中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (25): 5422-5433.doi: 10.12307/2025.504
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
基质细胞衍生因子1在软骨和软骨下骨稳态中的作用
梁智锋1,2,杨英才2,程千纲1,2,贾永兴1,2,王 博2
- 1山西医科大学,山西省太原市 030607;2山西医科大学附属运城市中心医院,山西省运城市 043100
-
收稿日期:2024-03-27接受日期:2024-05-17出版日期:2025-09-08发布日期:2024-12-26 -
通讯作者:杨英才,主任医师,山西医科大学附属运城市中心医院,山西省运城市 043100 -
作者简介:梁智锋,1998年生,广东省中山市人,汉族,2022年海南医学院毕业,医师,主要从事手足外伤和骨关节疾病研究。 -
基金资助:运城市卫生健康行业科技项目(YCKJYD-2022003),项目负责人:王博
Effect of stromal cell-derived factor-1 in cartilage and subchondral bone homeostasis
Liang Zhifeng1, 2, Yang Yingcai2, Cheng Qiangang1, 2, Jia Yongxing1, 2, Wang Bo2
- 1Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030607, Shanxi Province, China; 2Yuncheng Central Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Yuncheng 043100, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-27Accepted:2024-05-17Online:2025-09-08Published:2024-12-26 -
Contact:Yang Yingcai, Chief physician, Yuncheng Central Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Yuncheng 043100, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Liang Zhifeng, Physician, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030607, Shanxi Province, China; Yuncheng Central Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Yuncheng 043100, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Yuncheng City Health Industry Technology Project, No. YCKJYD-2022003 (to WB)
摘要:
文题释义:
基质细胞衍生因子1:是一种具有很强趋化活性的稳态/炎性趋化因子,属于CXC趋化因子家族成员,在关节软骨和软骨下骨中主要由肥大软骨细胞、未成熟成骨细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞表达。软骨/软骨下骨:软骨和软骨下骨作为一个功能整体维持关节内环境的平衡。骨性关节炎时,软骨和软骨下骨稳态失衡,导致软骨降解、软骨细胞肥大化、软骨下骨异常骨重塑和骨软骨界面异常血管生成增多。
摘要
背景:骨性关节炎是一种以软骨退变和软骨下骨异常骨重塑为特征的退行性病变。近年来,许多研究表明基质细胞衍生因子1在骨性关节炎的病理进展中发挥关键作用,靶向调控基质细胞衍生因子1及其CXC趋化因子受体4型和CXC趋化因子受体7型组成的信号通路是预防和治疗骨性关节炎的新方法。
目的:综述基质细胞衍生因子1参与调控软骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞及破骨细胞增殖、分化及凋亡的作用,以及这些细胞相互作用,探究导致软骨退变、软骨下骨异常骨重塑而加速骨性关节炎病理进展的机制,以期为骨性关节炎的防治提供新的思路。
方法:以“基质细胞衍生因子1,软骨,软骨细胞,软骨下骨,骨髓间充质干细胞,成骨细胞,破骨细胞,CXC趋化因子受体4型,CXC趋化因子受体7型”为中文检索词检索中国知网、万方和维普数据库,以“Stromal cell-derived factor 1,SDF-1,CXCL12,cartilage,chondrocyte,subchondral bone,mesenchymal stem cells,osteoblasts,osteoclasts,CXCR4,CXCR7”为英文检索词检索PubMed、Medline和Embase数据库,检索各数据库建库至2024年1月的相关文献,根据纳入和排除标准,最终纳入77篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①基质细胞衍生因子1调控软骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞迁移、增殖、分化和死亡,在维持软骨和软骨下骨稳态以及促进或抑制骨性关节炎软骨退变、软骨下骨异常骨重塑等病理过程中均发挥至关重要的作用,靶向调控基质细胞衍生因子1/CXC趋化因子受体4型/CXC趋化因子受体7型信号通路有望成为今后防治骨性关节炎研究的重点。②由于基质细胞衍生因子1亚型在组织之间表达量的差异,目前以基质细胞衍生因子1α研究最为广泛,基质细胞衍生因子1β和基质细胞衍生因子1γ的相关研究多集中在探索影响干细胞生物学行为、在调控软骨和软骨下骨稳态中的作用,与骨性关节炎的相关性尚不清楚。③基质细胞衍生因子1能够有效促进干细胞归巢至软骨损伤部位,并诱导其增殖、存活及成软骨分化和应用负载基质细胞衍生因子1的生物支架来改善软骨修复质量已成为软骨组织工程研究的热点;然而,已有研究表明基质细胞衍生因子1可促进骨髓间充质干细胞向肥大型软骨细胞分化,而新生软骨细胞肥大表型会造成软骨内骨形成,软骨细胞凋亡,整个组织发生血管化和骨化,影响最终软骨修复的质量;另外,不同支架与基质细胞衍生因子1组合在修复部分软骨损伤和全层软骨损伤时,再生组织不都是理想的透明软骨组织。因而,未来深入探寻基质细胞衍生因子1在干细胞生物学效应中的潜在机制以及基质细胞衍生因子1与支架组合在修复不同软骨缺损的最佳组合方式将有助于提升软骨修复质量。④目前有关CXC趋化因子受体4型拮抗剂的研究主要集中在AMD3100,T140和TN14003,且绝大部分处于基础实验阶段,有待临床转化。针对基质细胞衍生因子1/CXC趋化因子受体4型/CXC趋化因子受体7型信号通路开发的治疗药物、方法的安全性、有效性仍需大量的生物学和临床试验加以佐证。
中图分类号:
引用本文
梁智锋, 杨英才, 程千纲, 贾永兴, 王 博. 基质细胞衍生因子1在软骨和软骨下骨稳态中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(25): 5422-5433.
Liang Zhifeng, Yang Yingcai, Cheng Qiangang, Jia Yongxing, Wang Bo . Effect of stromal cell-derived factor-1 in cartilage and subchondral bone homeostasis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5422-5433.
中显著高于正常人(70 ng/mL),而关节滑液中SDF-1主要来自滑膜成纤维细胞分泌,其与软骨细胞CXCR4结合后,基质金属蛋白酶3表达上调而诱导软骨基质降解。滑膜切除后能有效降低血清SDF-1和基质金属蛋白酶水平,预防骨性关节炎软骨破坏[5]。这些研究提示,SDF-1/CXCR4参与骨性关节炎软骨退变的病理进展。随后相关领域学者围绕SDF-1/CXCR4导致骨性关节炎软骨退变的具体机制展开了广泛研究,靶向抑制SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路以延缓软骨退变为治疗骨性关节炎提供了新的思路。
随着对骨性关节炎发病机制的深入研究,学者们逐渐认识到骨性关节炎是累及滑膜、软骨、软骨下骨的全关节疾病,其中软骨下骨结构改变可能是骨性关节炎最早出现的病理变化,出现早于软骨退变,并可能是骨性关节炎的启动因素[6]。换而言之,骨性关节炎软骨下骨结构变化与软骨退变存在相关性,软骨退变可能继发于软骨下骨结构变化。研究表明,SDF-1α可促进骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的间充质干细胞的成软骨分化并增强软骨细胞增殖和成熟过程[7],这说明SDF-1α对于软骨稳态可能具有双重作用,既能上调基质金属蛋白酶表达水平来降解软骨基质,又能促进软骨细胞增殖及合成分泌胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖等细胞外基质成分以避免软骨降解或者说修复受损伤的软骨。同时也提示SDF-1α促进骨性关节炎软骨退变病理进展可能存在其他调控机制。在2017年,CHEN等[8]首次发现骨性关节炎患者软骨退变较重区域软骨下骨SDF-1α浓度较软骨退变较轻区域软骨下骨要高得多。在骨性关节炎动物模型中,应用AMD3100阻断SDF-1与CXCR4结合后,软骨下骨异常骨吸收较对照组明显改善,表明SDF-1也参与骨性关节炎软骨下骨异常骨重塑。还有研究应用微型渗透性输液泵将AMD3100直接泵入软骨下骨以抑制软骨下骨异常骨重塑,结果发现软骨SDF-1含量、软骨细胞分解标志物恢复至正常水平,表明SDF-1协调软骨下骨和软骨促进骨性关节炎的发生发展。总之,SDF-1在骨性关节炎病理进展的相关研究中,研究者们先后认识到其会导致滑膜炎、软骨退变、软骨下骨异常骨重塑以及软骨下骨与软骨之间存在串扰。SDF-1/CXCR4在骨性关节炎病理进展的示意图,见图3。
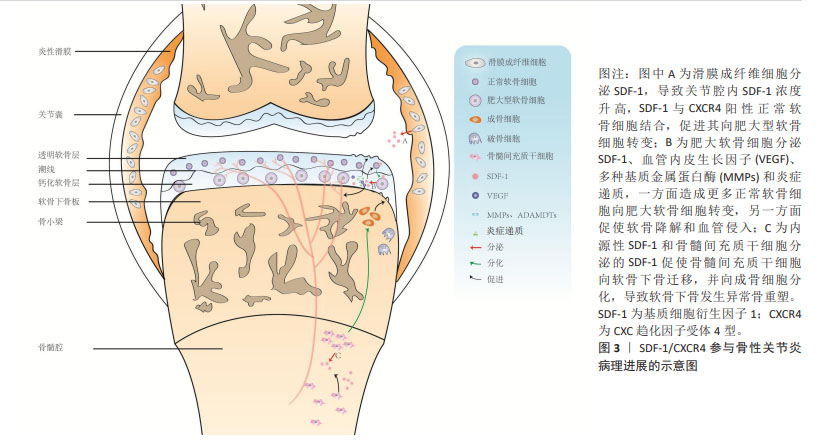
SDF-1与其受体CXCR4相互作用导致骨性关节炎病理进展的分子机制的初期研究主要集中在探索SDF-1对软骨细胞生物学行为(如增殖、存活及凋亡)以及常见软骨合成(如聚集蛋白聚糖)与分解(如基质金属蛋白酶13)标志物的变化。随着成像技术、免疫学、分子生物学、组织工程学的发展,对骨性关节炎的发病机制有更深入的认识,发现SDF-1参与骨性关节炎软骨下骨异常骨重塑。同期,由于SDF-1在促进干细胞迁移、增殖、存活及成软骨分化作用被阐明,探索其联合生物支架、其他生长因子在修复不同软骨缺损成为研究热点。近年来,逐渐认识到骨性关节炎软骨下骨显微结构变化与软骨退变之间的相关性,SDF-1对影响软骨和软骨下骨稳态因素的调控展开更深入的研究,如对H型血管的促生成作用。SDF-1在骨性关节炎领域的研究大事件及时间脉络图,见图4。

