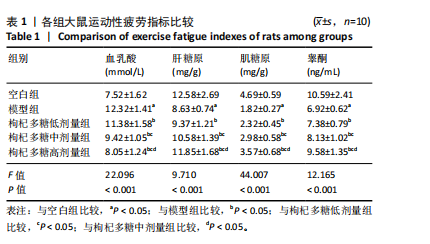
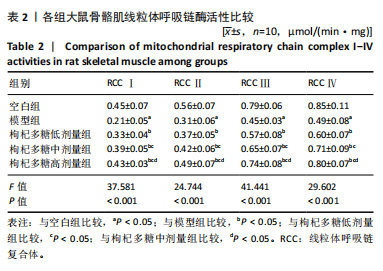
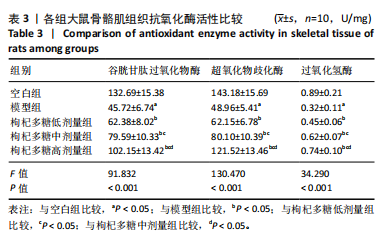
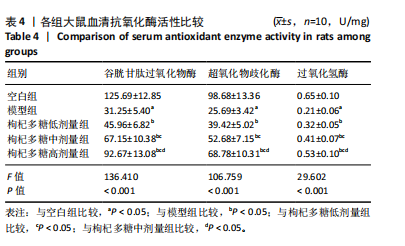
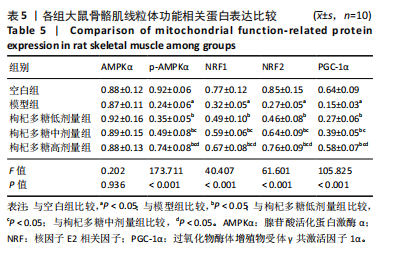
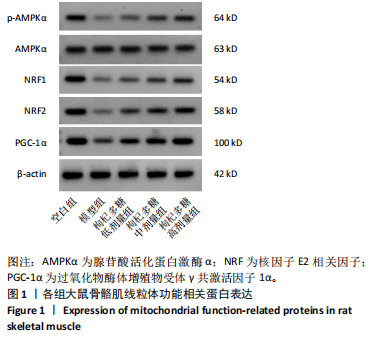
[1] MENGESTE AM, RUSTAN AC, LUND J. Skeletal muscle energy metabolism in obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2021;29(10):1582-1595.
[2] TAKEUCHI K, NAKAMURA M, KONRAD A, et al. Long-term static stretching can decrease muscle stiffness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2023;33(8):1294-1306.
[3] PELLEGRINO A, TIIDUS PM, VANDENBOOM R. Mechanisms of Estrogen Influence on Skeletal Muscle: Mass, Regeneration, and Mitochondrial Function. Sports Med. 2022;52(12):2853-2869.
[4] QUALLS AE, SOUTHERN WM, CALL JA. Mitochondria-cytokine crosstalk following skeletal muscle injury and disuse: a mini-review. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021;320(5):C681-C688.
[5] 张敏,岳坤,姜交华,等.枸杞子及其有效成分的药理作用研究进展[J].药物评价研究,2023,46(7):1611-1619.
[6] 盛伟,范文艳.枸杞多糖对小鼠耐缺氧及抗疲劳能力的影响[J].新乡医学院学报,2011,28(3):298-300.
[7] 孟繁博.运动联合枸杞多糖延缓衰老小鼠骨骼肌萎缩的机制研究[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2020.
[8] 李园,刘文杰,杨宁,等.原花青素对大负荷运动模型大鼠脾细胞自由基代谢及凋亡蛋白的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(49): 8026-8031.
[9] VYATKINA G, BHATIA V, GERSTNER A, et al. Impaired mitochondrial respiratory chain and bioenergetics during chagasic cardiomyopathy development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1689(2):162-173.
[10] PIGNANELLI C, CHRISTIANSEN D, BURR JF. Blood flow restriction training and the high-performance athlete: science to application. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021;130(4):1163-1170.
