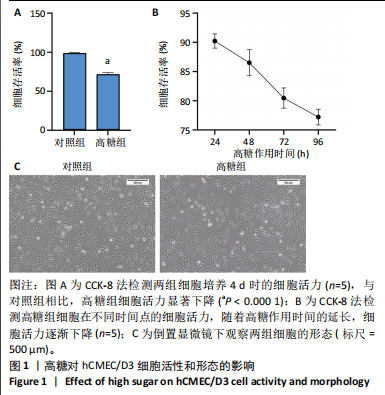
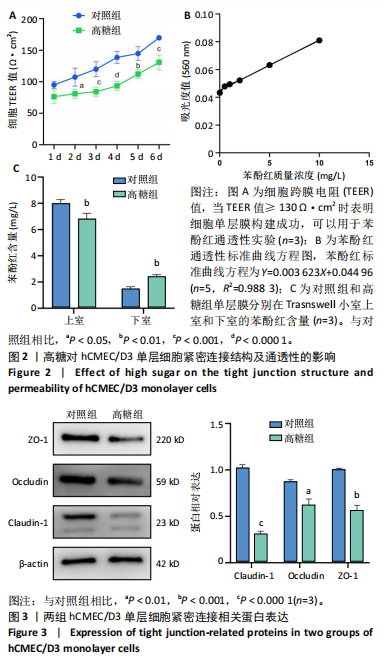
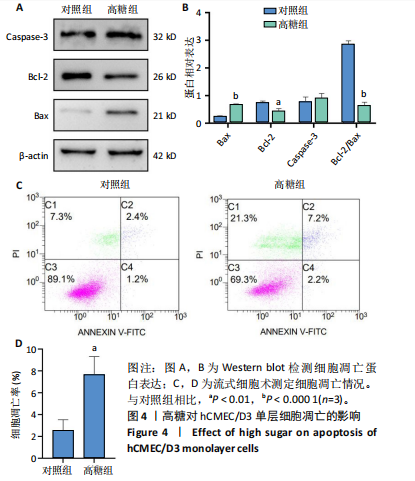
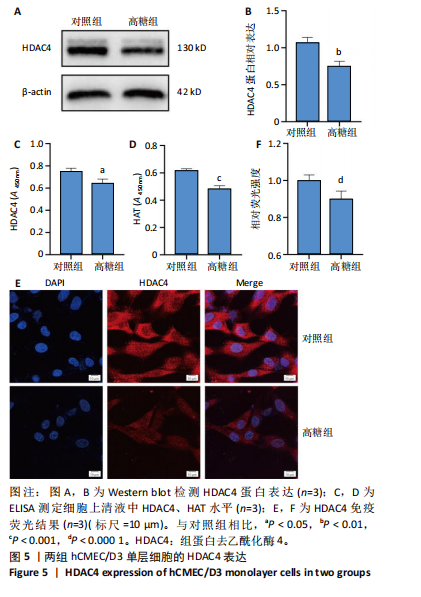
[1] SUN H, SAEEDI P, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119.
[2] ZHANG S, ZHANG Y, WEN Z, et al. Cognitive dysfunction in diabetes: abnormal glucose metabolic regulation in the brain. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1192602.
[3] 段云峰,许永劼,杨婷婷,等.高糖诱导HT-22小鼠海马神经元代谢记忆细胞模型的构建及影响[J].天津医药,2024,52(1):44-50.
[4] POPESCU BO, TOESCU EC, POPESCU LM, et al. Blood-brain barrier alterations in ageing and dementia. J Neurol Sci. 2009;283(1-2):99-106.
[5] BEI J, MIRANDA-MORALES EG, GAN Q, et al. Circulating Exosomes from Alzheimer’s Disease Suppress Vascular Endothelial-Cadherin Expression and Induce Barrier Dysfunction in Recipient Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;95(3):869-885.
[6] NAZARI H, SHRESTHA J, NAEI VY, et al. Advances in TEER measurements of biological barriers in microphysiological systems. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023;234:115355.
[7] SUGIYAMA S, SASAKI T, TANAKA H, et al. The tight junction protein occludin modulates blood-brain barrier integrity and neurological function after ischemic stroke in mice. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2892.
[8] ZHANG Q, LIU C, SHI R, et al. Blocking C3d+/GFAP+ A1 Astrocyte Conversion with Semaglutide Attenuates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Mice after Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2022;13(3):943-959.