2.2 SDF-1亚型在软骨和软骨下骨中作用的概述 SDF-1是一种分子质量为8 kD的小分子蛋白质,已发现其共有6种亚型,包括SDF-1α,SDF-1β,SDF-1γ,SDF-1δ,SDF-1ε和SDF-1φ,相应亚型基因分别编码89,93,119,120,90和100个氨基酸[9-10]。不同亚型之间均含有同一拓扑结构:N端为3-8个可变动的氨基酸,一个N端环状残基,外有一个α螺旋和3个反向平行的β折叠以及一个C末端α螺旋[11]。由于SDF-1α和SDF-1β结构相似,其差异仅是SDF-1β的C末端多4个氨基酸,且两者表达量及表达广度较其他亚型要高得多,因而目前大多数研究主要集中在SDF-1α和SDF-1β[1,10]。研究表明,SDF-1α在软骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞均有高水平表达,与其受体CXCR4结合后,在调控细胞迁移、增殖、分化、死亡以及软骨内成骨、软骨修复和骨性关节炎等生理病理过程都有至关重要的作用[11]。与SDF-1α相似,SDF-1β在骨髓间充质干细胞也有一定水平的表达,但SDF-1α mRNA表达水平明显高于SDF-1β,而外周血及骨髓间充质干细胞培养上清中可检测到的SDF-1β蛋白量较SDF-1α多[12]。
在生物学效应上,SDF-1β已被证明可促进骨髓间充质干细胞迁移、自噬、成骨分化及抑制凋亡,而对细胞增殖作用不显著[12-14]。MENDELSON等[14]应用负载SDF-1β明胶微球的胶原海绵观察其对多种干细胞迁移及软骨分化的作用,结果发现SDF-1β均在一定程度上促进骨髓间充质干细胞、脂肪干细胞和滑膜干细胞迁移至明胶微球,但明胶微球内Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖含量与对照组相比无明显差异,提示SDF-1β可能对骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化能力促进不明显。HERBERG等[13]构建过表达SDF-1β的骨髓间充质干细胞,发现其半胱天冬酶3表达降低,自噬相关蛋白表达增加;随后,将过表达SDF-1β的骨髓间充干细胞与过氧化氢共同培养时,发现与对照组相比,过表达SDF-1β的骨髓间充质细胞形态、结构相对正常,提示SDF-1β可能通过促进自噬、抑制凋亡来保护骨髓间充质干细胞免受过氧化氢诱导的细胞死亡。总之,SDF-1β相关研究较少,多数研究集中在探索其在干细胞迁移、增殖、分化和死亡中的作用,SDF-1β在调控软骨和软骨下骨中软骨细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞中的具体作用,以及与骨性关节炎的相关性尚不明确,缺少相关研究。
人类SDF-1γ,SDF-1δ,SDF-1ε和SDF-1φ于2006年由YU等[10]首次报道,在成人肝脏、肾脏、胰腺及胃肠道均有不同程度的表达,他们的前3个外显子与SDF-1α和SDF-1β完全相同,且都能刺激CXCR4阳性T淋巴母细胞发生迁移,差异仅在于羧基末端的结构上。SDF-1γ羧基末端较SDF-1α额外多30个氨基酸,由于该区域为4个重叠的BBXB基序,能极大提高其与硫酸肝素蛋白多糖的结合能力,同时也降低了其与同源受体CXCR4的亲和力(SDF-1α,SDF-1γ为15 nmol/L,350 nmol/L)[15]。另有研究表明,SDF-1α和SDF-1γ与CXCR7具有相似的亲和力[16]。最近,REN等[17]发现人骨髓间充质干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞系HS5和HS27a同时表达SDF-1γ和SDF-1α,但SDF-1γ分泌后与细胞膜表面的硫酸肝素蛋白多糖以高亲和力结合而被固定在细胞膜表面,这是其调控多发性骨髓瘤细胞黏附和耐药性的前提。敲除编码硫酸肝素基因,骨髓间充质干细胞表面SDF-1γ明显减少,对多发性骨髓瘤血细胞黏附和耐药性随之降低,证明SDF-1γ与硫酸肝素结合而固定在细胞膜表面的特性是其发挥生物学效应的基础。目前,SDF-1γ与糖胺聚糖相互作用以及SDF-1γ/CXCR4信号转导已证明在肿瘤发生、转移、耐药性以及多种器官发育、炎症细胞浸润及造血祖/干细胞迁移等均发挥重要作用,然而与SDF-1β一样,其在软骨和软骨下骨及骨软骨组织工程中的具体作用缺少相关研究[17-20]。
2.3 SDF-1/CXCR7与骨性关节炎概述 CXCR7最初从狗的甲状腺cDNA文库中筛选出来,被命名为狗受体基因1 (receptor dog cDNA1,RDC1),又因当时其配体尚不清楚,而被称为趋化因子孤儿受体(chemokine orphan receptor 1,CMKOR1)[21]。与CXCR4一样,CXCR7也是一种含有1个细胞外N端、3个细胞内环、3个细胞外环和1个细胞内C端的7次跨膜G蛋白偶联受体。在人类CXCR7基因定位于2q37.3,由12 617个碱基对组成[22]。最近KUANG等[23]报道骨性关节炎患者外周血单核细胞和关节滑膜中CXCR7表达水平较非骨性关节炎患者高,动物实验证实CXCR7抗体能显著抑制骨髓来源巨噬细胞向高浓度SDF-1区域迁移,并缓解条件性FGFR3基因缺失造成的小鼠滑膜炎及软骨破坏。解志波等[24]报道膝骨关节炎患者外周血巨噬细胞中CXCL12和CXCR7表达水平较正常健康人高,且与膝骨关节炎严重程度、膝关节疼痛和功能受限相关。这些研究提示SDF-1/CXCR7信号通路参与骨性关节炎的发生发展,通过靶向抑制SDF-1/CXCR7以减少循环巨噬细胞迁移至关节滑膜,缓解滑膜炎,保护关节软骨,有望成为防治骨性关节炎的新方法。然而,CXCR7在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨和成软骨过程中表达上调,应用CXCR7拮抗剂CCX771阻止SDF-1与CXCR7结合可抑制骨髓间充质干细胞多种关键成骨(如Runt-相关转录因子2和Sp7转录因子)和成软骨基因(如聚集蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原)的表达[25]。另外,过表达CXCR7的骨髓间充质干细胞具有促进滑膜巨噬细胞凋亡、调节T细胞分化、抑制滑膜细胞表达促炎因子及骨吸收标志物并促进抗炎因子表达等生物学效应,将其注入骨性关节炎动物模型踝关节内,可观察到滑膜炎、软骨退变和骨吸收程度较对照组减轻[25]。提示骨髓间充质干细胞SDF-1/CXCR7的激活一方面能缓解滑膜炎、软骨退变和抑制骨转换,从而缓解骨性关节炎的病理进展,另一方面促使自身向软骨细胞分化以修复软骨。因而,SDF-1/CXCR7信号通路在不同的细胞类型有不同的生物学效应,循环巨噬细胞SDF-1/CXCR7信号通路的激活可能造成关节滑膜炎,而骨髓间充质干细胞SDF-1/CXCR7信号通路的激活则有利于软骨修复及缓解骨性关节炎滑膜炎、软骨退变等病理过程。
大量研究表明,软骨下骨转换与骨性关节炎的病理进展密切相关。成骨细胞骨形成和破骨细胞骨吸收失衡会导致骨转换增加或减低,软骨下骨发生异常骨重塑。研究表明CXCR7激动剂VUF11207(能与CXCR7特异性高效结合)通过抑制SDF-1介导ERK磷酸化而下调核因子κB受体配体(receptor activator for nuclear factor-KB ligand,RANKL)、肿瘤坏死因子α及抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和CatK的表达,最终抑制破骨细胞分化及骨吸收活性,提示SDF-1与破骨细胞前体细胞CXCR7结合后可促进其分化及骨吸收活性[26]。目前,SDF-1/CXCR7调控软骨下骨破骨细胞的具体机制尚不清楚,缺乏相关研究。因此,后续研究可定量分析CXCR4和CXCR7在软骨下骨中的表达水平,以及SDF-1与CXCR7结合后调控破骨细胞增殖分化的潜在机制。
2.4 SDF-1在软骨细胞中的作用
2.4.1 细胞增殖 软骨细胞作为关节软骨中唯一的细胞类型,其增殖及合成分泌胶原、蛋白聚糖等细胞外基质成分的能力对于软骨修复至关重要,探索软骨细胞增殖的机制可为软骨修复提供新的见解。然而,SDF-1对软骨细胞增殖的调控作用在不同实验中有不同的结果,其原因有待进一步分析。目前研究表明,SDF-1既能促进软骨细胞增殖,又能抑制软骨细胞增殖。KIM等[27]研究发现SDF-1通过细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2(ERK1/2)和核转录因子κB信号通路上调软骨细胞周期蛋白D1的表达。由于细胞周期蛋白D1是细胞增殖的标志物,故SDF-1上调软骨细胞周期蛋白D1水平,可以认为其促进了软骨细胞增殖。而YANG等[28]研究表明,SDF-1抑制软骨细胞增殖,且SDF-1过表达抑制了microRNA-107过表达和敲除HOTAIR基因对软骨细胞的促增殖作用。
2.4.2 细胞死亡
细胞凋亡:又称为细胞程序性死亡,是细胞为维持内环境稳定,由基因调控的主动死亡的过程,这一过程细胞膜保持完整,无细胞内容物外溢,不会激活炎症反应[29]。目前SDF-1对软骨细胞凋亡的作用在不同的实验中也显示出不同的结果。WEI等[30]研究表明,SDF-1不改变凋亡过程中关键酶Caspase-3的水平。然而,XIANG等[31]应用细胞转染技术构建过表达CXCR4的原代软骨细胞,然后将其与SDF-1共同培养,发现细胞凋亡调节因子Caspase-3和Bax表达增加,而bcl表达降低,提示SDF-1促进原代软骨细胞凋亡。类似地,GAO等[32]研究表明,SDF-1增加椎间盘终板软骨细胞促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达,降低抗凋亡蛋白Bcl的表达。应用T10抑制SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路后,椎间盘终板软骨细胞凋亡率降低,提示SDF-1促进椎间盘终板软骨细胞凋亡。文章认为结果的差异可能与SDF-1的浓度、软骨细胞类型及处理软骨细胞的条件不同等原因有关。
细胞自噬:自噬是机体内高度保守的细胞降解胞内物质的过程,在缺氧、压力应激、营养不良及病原体等异常生理条件下,将受损的细胞器、变性或衰老的蛋白质等细胞成分降解并回收再利用,对维持细胞内环境稳态及细胞存活非常重要。在骨性关节炎的早期,自噬增加可清除软骨退变的有害物质,维持软骨稳态,保护软骨细胞。然而随着骨性关节炎的进展,过度自噬反而促使软骨细胞凋亡率增加,加速骨性关节炎的病理进程[29]。目前,体内外实验均证明SDF-1α可促进软骨细胞自噬,关节腔内注射SDF-1α可诱导骨性关节炎软骨向自噬表型转变。体外实验表明,SDF-1α与C57BL/6J小鼠软骨细胞表面的CXCR4结合后,通过抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)的磷酸化,使得自噬相关蛋白ULK-1,Beclin-1和LC3B表达增加,而自噬底物蛋白p62表达下降。敲除CXCR4基因或应用mTOR磷酸化激活剂MHY1485可逆转这一过程,证明SDF-1α通过CXCR4/mTOR信号轴促进软骨细胞自噬[33]。体内实验表明,与正常对照组相比,SDF-1处理组软骨组织中LC3-Ⅱ和Beclin-1蛋白表达增加,p62蛋白表达下降。关节内注射自噬抑制剂氯喹可逆转软骨组织LC3-Ⅱ和Beclin-1蛋白的表达,但p62蛋白表达水平没有如预期升高[28]。
细胞坏死:是急性、不可调控的细胞非程序性死亡过程。细胞破裂后,高迁移率蛋白族、基质金属蛋白酶及肿瘤坏死因子α等作为损伤相关分子模式进入周围组织,引起周围细胞和细胞外基质发生炎症反应,从而破坏组织稳态。目前研究已发现SDF-1在病理浓度