[11] 张锐,白海军,刘佳.松杉灵芝多糖结构分析及对小鼠运动性疲劳的缓解作用[J].中国食品添加剂,2023,34(4):69-78.
[12] HINDI SM, PETRANY MJ, GREENFELD E, et al. Enveloped viruses pseudotyped with mammalian myogenic cell fusogens target skeletal muscle for gene delivery. Cell. 2023;186(10):2062-2077.e17.
[13] LIM C, NUNES EA, CURRIER BS, et al. An Evidence-Based Narrative Review of Mechanisms of Resistance Exercise-Induced Human Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2022;54(9):1546-1559.
[14] 董健藤,李俊俊,刘一舟,等.肉苁蓉不同提取部位改善运动性与中枢性疲劳的药效学比较(英文)[J].中医科学杂志,2024,11(2): 222-231.
[15] 邹悦,萧闵,孟宇豪,等.基于p38 MAPK/NF-κB信号通路探讨淫羊藿多糖对运动性疲劳小鼠的影响及作用机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(10):20-28.
[16] 王海英,刘永敬,郭晓强.益母草活性生物碱益母草碱对大鼠运动性疲劳的缓解作用[J].分子植物育种,2024,22(2):593-600.
[17] 李娟,陈振起.黄精多糖对力竭运动大鼠外周血MAPK信号通路及炎症反应的影响[J].扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2023, 44(2):61-67.
[18] 郝文丽,陈志宝,赵蕊,等.枸杞多糖对亚健康小鼠免疫功能及抗疲劳作用的影响[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2015,28(7):693-697.
[19] WANG J, MA S, WU Q, et al. Effects of testis testosterone deficiency on gene expression in the adrenal gland and skeletal muscle of ducks. Br Poult Sci. 2023;64(3):312-320.
[20] PODLOGAR T, SHAD BJ, SEABRIGHT AP, et al. Postexercise muscle glycogen synthesis with glucose, galactose, and combined galactose-glucose ingestion. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023;325(6): E672-E681.
[21] MASCHARI D, SAXENA G, LAW TD, et al. Lactate-induced lactylation in skeletal muscle is associated with insulin resistance in humans. Front Physiol. 2022;13:951390.
[22] VERCELLINO I, SAZANOV LA. The assembly, regulation and function of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022; 23(2):141-161.
[23] 郭涛,贾新会.漆黄素对力竭运动大鼠骨骼肌细胞凋亡和线粒体功能的影响[J].分子植物育种,2024,22(4):1281-1289.
[24] HEDBERG-OLDFORS C, LINDGREN U, VISUTTIJAI K, et al. Respiratory chain dysfunction in perifascicular muscle fibres in patients with dermatomyositis is associated with mitochondrial DNA depletion. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2022;48(7):e12841.
[25] DONG H, TSAI SY. Mitochondrial Properties in Skeletal Muscle Fiber. Cells. 2023;12(17):2183.
[26] 陈泽芃,王辰龙,顾庆龙,等.增液八珍汤对慢传输型便秘大鼠超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽和一氧化氮的影响[J].安徽医药,2024, 28(7):1467-1471.
[27] KOSE SBE, KOCASARI FS. Protective effect of cinnamic acid on orthophenylphenol-induced oxidative stress in rats. Vet Res Forum. 2022;13(2):187-192.
[28] ABU SHELBAYEH O, ARROUM T, MORRIS S, et al. PGC-1α Is a Master Regulator of Mitochondrial Lifecycle and ROS Stress Response. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(5):1075.
[29] MOZAFFARITABAR S, KOLTAI E, ZHOU L, et al. PGC-1α activation boosts exercise-dependent cellular response in the skeletal muscle. J Physiol Biochem. 2024;80(2):329-335.
[30] YANG K, YANG M, SHEN Y, et al. Resveratrol Attenuates Hyperoxia Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats by Activating SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway. Am J Perinatol. 2024;41(8):1039-1049. |