[9] 刘洋,李嘉民,陈荣,等.白藜芦醇苷对脑缺血再灌注损伤小鼠血脑屏障的保护作用研究[J].天津医科大学学报,2022,28(3):278-283.
[10] POP V, SORENSEN DW, KAMPER JE, et al. Early brain injury alters the blood-brain barrier phenotype in parallel with β-amyloid and cognitive changes in adulthood. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(2):205-214.
[11] 苏嘉楠,安继仁,孙贵炎,等.基于AMPK/mTOR信号通路探讨中药复方益糖康对db/db小鼠血脑屏障通透性及紧密连接蛋白的影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2024,26(7):10-15.
[12] 袁小波,彭小珊,周丽丽,等.荞麦黄酮通过下调HMGB1抑制高糖诱导的人视网膜微血管内皮细胞损伤的研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2023,39(11):2311-2317.
[13] FASELIS C, KATSIMARDOU A, IMPRIALOS K, et al. Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):117-124.
[14] 王晨曦,王子瑞,俞澜.糖尿病肾病足细胞损伤病理机制及信号通路的研究进展[J].海南医学,2023,34(1):130-135.
[15] STODDART P, SATCHELL SC, RAMNATH R. Cerebral microvascular endothelial glycocalyx damage, its implications on the blood-brain barrier and a possible contributor to cognitive impairment. Brain Res. 2022;1780:147804.
[16] 杨俊瑶,王前, ZENG LINGFANG.组蛋白去乙酰化酶与血管重建[J].中华高血压杂志,2014,22(5):403-409.
[17] LIU Z, HUA W, JIN S, et al. Canagliflozin protects against hyperglycemia-induced cerebrovascular injury by preventing blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption via AMPK/Sp1/adenosine A2A receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024;968:176381.
[18] ZHU J, JI X, SHI R, et al. Hyperglycemia Aggravates the Cerebral Ischemia Injury via Protein O-GlcNAcylation. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;94(2):651-668.
[19] 李双月,刘淇麒,冯馨锐,等.组蛋白去乙酰化酶3与血管内皮细胞的关系[J].吉林医药学院学报,2018,39(3):201-203.
[20] SCHADER T, LÖWE O, RESCHKE C, et al. Oxidation of HDAC4 by Nox4-derived H2O2 maintains tube formation by endothelial cells. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101669.
[21] WEI Y, ZHOU F, ZHOU H, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells contribute to neovascularization of non-small cell lung cancer via histone deacetylase 7-mediated cytoskeleton regulation and angiogenic genes transcription. Int J Cancer. 2018;143(3):657-667.
[22] KANG Y, KIM J, ANDERSON JP, et al. Apelin-APJ signaling is a critical regulator of endothelial MEF2 activation in cardiovascular development. Circ Res. 2013;113(1):22-31.
[23] SANDO R 3RD, GOUNKO N, PIERAUT S, et al. HDAC4 governs a transcriptional program essential for synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell. 2012;151(4):821-834.
[24] SPALLOTTA F, ROSATI J, STRAINO S, et al. Nitric oxide determines mesodermic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells by activating class IIa histone deacetylases: potential therapeutic implications in a mouse model of hindlimb ischemia. Stem Cells. 2010;28(3):431-442.
[25] 许雯,许永劼,刘歆蕾,等. TSA对不同糖浓度下小鼠海马神经元HT-22细胞凋亡的影响[J].天津医药,2021,49(4):349-353.
[26] 黄晶晶.基于静电纺纳米纤维膜的Caco-2细胞模型构建及其槲皮素吸收机制研究[D].杭州:浙江工商大学,2019.
[27] PARK JS, CHOE K, KHAN A, et al. Establishing Co-Culture Blood-Brain Barrier Models for Different Neurodegeneration Conditions to Understand Its Effect on BBB Integrity. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5283.
[28] 张翼,杨凯丽,毕嘉谣,等.薄荷醇、苏合香挥发油对川芎嗪纳米粒跨血脑屏障模型转运行为的影响[J].环球中医药,2022,15(2):188-196.
[29] 丁怡丹.基于hCMEC/D3细胞单层膜作为血脑屏障模型的地西泮低氧转运研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2020.
[30] KADRY H, NOORANI B, CUCULLO L. A blood-brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment, and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020;17(1):69.
[31] TOTH AE, NIELSEN MS. Sortilins in the blood-brain barrier: impact on barrier integrity. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(3):549-550.