(≥200 ng/mL)时,通过激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases,MAPK)/p38通路诱导软骨细胞坏死[30]。另有研究表明SDF-1以剂量依赖的方式促进软骨细胞坏死[28]。
细胞焦亡:又称细胞炎性坏死,是一种以炎症小体激活、细胞质膜空隙形成、细胞裂解、促炎递质大量释放为特征的程序性细胞死亡。NLRP3作为一种炎症小体感受器,在识别损伤相关分子模式后激活半胱天冬酶,活性半胱天冬酶继而促进白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18和GSDMD的成熟和分泌,GSDMD最终导致细胞肿胀、穿孔和死亡,即细胞焦亡[34]。换而言之,炎症小体NLRP3与细胞焦亡密切相关。因而,多数研究通过探索炎症小体NLRP3及其调节因子在骨性关节炎中的作用及潜在机制来揭示细胞焦亡在骨性关节炎中的具体作用。目前,已有研究表明,SDF-1通过激活腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)信号通路,抑制炎症小体NLRP3,进而抑制骨性关节炎滑膜细胞焦亡[35]。然而该研究纳入的样本量较少,其结果仍需更多高质量的实验加以验证。总的来说,探索SDF-1在骨性关节炎细胞焦亡中作用的研究较少,其相关通路、基因以及与细胞其他死亡方式(如凋亡和铁坏死)之间的相互作用和调节机制仍需进一步研究。
2.4.3 细胞分化 在成年个体中,大多数软骨细胞处于相对静止状态,只有少数软骨细胞表现为肥大分化和去分化[36]。生理情况下,软骨细胞肥大分化存在于软骨内成骨过程中:间充质干细胞在将要成骨部位聚集分化为软骨细胞,然后软骨细胞增殖并分泌富含Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖的软骨基质。根据软骨细胞的增殖情况,生长板(软骨内成骨的场所)分为3个分区,即静息区、增殖区和肥大区[37]。静息区软骨细胞能够自我更新并进入增殖区形成具有快速增殖能力的增殖型软骨细胞。增殖型软骨细胞的快速增殖可保证足够多的软骨细胞进行肥大分化。在增殖区最下端,软骨细胞停止增殖,进入肥大区进行肥大性分化。肥大型软骨细胞体积迅速扩大并逐渐形成终末肥大软骨细胞。然后,终末肥大软骨细胞凋亡或转分化为成骨细胞。软骨基质随着血管、破骨细胞的侵入逐渐矿化,最终实现成骨取代软骨基质,完成新骨形成。由此可见,软骨细胞肥大分化是从软骨内成骨到软骨基质矿化逐渐发展的过程。在这一过程中,肥大软骨细胞通过分泌Ⅴ型胶原、Ⅹ型胶原、碱性磷酸酶及基质金属蛋白酶13,以降解细胞外基质,并促进血管侵入及成骨和破骨细胞迁入,最终使得软骨组织周围基质逐渐钙化,新骨形成[38]。还有研究发现,SDF-1在邻近生长板的骨髓中高表达,其受体CXCR4在生长板肥大区高度表达[39]。SDF-1与CXCR4结合后,促进增殖型软骨细胞肥大化,并增加其表达Ⅹ型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶13和Runt-相关转录因子2(runt-related transcription factor 2,Runx2),参与生理性软骨内成骨。
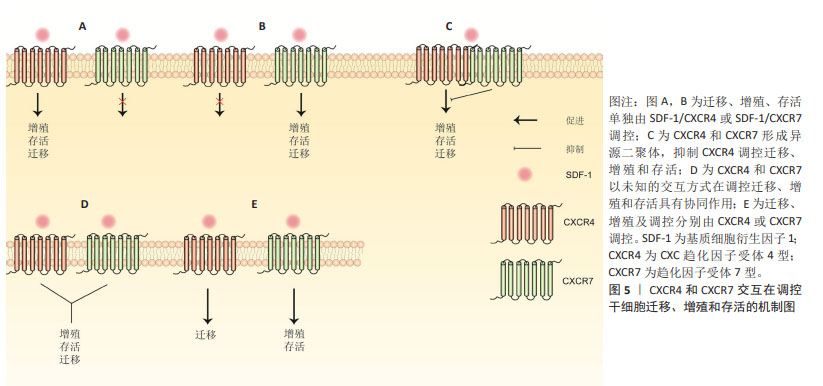
2.4.4 软骨修复 成熟关节软骨由于缺乏血管、神经和淋巴管,且其主要组成成分软骨细胞为高度终末分化细胞,使得关节软骨在创伤、长期磨损及异常负荷等机械因素及肥胖、糖尿病等代谢因素损伤后,其自我修复能力非常有限[40]。软骨修复技术主要包括骨髓刺激、自体/同种异体骨软骨移植以及软骨组织工程等。骨髓刺激应用电钻穿透软骨下骨至骨髓腔,使血细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞动员至缺损处而达到软骨修复的目的,但这种情况下仅有少量的干细胞和生长因子被招募至软骨缺损,不足以再生出透明软骨[41]。此时,仅能产生纤维软骨填充缺损,而纤维软骨与周围正常透明软骨不能形成有效的长久黏合,其机械性能和耐磨损能力不如天然透明软。自体/同种异体骨软骨移植利用自身非负重区或异体供者的软骨组织植入到缺损处,能再生透明软骨,迅速达到愈合效果,但自体骨软骨移植存在取材部位损伤、异体骨软骨移植存在疾病传播风险、供体移植物来源有限、免疫排斥反应及价格昂贵等缺点,限制其在临床上广泛应用[40,42]。近年来,随着生物材料科学、细胞生物学及生物力学等学科领域的不断发展进步,基于间充质干细胞的再生医学为修复软骨缺损提供一种很有希望的治疗策略。骨髓间充质干细胞来源广泛、具有较强的自我增殖以及向软骨细胞分化潜能,并能保存软骨细胞表型的稳定,使其作为软骨组织工程的“种子细胞”广泛应用于修复软骨缺损[36]。研究表明,足够数量的间充质干细胞在合适的时间归巢到软骨损伤部位是保证软骨修复质量的关键,而骨髓间充质干细胞归巢能力与软骨损伤局部SDF-1浓度以及骨髓间充质干细胞自身CXCR4和(或)CXCR7表达水平相关[43-45]。然而,有关SDF-1调控骨髓间充质干细胞归巢的研究主要集中在SDF-1/CXCR4,而对SDF-1/CXCR7及SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7研究较少,因此文章主要描述SDF-1/CXCR4在骨髓间充质干细胞归巢以及其用于软骨组织工程再生软骨的相关研究,对SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7调控干细胞迁移、增殖及存活的可能机制总结至图5。
WYNN等[43]于2004年首次报道人骨髓间充质干细胞表面表达低水平的功能性CXCR4,且以剂量依赖方式向SDF-1高浓度区域迁移,在SDF-1质量浓度为30 ng/mL时有最大的迁移率。SHI等[46]于2007年首次报道上调人骨髓间充质干细胞CXCR4表达水平能够明显增强其归巢到骨髓:经过细胞因子刺激的人骨髓间充质干细胞CXCR4表达显著增加,且将其注入小鼠体内24 h后,流式细胞仪证实骨髓中PKH26标记的骨髓间充质干细胞数量约为对照组的7倍。自此,通过外源性注入SDF-1、慢病毒转染技术使骨髓间充质干细胞过表达CXCR4和SDF-1预处理骨髓间充质干细胞或生物支架材料等在心肌、骨再生领域展开了广泛的研究。直到2012年,SUKEGAWA等[47]将负载SDF-1的超纯海藻酸凝胶用于修复兔全层软骨损伤,发现再生软骨组织蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白含量及压缩模量明显大于对照组,首次阐明SDF-1在修复软骨中的作用,即SDF-1通过增加骨髓间充质干细胞在软骨损伤区域的归巢率来改善软骨修复质量。后续研究主要集中在探寻SDF-1与不同生物支架之间的最佳组合,以提高骨髓间充质干细胞归巢、增殖、存活、软骨分化及维持表型的稳定,进而再生理想透明软骨。
MUSTAPICH等[48]将50 ng/mL SDF-1负载到明胶-Ⅰ型胶原支架,通过招募内源性骨髓性间充质干细胞和诱导软骨分化来修复大鼠股骨远端全层软骨损伤,植入后8周显示软骨缺损被含大量蛋白聚糖的成熟软骨组织填充,修复表面光滑平整,与周围正常组织相似且无明显分界。然而,CHEN等[49]将150 ng/mL SDF-1α负载到丝素蛋白多孔明胶支架用来修复大鼠股骨远端全层软骨损伤时,植入后12周显示软缺损处仅被少量软而脆的纤维组织填充,与周围正常组织分界清楚。在大型动物尤卡坦小型猪股骨远端全层软骨缺损模型中也观察到了相似的结果[50]:负载SDF-1的纳米纤维透明质酸支架植入12周后,缺损处仅被纤维组织(蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原都少)填充。另外,与单纯支架组相比,国际软骨修复协会(International Cartilage Repair Society,ICRS)评分和Oswestry关节镜(Oswestry Arthroscopic Scoring system,OAS)评分均较低,机械性能也较差,这表明负载SDF-1的支架并没有显著改善全层软骨损伤的软骨修复质量,其原因可能是SDF-1在招募内源性骨髓间充质干细胞的同时,将表达CXCR4的淋巴细胞、巨噬细胞等炎症细胞也一同招募至软骨缺损处,而炎症细胞通过分泌炎症递质、基质降解酶等破坏再生软骨组织,最终导致软骨缺损处无法完全再生关节软骨,恢复原有的功能状态[50]。另外,研究表明SDF-1还能通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞向肥大软骨细胞分化,而新生软骨细胞肥大表型会造成软骨内骨形成,软骨细胞凋亡,整个组织发生血管化、骨化,影响最终软骨修复的质量[40,51]。
总之,种子细胞、支架材料及理化刺激因子(如趋化因子)作为关节软骨组织工程的3要素,对于产生理想的再生透明软骨的重要性不言而喻。SDF-1负载不同支架材料显示出不同的软骨修复质量,提示探寻三者最佳组合可促进软骨更好地再生。另外,更深入地探索SDF-1在骨髓间充质干细胞向肥大表型软骨细胞分化的作用及潜在机制将有助于更好地修复软骨。SDF-1参与调控骨髓间充质干细胞和软骨细胞增殖、分化及死亡的相关实验汇总,见表1。
2.5 SDF-1在软骨下骨中的作用 SDF-1表达水平在骨性关节炎患者软骨下骨中显著升高,且其表达水平与骨性关节炎严重程度相关[8]。SDF-1主要由软骨下骨内的成骨细胞以自分泌或旁分泌的形式生成,并通过与CXCR-4阳性骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞结合以参与软骨下骨微环境的调控[52]。
2.5.1 SDF-1对破骨细胞的作用 破骨细胞由血系单核-巨噬细胞前体细胞融合而成,是软骨下骨中唯一负责骨吸收的细胞。生理条件下,血管内皮细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞和成骨细胞均表达高水平SDF-1,SDF-1使循环破骨细胞前体归巢到骨,并促进其融合成多核破骨细胞。此外,SDF-1还能通过下调关键促凋亡Bcl-2家族成员Bim蛋白表达水平逆转RANKL和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子撤退引起的破骨细胞凋亡而维持其存活[44]。由此可见,SDF-1促进破骨细胞前体迁移、早期发育和存活,在维持正常骨形成及骨重建中发挥重要作用。
当破骨细胞数量或活性异常时会打破软骨下骨稳态的动态平衡,从而诱发骨性关节炎。在骨性关节炎的早期阶段,由于破骨细胞数量较成骨细胞增加更为显著,导致软骨下骨以骨吸收为主[53]。而软骨下骨中破骨细胞增加的原因可能是由于关节异常机械负荷作用于软骨下骨局部骨髓间充质干细胞后,通过Wnt5a/Ror2途径促进其表达SDF-1和RANKL,SDF-1与骨髓或循环中的破骨细胞前体细胞CXCR4结合后被募集至软骨下骨,然后在RANKL的作用下,破骨细胞前体细胞通过Ca2+/NFAT信号通路分化为破骨细胞[54]。此外,DONG等[55]将小鼠胫骨和股骨分离出来的骨髓单核细胞与RANKL和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子共同培养以诱导破骨细胞生成,加入SDF-1能显著促进该过程。作者进一步探索机制,发现SDF-1激活破骨细胞前体细胞MAPK(包括p38和ERK1/2)信号通路,促进其分化为破骨细胞并上调破骨细胞相关蛋白如抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和组织蛋白酶K(cathepsin K,CatK)的表达,进而影响破骨细胞活性,发挥骨吸收作用。应用骨性关节炎动物模型进行体内研究表明,软骨下骨体积分数和骨小梁厚度降低、骨小梁间距增大,而应用AMD3100后软骨下骨吸收程度减轻。因此SDF-1通过促进破骨细胞迁移、增殖分化及骨吸收活性,参与早期骨性关节炎软骨下骨重塑,调控SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路可能是预防早期骨性关节炎骨小梁丢失的新策略。SDF-1参与调控破骨细胞细胞迁移、增殖、分化及凋亡的相关实验汇总[44,55-58],见表2。
