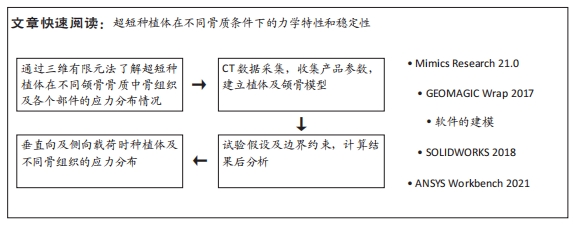
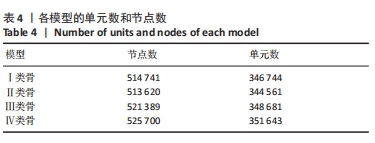
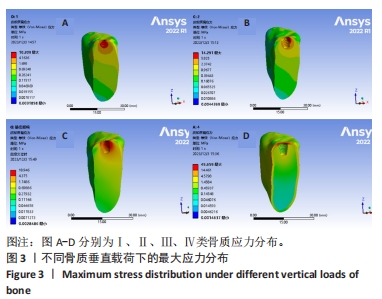
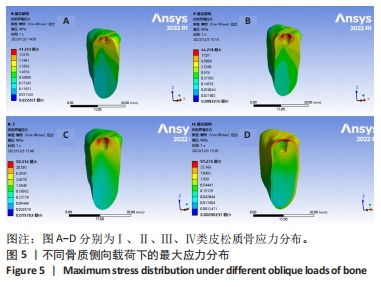
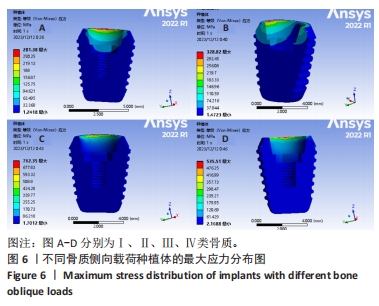
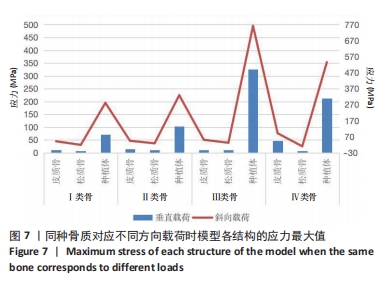
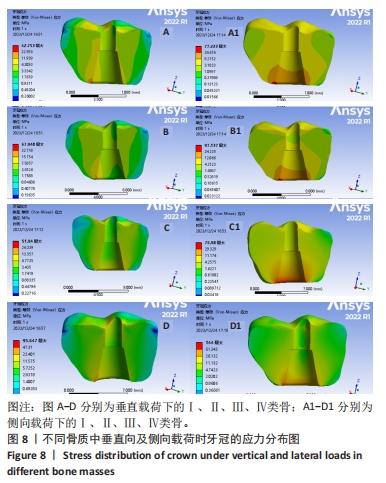
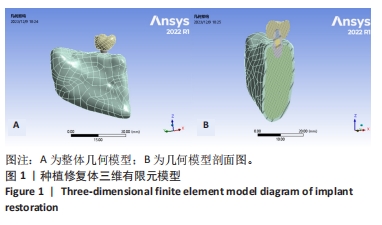
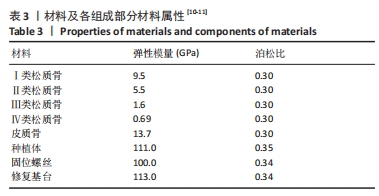
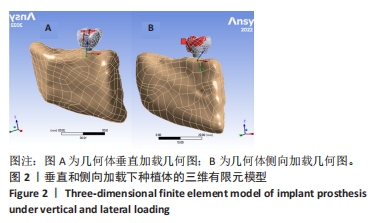
[1] YONGHUI C, ZHIYU C, DINGGUO Z, et al.Inlay osteotome sinus floor elevation with concentrated growth factor application and simultaneous short implant placement in severely atrophic maxilla.Sci Rep. 2016:6:27348.
[2] 叶芷君,徐普.超短种植体在萎缩后牙区的临床研究进展[J].成都医学院学报,2021,16(5):673-675.
[3] 吴越琳,刘加荣.三维有限元分析在口腔医学领域的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2021,41(7):659-663.
[4] 李征,王媛,田梦婷 ,等.桩核表面制备不同形式固位槽及使用不同黏结剂对固位力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(34): 5508-5513.
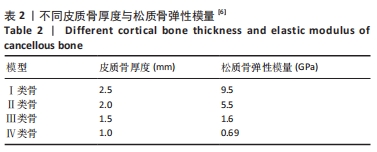
[5] 康非吾,卢军,潘可风.种植区骨皮质厚度对种植体骨界面应力分布的影响[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2006,27(1):31-33.
[6] LIU C, XING Y, LI Y, et al. Bone quality effect on short implants in the edentulous mandible: a finite element study. BMC Oral Health. 2022; 22(1):139.
[7] 孙江伟,王俊祥,白布加甫·叶力思,等.不同光滑颈圈种植体修复时应力分布的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(7): 1004-1011.
