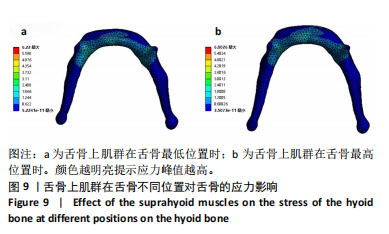
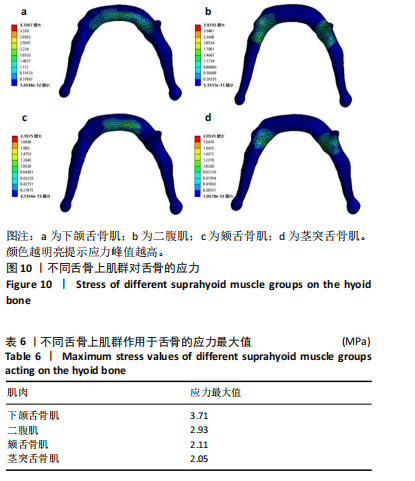
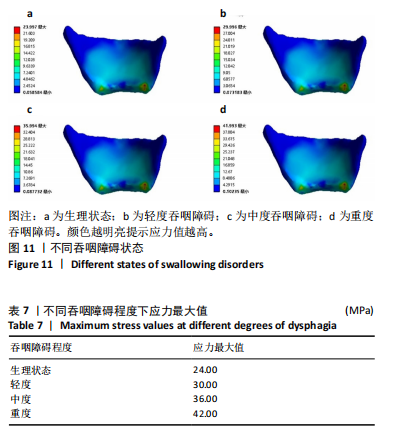
[1] 刘悦文, 郭琪, 于莹. 老年人口咽吞咽障碍的筛查工具及康复治疗方法的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(3):361-365.
[2] CHRISTMAS C, ROGUS-PULIA N. Swallowing Disorders in the Older Population. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(12):2643-2649.
[3] 刘雅鑫, 蒋运兰, 黄孝星, 等. 中国老年人吞咽障碍患病率的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(12):1496-1502,1512.
[4] 何君芳, 任亚子, 白佳佳, 等.吞咽障碍治疗相关研究计量学分析[J].西部中医药,2018,31(6):69-72.
[5] 袁盈, 蔡向红, 陈枫, 等.天突深刺治疗中风后吞咽障碍临床疗效观察[J]. 针刺研究,2019,44(1):47-50.
[6] 李眺, 陈卓铭, 金小千, 等.基于超声可视化测量舌骨-下颌骨运动评估针刺治疗脑梗死后吞咽障碍疗效的临床研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2023, 38(9):1247-1251.
[7] 刘潇, 张彬, 任力娟, 等.女性盆底功能障碍性疾病中肛提肌的有限元应力分析[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2017,11(9):1609-1612.
[8] 陈博韬. 足踝三维有限元模型建立与分歧韧带损伤的有限元研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2022.
[9] 曹子君, 王芳, 何耀广, 等.糖尿病患者足底压力和鞋垫减压结构的有限元分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2021,27(7):852-858.
[10] 詹民民. 基于粘弹理论的咀嚼吞咽过程生物力学研究[D].无锡:江南大学, 2018.
[11] 王兴林.吞咽障碍的生物力学变化及电刺激治疗机制[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2013,35(12):938-940.
[12] Huang Q, Zhang C, Bai H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of two modified intramedullary fixation system for treating unstable femoral neck fractures: A finite element analysis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1116976.
[13] Warren JL, Yoo JE, Meyer CA, et al. Automated finite element approach to generate anatomical patient-specific biomechanical models of atherosclerotic arteries from virtual histology-intravascular ultrasound. Front Med Technol. 2022;4:1008540.
[14] Kulczyk T, Rychlik M, Lorkiewicz-Muszyńska D, et al. Computed Tomography versus Optical Scanning: A Comparison of Different Methods of 3D Data Acquisition for Tooth Replication. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:4985121.
[15] 周宁, 杨帆, 时亚松, 等.基于ANSYS的真实软组织物理建模与穿刺仿真[J]. 河北大学学报(自然科学版),2015,35(2):188-192.
[16] 李鹏, 梁瑞, 申龙朵, 等. 应用Mimics和ANSYS软件建立下颌骨三维有限元模型的方法学研究 [J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2012,28(6):709-713.
[17] 赵雪岩, 黄任含, 楼航迪, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征的生物力学研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2009,45(5):737-742.