2.5.2 SDF-1对骨髓间充质干细胞和成骨细胞的作用 骨髓间充质干细胞具有无限增殖及在多种诱导因子作用下向成骨细胞系分化的潜能,使其作为种子细胞广泛应用于骨再生领域[59]。根据不同的分化阶段,成骨细胞系依次分化为骨祖细胞、前成骨细胞和成骨细胞。成骨细胞经过多种细胞外基质矿化后逐渐成熟为骨细胞。与对照组相比,骨性关节炎患者及动物模型软骨下骨聚集较多的骨髓间充质干细胞和前成骨细胞,提示软骨下骨异常骨重塑与骨髓间充质干细胞和成骨细胞密切相关[53-60]。
MENG等[61]应用慢病毒转染技术构建过表达或低表达SDF-1α的骨髓间充质干细胞来探索SDF-1α对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化的作用,发现过表达SDF-1α骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞周期蛋白D1、成骨分化关键转录因子Runx2和矿化相关基因碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素表达均上调,表明SDF-1体外促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化。随后作者通过小鼠骨性关节炎模型以验证骨髓间充质干细胞在软骨下骨硬化的作用,发现骨性关节炎造模术后8周时,软骨下骨SDF-1水平、骨髓间充质干细胞特异表面标记物CD44和CD90以及Runx2和骨钙素表达均显著增加,骨体积分数和骨密度同步升高,而应用AMD3100拮抗SDF-1受体CXCR4后,上述标志物表达均下降,软骨下骨硬化程度减轻,表明SDF-1促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化,进而加重软骨下骨硬化。对于此过程的分子机制研究,近年来发现SDF-1将骨髓间充质干细胞募集到软骨下骨后,通过ERK,JAK2/STAT3,Wnt/β-Catenin以及LncRNA-H19/miR-214-5p/骨形态发生蛋白2途径使其向成骨分化而加重软骨下骨硬化[60,62-64]。
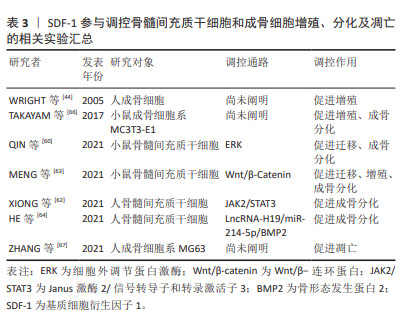
成骨细胞主要由骨髓间充质干细胞分化而来,表达SDF-1及其受体CXCR4,是软骨下骨稳态中对抗破骨细胞骨吸收作用的骨形成细胞。研究表明骨性关节炎患者软骨下骨成骨细胞数量较非骨性关节炎患者显著增加,提示成骨细胞参与软骨下骨异常骨重塑[53]。进一步研究发现,骨性关节炎患者及动物模型软骨下骨前成骨细胞SDF-1的表达水平增加且受到雷帕霉素复合体1(mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1,mTORC1)的正向调控,即前成骨细胞中mTORC1激活后可以促进自身表达和分泌SDF-1。SDF-1与成骨细胞CXCR4结合后,通过调控成骨细胞增殖及Ⅰ型胶原分泌,参与软骨下骨异常骨形成[65]。因此,调控成骨细胞SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路有助于改善软骨下骨异常骨形成,为治疗骨性关节炎提供新的思路。SDF-1参与调控骨髓间充质干细胞和成骨细胞增殖、分化及凋亡的相关实验汇总[44,62-67],见表3。
2.6 SDF-1在软骨和软骨下骨之间的串扰 软骨下骨是关节软骨和骨髓之间的皮质骨(亦称为软骨下骨板)和松质骨(亦称为骨小梁),在维持软骨完整性、软骨细胞合成分解代谢动态平衡、传递机械负荷中发挥重要作用[68]。当软骨下骨发生过度骨吸收或异常骨形成时,由于软骨下骨弹性形变和减震能力降低,关节软骨机械负荷分布不均匀或出现局部应力集中,软骨细胞合成分解代谢失衡,导致关节软骨容易发生退变[60,69]。研究表明,SDF-1串扰软骨下骨和软骨以促进骨性关节炎的进展。软骨下骨高水平SDF-1一方面通过募集并诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞或破骨细胞分化,导致骨形成和吸收失衡,软骨下骨板变薄、孔隙率增加及骨小梁间距增大,另一方面通过上调p-ERK和p-AKT水平显著增加H血管内皮细胞标志物CD31/Emcn,导致软骨下骨异常血管生成,最终造成软骨下骨中的SDF-1向软骨迁移增加[60,69]。SDF-1与CXCR4阳性软骨细胞结合后促进转化生长因子β超家族Ⅰ型激活素受体样激酶5(activin receptor-like kinase 5,ALK5)向转化生长因子β超家族Ⅰ型激活素受体样激酶1转变(activin receptor-like kinase 1,ALK1),ALK1/ALK5比值升高,最终导致软骨细胞分解标志物基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMTS5表达增加,软骨细胞外基质降解、软骨细胞功能改变[69]。在骨性关节炎动物模型中,应用微型渗透性输液泵将AMD3100直接泵入软骨下骨,可抑制软骨下骨异常骨重塑,减少软骨SDF-1的含量并恢复软骨细胞ALK1/ALK5比值至正常水平,进而降低软骨细胞分解标志物的表达[69]。由此可见,SDF-1通过调控骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞增殖分化以及血管异常形成来参与软骨下骨病理性重塑间接导致软骨退变。另外,SDF-1还能诱导软骨细胞肥大分化,使其高度表达基质金属蛋白酶13和碱性磷酸酶,直接导致软骨降解及软骨基质钙化[61]。此外,肥大软骨细胞表达SDF-1及其受体CXCR4增多,促使更多的软骨细胞向肥大表型分化,加速软骨退变[70]。因此,调控SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路有利于恢复软骨下骨稳态、减少骨软骨界面血管异常形成及软骨细胞肥大化,延缓骨性关节炎的病理进展。
2.7 CXCR4拮抗剂在骨性关节炎病理进展过程中的调控作用 目前,已有许多研究表明SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路在骨性关节炎的发生发展中起着关键性作用,而CXCR4受体拮抗剂在防治骨性关节炎软骨退变和软骨下骨异常骨重塑的研究也日益增多。CXCR4受体拮抗剂主要包括AMD3100,T140,TN14003,其中AMD3100是CXCR4的特异性部分阻滞剂,即特异性阻断SDF-1与其配体CXCR4结合效果不完全;T140为CXCR4的反向阻滞剂,阻断SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路较AMD3100强;TN14003为T140衍生物,能完全拮抗剂CXCR4,是目前最有效的鲎肽拮抗剂[71]。李彦林团队[72-73]应用豚鼠自发性骨性关节炎模型以研究这3种拮抗剂在体内关节软骨退变中的作用,结果表明3种拮抗剂均能靶向抑制SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路,降低软骨组织中基质金属蛋白酶3,9,13以及炎症因子白细胞介素1和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达和分泌,减少Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白多糖的降解,从而延缓关节软骨退行性变,其中TN14003的调节作用最强。该团队进一步探索其内在的分子机制,发现与单纯模型组相比,经过AMD3100治疗的模型大鼠滑膜和软骨组织中金属蛋白组织抑制因子3(Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3,TIMP-3)和Smad3阳性细胞显著增多。TIMP-3是内源性金属蛋白酶抑制剂,能有效抑制基质金属蛋白酶和ADAMTSs,保护软骨细胞外基质不被降解和重塑[74]。随后,该团队将沉默CXCR4基因的白细胞介素1预处理软骨细胞与SDF-1共同培养来模拟体外阻断SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路,发现聚集蛋白多糖酶和ADAMTS-5表达下降,而TIMP-3和转化生长因子β1表达增多;然后,将转化生长因子β1预处理的软骨细胞与AMD3100或Akt抑制剂LY303511共同培养,发现AMD3100通过上调p-Akt水平,促进转化生长因子β1诱导的SD大鼠软骨细胞中TIMP-3表达。总之,AMD3100通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,促使TIMP-3水平上调,抑制聚集蛋白多糖酶和ADAMTS-5的表达,从而延缓关节软骨退变[75]。此外,AMD3100还能减少骨髓间充质干细胞募集、成骨分化和骨吸收,使软骨下骨异常成骨恢复至正常水平[60]。然而,由于AMD3100为CXCR4部分阻滞剂且细胞毒性大,限制其应用于临床[76]。
TN14003作为T140的衍生物,其细胞毒性和血清稳定性明显优于T140,且为CXCR4完全阻滞剂,有望成为治疗骨性关节炎更为有效的药物。JIA等[77]微阵列分析SDF-1或SDF-1+TN14003预处理的人软骨细胞存在差异表达的miRNA,发现miR-146a-5p显著上调。进一步深入研究表明,TN14003通过上调miR-146a-5p,从而降低软骨细胞CXCR4和基质金属蛋白酶3表达,增加聚集蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达,延缓关节软骨退化。