[32] ZAPATA-ACEVEDO JF, MANTILLA-GALINDO A, VARGAS-SÁNCHEZ K, et al. Blood-brain barrier biomarkers. Adv Clin Chem. 2024;121:1-88.
[33] ARCHIE SR, AL SHOYAIB A, CUCULLO L. Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in CNS Disorders and Putative Therapeutic Targets: An Overview. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(11):1779.
[34] COHEN J, MATHEW A, DOURVETAKIS KD, et al. Recent Research Trends in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells. 2024;13(6):511.
[35] GUO P, ZHANG WJ, LIAN TH, et al. Alzheimer’s disease with sleep insufficiency: a cross-sectional study on correlations among clinical characteristics, orexin, its receptors, and the blood-brain barrier. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(8):1757-1762.
[36] XU Y, LI H, CHEN G, et al. Radix polygoni multiflori protects against hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in diabetic encephalopathy by inhibiting the HDAC4/JNK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113427.
[37] GUPTA M, PANDEY S, RUMMAN M, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying hyperglycemia associated cognitive decline. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022;14:57-63.
[38] SEBASTIAN MJ, KHAN SK, PAPPACHAN JM, et al. Diabetes and cognitive function: An evidence-based current perspective. World J Diabetes. 2023;14(2):92-109.
[39] LEE SWL, ROGOSIC R, VENTURI C, et al. A Human Neurovascular Unit On-a-Chip. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2373:107-119.
[40] QI D, LIN H, HU B, et al. A review on in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) based on hCMEC/D3 cells. J Control Release. 2023;358: 78-97.
[41] ZHAO Y, GAN L, REN L, et al. Factors influencing the blood-brain barrier permeability. Brain Res. 2022;1788:147937.
[42] YUN JH, LEE DH, JEONG HS, et al. STAT3 activation in microglia increases pericyte apoptosis in diabetic retinas through TNF-ɑ/AKT/p70S6 kinase signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;613:133-139.
[43] GUO X, SHI Y, DU P, et al. HMGB1/TLR4 promotes apoptosis and reduces autophagy of hippocampal neurons in diabetes combined with OSA. Life Sci. 2019;239:117020.
[44] ZHENG X, REN B, GAO Y. Tight junction proteins related to blood-brain barrier and their regulatory signaling pathways in ischemic stroke. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115272.
[45] CONG X, KONG W. Endothelial tight junctions and their regulatory signaling pathways in vascular homeostasis and disease. Cell Signal. 2020;66:109485.
[46] YIN H, RAN Z, LUO T, et al. BCL-3 Promotes Intracerebral Hemorrhage Progression by Increasing Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability, Inflammation, and Cell Apoptosis via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mediators Inflamm. 2023;2023:1420367.
[47] LOCATELLI L, INGLEBERT M, SCRIMIERI R, et al. Human endothelial cells in high glucose: New clues from culture in 3D microfluidic chips. FASEB J. 2022;36(2):e22137.
[48] SCHALKWIJK CG, MICALI LR, WOUTERS K. Advanced glycation endproducts in diabetes-related macrovascular complications: focus on methylglyoxal. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2023;34(1):49-60.
[49] LUO L, AN Y, GENG K, et al. High glucose-induced endothelial STING activation inhibits diabetic wound healing through impairment of angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;668:82-89.
[50] CLYNE AM. Endothelial response to glucose: dysfunction, metabolism, and transport. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021;49(1):313-325.
[51] LI X, JIN Q, YAO Q, et al. Placental Growth Factor Contributes to Liver Inflammation, Angiogenesis, Fibrosis in Mice by Promoting Hepatic Macrophage Recruitment and Activation. Front Immunol. 2017;8:801.
[52] SUN C, XIE K, YANG L, et al. HDAC6 Enhances Endoglin Expression through Deacetylation of Transcription Factor SP1, Potentiating BMP9-Induced Angiogenesis. Cells. 2024;13(6):490.
[53] 刘丹,杨锡彤,王光明.组蛋白去乙酰化酶4在缺血性卒中失调的研究进展[J].重庆医学,2021,50(24):4270-4274.
[54] SHEN Z, BEI Y, LIN H, et al. The role of class IIa histone deacetylases in regulating endothelial function. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1091794.
[55] LIU ZM, WANG X, LI CX, et al. SP1 Promotes HDAC4 Expression and Inhibits HMGB1 Expression to Reduce Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory Response after Sepsis. J Innate Immun. 2022;14(4):366-379.
|