[8] 李希光,郅克谦,高岭,等.基于三维有限元评价种植体不同倾斜角度在上颌后牙区骨量不足的应力分析[J].口腔医学研究,2019, 35(7):671-675.
[9] 热依拉·库尔班,霞黑达·依拉尔江,陈欣,等.超短种植体不同修复方式的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30): 4824-4829.
[10] 施梦汝,谢伟丽,施武阁,等.柱形锥形种植体在不同种植深度的三维有限元研究[J].口腔医学,2019,39(7):577-580.
[11] 鲍中波.骨质条件和种植体外形对ISRPD种植体承载能力影响的有限元分析[D].大连:大连医科大学,2021.
[12] 李春.口腔种植与传统固定义齿修复牙列缺损的疗效对比[J].临床医学工程,2021,28(4):481-482.
[13] NEJAT N, ÖNDER G, EMIN MK. Extra-Short Implants with Osteotome Sinus Floor Elevation: A Prospective Clinical Study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(2):415-422.
[14] LOMBARDO G, MARINCOLA M, SIGNORIELLO A, et al.Single-Crown, Short and Ultra-Short Implants, in Association with Simultaneous Internal Sinus Lift in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla: A Three-Year Retrospective Study.Materials (Basel). 2020;13(9):2208.
[15] RAMEH S, MENHALL A, YOUNES R.Key factors influencing short implant success.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;24(3):263-275.
[16] JOJI M, SHRUTHI E, SURESH S, et al.Clinical outcomes of ultrashort sloping shoulder implant design: A survival analysis.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(4):646-652.
[17] LOMBARDO G, SIGNORIELLO A, PARDO A, et al. Short and ultra-short(<6-mm)locking-taper implants supporting single crowns in posterior areas (part II): A 5-year retrospective study on periodontally healthy patients and patients with a history of periodontitis.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2022;24(4):455-467.
[18] CASTELLANOS-COSANO L, RODRIGUEZ-PEREZ A, SPINATO S, et al. Descriptive retrospective study analyzing relevant factors related to dental implant failure. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2019;24(6): e726-e738.
[19] 白布加甫·叶力思,热娜古丽·买合木提,艾孜买提江·赛依提,等.上颌中切牙联冠种植修复体在不同咬合方式中的应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):567-572.
[20] NIROOMAND MR, ARABBEIKI M. Effect of the dimensions of implant body and thread on bone resorption and stability in trapezoidal threaded dental implants: a sensitivity analysis and optimization. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;23(13):1005-1013.
[21] SUMRA N, DESAI S, KULSHRESTHA R, et al. Analysis of micromovements and peri-implant stresses and strains around ultra-short implants-A three-dimensional finite-element method study.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2021;25(4):288-294.
[22] LANA CZ, MARTIN F, ANDREAS R, et al.Biomechanical finite element analysis of short-implant-supported, 3-unit, fixed CAD/CAM prostheses in the posterior mandible.Int J Implant Dent. 2022;8(1):8.
[23] 丁熙,朱形好,廖胜辉,等.种植牙即刻负载与延期负载的生物力学三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2007,27(10):519-522.
[24] 许月丹,金鑫阳,赵维家,等.种植义齿的咬合设计[J].口腔医学, 2020,40(12):1124-1128.
[25] LI T, KONG L, WANG Y, et al. Selection of optimal dental implant diameter and length in type IV bone: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;38(10):1077-1083.
[26] LINETSKIY I, DEMENKO V, LINETSKA L, et al.Impact of annual bone loss and different bone quality on dental implant success–A finite element study.Comput Biol Med. 2017;91:318-325.
[27] 王媛,张杨.不同下颌骨密度对4颗种植体支持Locator式覆盖义齿的有限元生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(22): 3492-3497.
[28] HUANG HL, HSU JT, FUH LJ, et al. Biomechanical simulation of various surface roughnesses and geometric designs on an immediately loaded dental implant. Comput Biol Med. 2010;40(5):525-532.
[29] BARÃO VA, DELBEN JA, LIMA J, et al. Comparison of different designs of implant-retained overdentures and fixed full-arch implant-supported prosthesis on stress distribution in edentulous mandible--a computed tomography-based three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2013;46(7):1312-1320.
[30] BASHUTSKI JD, D’SILVA NJ, WANG HL.Implant compression necrosis: current understanding and case report.J Periodontol. 2009;80(4):700-704.
[31] 陈俊良,刘旭琳,张潇月,等.短种植体修复牙槽骨严重吸收的下颌第二磨牙的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(3):246-250.
[32] YALÇıN M, KAYA B, LAÇIN N, et al. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of the Effect of Endosteal Implants with Different Macro Designs on Stress Distribution in Different Bone Qualities. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019;34(3):e43–e50.
[33] 施斌,吴涛.种植修复体机械并发症的原因、预防及处理[J].口腔疾病防治,2018,26(7):415-421.
[34] 施斌,晏奇,伍昕宇.短种植体(≤6mm)的临床应用与并发症[J].口腔疾病防治,2020,28(3):137-145. |