| 1] MURPHY PM, HEUSINKVELD L. Multisystem multitasking by CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and ACKR3. Cytokine. 2018;109:2-10. [2] NAGASAWA T, KIKUTANI H, KISHIMOTO T. Molecular cloning and structure of a pre-B-cell growth-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(6):2305-2309. [3] SHIROZU M, NAKANO T, INAZAWA J, et al. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF1) gene. Genomics. 1995;28(3):495-500. [4] KANBE K, TAKAGISHI K, CHEN Q. Stimulation of matrix metalloprotease 3 release from human chondrocytes by the interaction of stromal cell-derived factor 1 and CXC chemokine receptor 4. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(1):130-137. [5] KANBE K, TAKEMURA T, TAKEUCHI K, et al. Synovectomy reduces stromal-cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) which is involved in the destruction of cartilage in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol. 2004;86(2):296-300. [6] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJR, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet (London, England). 2015;386(9991):376-387. [7] GUANG LG, BOSKEY AL, ZHU W. Regulatory role of stromal cell-derived factor-1 in bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced chondrogenic differentiation in vitro. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(11):1825-1833. [8] CHEN Y, LIN S, SUN Y, et al. Attenuation of subchondral bone abnormal changes in osteoarthritis by inhibition of SDF-1 signaling. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(6):986-994. [9] GLEICHMANN M, GILLEN C, CZARDYBON M, et al. Cloning and characterization of SDF-1gamma, a novel SDF-1 chemokine transcript with developmentally regulated expression in the nervous system. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12(6):1857-1866. [10] YU L, CECIL J, PENG SB, et al. Identification and expression of novel isoforms of human stromal cell-derived factor 1. Gene. 2006;374:174-179. [11] MURPHY JW, YUAN H, KONG Y, et al. Heterologous quaternary structure of CXCL12 and its relationship to the CC chemokine family. Proteins. 2010;78(5):1331-1337. [12] HERBERG S, FULZELE S, YANG N, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1β potentiates bone morphogenetic protein-2-stimulated osteoinduction of genetically engineered bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(1-2):1-13. [13] HERBERG S, SHI X, JOHNSON MH, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1β mediates cell survival through enhancing autophagy in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58207. [14] MENDELSON A, FRANK E, ALLRED C, et al. Chondrogenesis by chemotactic homing of synovium, bone marrow, and adipose stem cells in vitro. FASEB J. 2011;25(10):3496-3504. [15] LAGURI C, SADIR R, RUEDA P, et al. The novel CXCL12gamma isoform encodes an unstructured cationic domain which regulates bioactivity and interaction with both glycosaminoglycans and CXCR4. PLoS One. 2007;2(10):e1110. [16] RUEDA P, BALABANIAN K, LAGANE B, et al. The CXCL12gamma chemokine displays unprecedented structural and functional properties that make it a paradigm of chemoattractant proteins. PLoS One. 2008; 3(7):e2543. [17] REN Z, LANTERMANS H, KUIL A, et al. The CXCL12gamma chemokine immobilized by heparan sulfate on stromal niche cells controls adhesion and mediates drug resistance in multiple myeloma. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):11. [18] JUNG Y, KIM JK, LEE E, et al. CXCL12γ induces human prostate and mammary gland development. Prostate. 2020;80(13):1145-1156. [19] FRANCO D, RUEDA P, LENDíNEZ E, et al. Developmental expression profile of the CXCL12gamma isoform: insights into its tissue-specific role. Anatomical Record (Hoboken, NJ: 2007). 2009;292(6):891-901. [20] RAY P, STACER AC, FENNER J, et al. CXCL12-γ in primary tumors drives breast cancer metastasis. Oncogene. 2015;34(16):2043-2051. [21] LIBERT F, PARMENTIER M, LEFORT A, et al. Complete nucleotide sequence of a putative G protein coupled receptor: RDC1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18(7):1917. [22] LIBERT F, PASSAGE E, PARMENTIER M, et al. Chromosomal mapping of A1 and A2 adenosine receptors, VIP receptor, and a new subtype of serotonin receptor. Genomics. 1991;11(1):225-227. [23] KUANG L, WU J, SU N, et al. FGFR3 deficiency enhances CXCL12-dependent chemotaxis of macrophages via upregulating CXCR7 and aggravates joint destruction in mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(1): 112-122. [24] 解志波,陈科明,黄从伍,等.膝骨关节炎患者巨噬细胞趋化力与疾病严重程度的相关性[J].中国骨伤,2023,36(6):514-518. [25] WEI ST, HUANG YC, CHIANG JY, et al. Gain of CXCR7 function with mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates experimental arthritis via enhancing tissue regeneration and immunomodulation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):314. [26] NUGRAHA A, KITAURA H, OHORI F, et al. C‑X‑C receptor 7 agonist acts as a C‑X‑C motif chemokine ligand 12 inhibitor to ameliorate osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Mol Med Rep. 2022;25(3):78. [27] KIM GW, HAN MS, PARK HR, et al. CXC chemokine ligand 12a enhances chondrocyte proliferation and maturation during endochondral bone formation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(6):966-974. [28] YANG T, LI C, LI Y, et al. MicroRNA-146a-5p alleviates the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by inhibiting SDF-1/CXCR4-induced chondrocyte autophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;117:109938. [29] 赵奎,潘润桑,蓝奉军,等.