[18] TSOU L.The effects of muscle aging on hyoid motion during swallowing: a study using a 3D biomechanical model. University of British Columbia. 2012.
[19] 李宁, 李进让, 孙建军, 等. 健康成年人咽部吞咽功能客观参数的测量[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2012,47(11):884-883.
[20] 杨晓琼,向莹媛,廖梅红,等.分期针刺治疗脑卒中后吞咽障碍的临床观察[J].江西中医药,2024,55(6):54-57.
[21] 邵天祥, 金欣, 陈晓锋, 等.舌骨喉复合体运动与咽期吞咽障碍关系的研究进展[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2023,8(7):178-181.
[22] 刘春.不同舌骨上肌群加强训练方法在脑卒中吞咽障碍患者中的应用效果[J].中国医学创新,2024,21(30):82-86.
[23] ALVES MRM, OLIVEIRA NETO IC, ZICA GM, et al. Hyoid displacement patterns in healthy swallowing. Einstein (Sao Paulo). Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2022;20:eAO6268.
[24] 房芳芳,王孝文,郭振丽.基于VFSS检查结果观察脑卒中后咽期吞咽障碍患者吞咽咽期舌骨和喉向前、向上移动距离及速率变化[J].山东医药,2024, 64(21):57-59.
[25] 白林.针刺舌骨上肌群对脑卒中后口腔期吞咽障碍的临床疗效观察[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江中医药大学,2023.
[26] 常丽.超声引导下针刺环咽肌及舌骨上肌群对脑卒中后咽期吞咽障碍患者的临床研究[J].现代医学与健康研究电子杂志,2023,7(13):7-9.
[27] 贺凯,邢文华,李峰,等.有限元法在脊柱胸腰段骨折生物力学分析中的应用及发展方向[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(15):3244-3252.
[28] 卜寒梅,王旭,冯天笑,等.不同条件下旋提手法对颈椎关节突关节软骨应力的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2024,32(3):35-39+44.
[29] 周宗昊,罗思阳,陈佳文,等.生物可吸收板与微型钛板在不同骨质下颌骨骨折固定中的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(4):818-826.
[30] PELTERET JP, REDDY BD. Computational model of soft tissues in the human upper airway. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2012;28(1):111-132.
[31] 张岳,乔海,李幸芳,等.颌骨的逆向建模及咀嚼肌牵动的有限元分析[J].科技与创新,2020(22):1-3.
[32] HANNAM AG, STAVNESS I, LLOYD JE, et al. A dynamic model of jaw and hyoid biomechanics during chewing. J Biomech. 2008;41(5):1069-1076.
[33] 叶萍, 李兆申, 许国铭, 等.反流性食管炎患者食管动力学临床研究[J].第二军医大学学报,2001,22(3):204-206.
[34] 任攀.食管的各向异性本构模型研究及模拟分析[D].成都:西南交通大学, 2021.
[35] 李振亚,王光明,徐元顺.吞咽造影录像检查定量评价脑卒中患者吞咽功能改变[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2022,19(6):361-364.
[36] 唐安丽.脑卒中后吞咽障碍患者颏下肌群功能和舌骨运动的特征研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2022.
[37] 王丽琦,田力,邓苗苗.超声定量评估脑卒中后吞咽障碍患者颏舌骨肌[J].中国医学影像技术,2023,39(3):425-428.
[38] 谢亚青,毛忠南,张晓凌,等.基于Drp1、Opa1蛋白与线粒体联系探讨针刺二腹肌前腹治疗卒中后吞咽障碍的作用机制[J].中医药信息,2022,39(3):85-88.
[39] 陈春花,卓春和,梁沛君.颏下超声测量舌肌厚度变化舌骨位移幅度与口咽期吞咽障碍脑性瘫痪患儿吞咽功能病情程度及肌肉纤维化的相关性分析[J].中国妇幼保健,2020,35(22):4263-4266.
[40] 陈兆聪,曹君妍,喻勇,等.鼻咽癌放疗后吞咽困难患者肌肉纤维化与舌骨位移的相关性研究[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2017,39(12):903-907.
[41] 徐雷鸣. 二腹肌后腹影像解剖研究及其意义[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2005.
[42] 郝义勇, 徐浩铜, 向轲, 等. 利用可视人项目与CT研究左膈下腹膜外间隙空间关系[J]. 西南国防医药,2015,25(9):938-941. |