia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS One. 2022; 17(3):e0265221.
[11] 孔心甜,谢舟煜,徐景崧,等.摩腹对2型糖尿病大鼠胰岛素抵抗和胰腺GLP-1r的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(4):998-1000.
[12] XIE Y, HUAN MT, SANG JJ, et al. Clinical Effect of Abdominal Massage Therapy on Blood Glucose and Intestinal Microbiota in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2286598.
[13] 蒙蒙,胡冠宇,吴兴全,等.推拿干预2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌功能及肌纤维类型的转换[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(35):5628-5633.
[14] MUSALE V, WASSERMAN DH, KANG L. Extracellular matrix remodelling in obesity and metabolic disorders. Life Metab. 2023;2(4):load021.
[15] 郭义.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2021:253-269.
[16] AHMAD K, LEE EJ, MOON JS, et al. Multifaceted Interweaving Between Extracellular Matrix, Insulin Resistance, and Skeletal Muscle. Cells. 2018;7(10):148.
[17] HASHIMOTO Y, TAKAHASHI F, OKAMURA T, et al. Diet, exercise, and pharmacotherapy for sarcopenia in people with diabetes. Metabolism. 2023;144: 155585.
[18] SALOM VENDRELL C, GARCÍA TERCERO E, MORO HERNÁNDEZ JB, et al. Sarcopenia as a Little-Recognized Comorbidity of Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of the Diagnosis and Treatment. Nutrients. 2023;15(19):4149.
[19] TAN BL, NORHAIZAN ME. Effect of High-Fat Diets on Oxidative Stress, Cellular Inflammatory Response and Cognitive Function. Nutrients. 2019;11(11):2579.
[20] RUIZ-OJEDA FJ, MÉNDEZ-GUTIÉRREZ A, AGUILERA CM, et al. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling of Adipose Tissue in Obesity and Metabolic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4888.
[21] TAM CS, CHAUDHURI R, HUTCHISON AT, et al. Skeletal muscle extracellular matrix remodeling after short-term overfeeding in healthy humans. Metabolism. 2017;67:26-30.
[22] CHEN J, CHEN H, DONG X, et al. Deficiency of skeletal muscle Agrin contributes to the pathogenesis of age-related sarcopenia in mice. Cell Death Dis. 2024; 15(3):201.
[23] TAN S, GUNENDI Z, MERAY J, et al. The evaluation of muscle strength and architecture in type 1 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22(1):153.
[24] SCHMIDT L, SAYNISCH M, HOEGSBJERG C, et al. Spatial proteomics of skeletal muscle using thin cryosections reveals metabolic adaptation at the muscle-tendon transition zone. Cell Rep. 2024;43(7):114374.
[25] 郭皓泽.推拿干预2型糖尿病肌少症患者的临床观察及效应机制研究[D].长春:长春中医药大学,2024.
[26] VAN PELT DW, LAWRENCE MM, MILLER BF, et al. Massage as a Mechanotherapy for Skeletal Muscle. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2021;49(2):107-114.
[27] AYDIN O, ZHANG X, NUETHONG S, et al. Neuromuscular actuation of biohybrid motile bots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(40):19841-19847.
[28] ALEKSANDROWICZ R, STRĄCZKOWSKI M. Link between insulin resistance and skeletal muscle extracellular matrix remodeling. Endocr Connect. 2023; 12(5):e230023.
[29] VEGA-MARTÍN E, GONZÁLEZ-MORENO D, SANZ-GÓMEZ M, et al. Upregulation in Inflammation and Collagen Expression in Perirenal but Not in Mesenteric Adipose Tissue from Diabetic Munich Wistar Frömter Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(23):17008.
[30] 高天姣,马德慧,韩怡然,等.基于SIRT1/PGC-1α通路探讨腹部推拿对肥胖2型糖尿病模型大鼠抗炎作用机制研究[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(8):2028-2030.
[31] RUBIO-RUIZ ME, GUARNER-LANS V, PÉREZ-TORRES I, et al. Mechanisms Underlying Metabolic Syndrome-Related Sarcopenia and Possible Therapeutic Measures. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):647.
[32] SOSLOW JH, XU M, SLAUGHTER JC, et al. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Cardiomyopathy. J Card Fail. 2019;25(4):259-267.
[33] ZHAO N, LIU B, LIU SW, et al. The Combination of Electroacupuncture and Massage Therapy Alleviates Myofibroblast Transdifferentiation and Extracellular Matrix Production in Blunt Trauma-Induced Skeletal Muscle Fibrosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:5543468.
[34] BOLLINGER LM. Potential contributions of skeletal muscle contractile dysfunction to altered biomechanics in obesity. Gait Posture. 2017;56:100-107.
[35] WANG G, CONG D, JU H, et al. Community intervention study of viscera massage in overweight/obese type 2 diabetes high-risk population. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(48):e27932. |