骨关节炎中自噬与凋亡相互作用的分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(18):2912-2917. [30] WEI L, SUN X, KANBE K, et al. Chondrocyte death induced by pathological concentration of chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1. J Rheumatol. 2006;33(9):1818-1826. [31] XIANG Y, LI Y, YANG L, et al. miR-142-5p as a CXCR4-targeted microRNA attenuates SDF-1-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation via inactivating MAPK signaling pathway. Biochem Res Int. 2020;2020:4508108. [32] GAO ZY, YU LL, SHI BX, et al. T140 inhibits apoptosis and promotes proliferation and matrix formation through the SDF-1/CXC receptor-4 signaling pathway in endplate chondrocytes of the rat intervertebral discs. World Neurosurg. 2020;133:e165-e172. [33] LI J, CHEN H, CAI L, et al. SDF-1α promotes chondrocyte autophagy through CXCR4/mTOR signaling axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1710. [34] CHEN Y, ZENG D, WEI G, et al. Pyroptosis in osteoarthritis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17: 791-803. [35] WANG S, MOBASHERI A, ZHANG Y, et al. Exogenous stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) suppresses the NLRP3 inflammasome and inhibits pyroptosis in synoviocytes from osteoarthritic joints via activation of the AMPK signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 2021;29(3): 695-704. [36] LI J, CHEN H, ZHANG D, et al. The role of stromal cell-derived factor 1 on cartilage development and disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(3):313-322. [37] LUI JC. Home for a rest: stem cell niche of the postnatal growth plate. J Endocrinol. 2020;246(1):R1-R11. [38] 薛松,姜亚飞,桑伟林,等.肥大软骨细胞在骨关节炎发病中的作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(6):522-526. [39] WEI L, KANBE K, LEE M, et al. Stimulation of chondrocyte hypertrophy by chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1 in the chondro-osseous junction during endochondral bone formation. Dev Biol. 2010;341(1):236-245. [40] 马丁,师东良,李姣,等.关节软骨损伤再生修复研究进展[J].生命科学,2021,33(11):1353-1362. [41] RICHTER W. Mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage in situ regeneration. J Intern Med. 2009;266(4):390-405. [42] GUO X, MA Y, MIN Y, et al. Progress and prospect of technical and regulatory challenges on tissue-engineered cartilage as therapeutic combination product. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:501-518. [43] WYNN RF, HART CA, CORRADI-PERINI C, et al. A small proportion of mesenchymal stem cells strongly expresses functionally active CXCR4 receptor capable of promoting migration to bone marrow. Blood. 2004;104(9):2643-2645. [44] WRIGHT LM, MALONEY W, YU X, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 binding to its chemokine receptor CXCR4 on precursor cells promotes the chemotactic recruitment, development and survival of human osteoclasts. Bone. 2005;36(5):840-853. [45] SORDI V, MALOSIO ML, MARCHESI F, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells express a restricted set of functionally active chemokine receptors capable of promoting migration to pancreatic islets. Blood. 2005;106(2):419-427. [46] SHI M, LI J, LIAO L, et al. Regulation of CXCR4 expression in human mesenchymal stem cells by cytokine treatment: role in homing efficiency in NOD/SCID mice. Haematologica. 2007;92(7):897-904. [47] SUKEGAWA A, IWASAKI N, KASAHARA Y, et al. Repair of rabbit osteochondral defects by an acellular technique with an ultrapurified alginate gel containing stromal cell-derived factor-1. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2012;18(9-10):934-945. [48] MUSTAPICH T, SCHWARTZ J, PALACIOS P, et al. A novel strategy to enhance microfracture treatment with stromal cell-derived factor-1 in a rat model. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;8:595932. [49] CHEN Y, WU T, HUANG S, et al. Sustained release SDF-1α/TGF-β1-loaded silk fibroin-porous gelatin scaffold promotes cartilage repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(16):14608-14618. [50] MARTIN AR, PATEL JM, LOCKE RC, et al. Nanofibrous hyaluronic acid scaffolds delivering TGF-β3 and SDF-1α for articular cartilage repair in a large animal model. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:170-182. [51] CHEN X, LIANG XM, ZHENG J, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α regulates chondrogenic differentiation via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2023;15(5):490-501. [52] YANG J, LI Y, LIU Y, et al. Role of the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway in cartilage and subchondral bone in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis induced by overloaded functional orthopedics in rats. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):330. [53] LIN C, LIU L, ZENG C, et al. Activation of mTORC1 in subchondral bone preosteoblasts promotes osteoarthritis by stimulating bone sclerosis and secretion of CXCL12. Bone Res. 2019;7(1):5. [54] YANG T, ZHANG J, CAO Y, et al. Wnt5a/Ror2 mediates temporomandibular joint subchondral bone remodeling. J Dent Res. 2015;94(6):803-812. [55] DONG Y, LIU H, ZHANG X, et al. Inhibition of SDF-1α/CXCR4 signalling in subchondral bone attenuates post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(6):943. [56] GOTO Y, AOYAMA M, SEKIYA T, et al. CXCR4+ CD45- cells are niche forming for osteoclastogenesis via the SDF-1, CXCL7, and CX3CL1 signaling pathways in bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2016;34(11):2733-2743. [57] SHIMA K, KIMURA K, ISHIDA M, et al. C-X-C motif chemokine 12 enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vivo. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;103(4):431-442. [58] ADAPALA NS, ROOT S, LORENZO J, et al. PI3K activation increases SDF-1 production and number of osteoclast precursors, and enhances SDF-1-mediated osteoclast precursor migration. Bone Rep. 2019;10:100203. [59] 李园琦,林海,罗红蓉,等.线粒体自噬与骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化的关联[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(31):4954-4960. [60] QIN H, ZHAO X, HU YJ, et al. Inhibition of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis to alleviate abnormal bone formation and angiogenesis could improve the subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021:1-13. [61] MENG Z, XIN L, FAN B. SDF-1α promotes subchondral bone sclerosis and aggravates osteoarthritis by regulating the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord. 2023;24(1):275. [62] XIONG W, GUO X, CAI X. SDF-1/CXCR4 axis promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs through the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2021;59(3):187-194. [63] MENG Z, FENG G, HU X, et al. SDF factor-1α promotes the migration, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2021;30(2):106-117. [64] HE Q, LI R, HU B, et al. Stromal cell‐derived factor‐1 promotes osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the lncRNA‐H19/miR‐214‐5p/BMP2 axis. J Gene Med. 2021;23(9):e3366. [65] LISIGNOLI G, TONEGUZZI S, PIACENTINI A, et al. CXCL12 (SDF-1) and CXCL13 (BCA-1) chemokines significantly induce proliferation and collagen type I expression in osteoblasts from osteoarthritis patients. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(1):78-85. [66] TAKAYAMA T, DAI J, TACHI K, et al. The potential of stromal cell-derived factor-1 delivery using a collagen membrane for bone regeneration. J Biomater Appl. 2017;31(7):1049-1061. [67] ZHANG Z, WU H, HUANG S, et al. AMD3465 (hexahydrobromide) rescues the MG63 osteoblasts against the apoptosis induced by high glucose. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138:111476. [68] YILDIRIM N, AMANZHANOVA A, KULZHANOVA G, et al. Osteochondral Interface: Regenerative Engineering and Challenges. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(3):1205-1223. [69] QIN HJ, XU T, WU HT, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 axis coordinates crosstalk between subchondral bone and articular cartilage in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2019;125:140-150. [70] TOILLON I, VAN EEGHER S, PIGENET A, et al. Hypertrophic chondrocyte differentiation mediates osteochondral angiogenesis through SDF-1/CXCR4 axis during osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30: S323-S323. [71] 蒙旭晗,李彦林,毛健宇,等. CXCR4受体拮抗剂在骨性关节炎软骨退变中的作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(5):424-427. [72] 何璐,李彦林,蒙旭晗,等. C-X-C趋化因子受体4拮抗剂延缓豚鼠关节软骨的退变[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(14):2150-2154. [73] WANG G, LI Y, MENG X, et al. The study of targeted blocking SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway with three antagonists on MMPs, type II collagen, and aggrecan levels in articular cartilage of guinea pigs. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):195. [74] GREEN J, TINSON RAJ, BETTS JHJ, et al. Suramin analogues protect cartilage against osteoarthritic breakdown by increasing levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 3 (TIMP-3) in the tissue. Bioorg Med Chem. 2023;92:117424. [75] LU W, HE Z, SHI J, et al. AMD3100 attenuates post-traumatic osteoarthritis by maintaining transforming growth factor-β1-induced expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1554. [76] LIAO YX, FU ZZ, ZHOU CH, et al. AMD3100 reduces CXCR4-mediated survival and metastasis of osteosarcoma by inhibiting JNK and Akt, but not p38 or Erk1/2, pathways in in vitro and mouse experiments. Oncol Rep. 2015;34(1):33-42. [77] JIA D, LI Y, HAN R, et al. miR‑146a‑5p expression is upregulated by the CXCR4 antagonist TN14003 and attenuates SDF‑1‑induced cartilage degradation. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):4388-4400. |
| [1] | 韩海慧, 冉 磊, 孟晓辉, 辛鹏飞, 向 峥, 边艳琴, 施 杞, 肖涟波. 靶向成纤维细胞生长因子受体1信号改善类风湿关节炎的骨破坏[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [2] | 赵济宇, 王少伟. 叉头框转录因子O1信号通路与骨代谢[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [3] | 朱汉民, 王 松, 肖文琳, 张文静, 周 茜, 何 烨, 李 微, . 线粒体自噬调控骨代谢[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [4] | 尹 路, 蒋川锋, 陈俊杰, 易 明, 王子赫, 石厚银, 汪国友, 沈骅睿. 沙苑子苷A对关节软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [5] | 王文涛, 侯振扬, 王熠军, 徐耀增. Apelin-13抑制巨噬细胞M1极化缓解全身炎症性骨丢失[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [6] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [7] | 艾克帕尔·艾尔肯, 陈晓涛, 吾凡别克·巴合提. 成骨诱导人牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体促进炎症微环境下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [8] | 章镇宇, 梁秋健, 杨 军, 韦相宇, 蒋 捷, 黄林科, 谭 桢. 新橙皮苷治疗骨质疏松症的靶点及对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [9] | 杨治航, 孙祖延, 黄文良, 万 喻, 陈仕达, 邓 江. 神经生长因子促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化并抑制肥大分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [10] | 李岳尧, 张 民, 杨家驹. 肉苁蓉苷A通过JNK/MAPK通路抑制破骨细胞活性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [11] | 朗么磋, 张义林, 汪 莉. miR-338-3p靶向核因子κB受体活化因子配体影响牙槽骨成骨细胞增殖及凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 899-907. |
| [12] | 项 攀, 车艳军, 罗宗平. 压应力激活SOST/Wnt/β-catenin通路诱导软骨终板细胞退变[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [13] | 肖 放, 黄 雷, 王 琳. 磁性纳米材料与磁场效应加速骨损伤修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [14] | 孙现娟, 王秋花, 张锦艺, 杨杨杨, 王文双, 张晓晴. 不同静电纺丝膜上骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖与成血管平滑肌分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [15] | 马维邦, 徐 哲, 喻 乔, 欧阳东, 张如国, 罗 伟, 谢阳江, 刘 琛. 骨关节炎关节液外泌体中软骨退变相关基因筛选及细胞学验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年1月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2024年1月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、万方、维普、PubMed、Medline和Embase数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“基质细胞衍生因子1,软骨,软骨细胞,软骨下骨,骨髓间充质干细胞,成骨细胞,破骨细胞,CXC趋化因子受体4型,CXC趋化因子受体7型”,英文检索词为“Stromal cell-derived factor 1,SDF-1,CXCL12,cartilage,chondrocyte,subchondral bone,mesenchymal stem cells,osteoblasts,osteoclasts,CXCR4,CXCR7” 。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、期刊论文和学位论文。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 中英文数据库检索策略,见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①SDF-1与软骨和软骨细胞相关性研究;②SDF-1与骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞相关性研究;③SDF-1与软骨和软骨下骨稳态相关研究;④CXCR4和CXCR7拮抗剂用于治疗骨性关节炎的相关性研究;⑤优先选择近3-5年内的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①标题和摘要与主题不相关的文献;②重复、陈旧和质量较低的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 在15 838篇文献中,优先选择近3-5年的文献,阅读文献标题和摘要排除与此综述主题相关性不高的文献,最终纳入77篇文章进行综述,其中包括中文数据库(中国知网、万方及维普)7篇,PubMed和Medline数据库69篇,Embase数据库1篇。文献检索流程图见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 以往综述大多单一的关注SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路在骨性关节炎软骨退变和软骨下骨异常骨重塑、软骨修复及CXCR4拮抗剂在延缓骨性关节炎病理进展中的作用,对SDF-1/CXCR4串扰软骨下骨和软骨以加速骨性关节炎病理进展、SDF-1/CXCR7信号通路在软骨和软骨下骨中的生物学效应、软骨修复及SDF-1/CXCR7与骨性关节炎的相关系未能全面阐述。因而,作者广泛查阅国内外相关文献,通过总结归纳SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7在调控软骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞影响软骨和软骨下骨稳态中的因素发现:①SDF-1/CXCR4调控软骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞迁移、增殖、分化及死亡,从而促进软骨退变及软骨下骨异常骨重塑或增强软骨修复能力及抑制软骨下骨异常骨重塑。②SDF-1/CXCR4串扰软骨下骨和软骨以加速骨性关节炎病理进展。SDF-1一方面促进软骨细胞肥大化,使其表达基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13增多而直接降解软骨细胞外基质,另一方面通过多种信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞增殖、迁移及分化,导致软骨下骨发生异常骨重塑和异常血管生成增多,继而造成关节软骨机械负荷分布不均匀或出现局部应力集中,软骨细胞合成分解代谢失衡,关节软骨易于发生退变。③SDF-1/CXCR7同样参与骨性关节炎滑膜炎、软骨下骨异常骨吸收的病理过程。④多种干细胞(如骨髓间充质干细胞、脂肪间充质干细胞及胚胎干细胞)共表达CXCR4和CXCR7,SDF-1/CXCR4和SDF-1/CXCR7调控干细胞生物学行为(如迁移、增殖和存活)有所差异,其原因可能是CXCR4和CXCR7两种受体之间存在复杂且多变的交互关系(如异源二聚体)造成的。
3.3 综述的局限性 目前缺少SDF-1α以外的亚型以及SDF-1/CXCR7在调控软骨和软骨下骨稳态中的相关研究,不同亚型之间对软骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞迁移、增殖、分化和死亡有何差异尚不清楚,有待未来研究探索。
3.4 综述的重要意义 此综述深入总结分析SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7在软骨和软骨下骨稳态中的作用,加深了骨性关节炎发病机制的认识,为探寻预防和治疗骨性关节炎提供新的理论依据。另外,此综述还详细阐述SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7在干细胞迁移、归巢、增殖、分化和存活中的作用,为SDF-1更好地应用于软骨组织工程以改善不同软骨缺损修复质量提供新的思路。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 ①软骨退变、软骨下骨异常骨重塑和滑膜炎彼此相互联系,在骨性关节炎发生发展中具有重要作用,进一步分析SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7在3者中相互调控的作用及潜在机制,将有助于明确SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7在骨性关节炎不同病理阶段的特点,从而开发更有针对性且不良反应小的药物或方法来防治骨性关节炎。②SDF-1亚型结构上的差异是其生物学效应不同的基础。进一步剖析SDF-1亚型羧基末端结构对其活性、组织表达量、受体亲和力等方面的影响,将有助于阐明亚型之间调控细胞迁移、增殖、分化及死亡中的差异,为精确调控SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7以延缓骨性关节炎病理进展及更好地修复软骨病变提供理论基础。③尽管SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7轴促进干细胞迁移、归巢、增殖、分化和存活,有利于软骨修复,但已有研究表明SDF-1促进骨髓间充质干细胞向肥大型软骨细胞分化,而新生软骨细胞肥大表型会造成软骨内骨形成,软骨细胞凋亡,整个组织发生血管化和骨化,影响最终软骨修复的质量。因而,进一步探寻SDF-1造成干细胞向肥大型软骨细胞分化的潜在机制,以期维持目的表型、抑制肥大表型,提高软骨修复质量。④针对SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7开发的治疗药物、治疗方法的安全性、有效性仍需进行大量的生物学和临床试验加以佐证。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
基质细胞衍生因子1:是一种具有很强趋化活性的稳态/炎性趋化因子,属于CXC趋化因子家族成员,在关节软骨和软骨下骨中主要由肥大软骨细胞、未成熟成骨细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞表达。#br#软骨/软骨下骨:软骨和软骨下骨作为一个功能整体维持关节内环境的平衡。骨性关节炎时,软骨和软骨下骨稳态失衡,导致软骨降解、软骨细胞肥大化、软骨下骨异常骨重塑和骨软骨界面异常血管生成增多。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
基质细胞衍射因子1与CXC趋化因子受体4型和CXC趋化因子受体7型相互作用,激活多种下游信号通路,对软骨内成骨、骨形成、血管形成、多种器官发育、伤口愈合、炎症、骨性关节炎和肿瘤等生理和病理过程均有重要的影响。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||