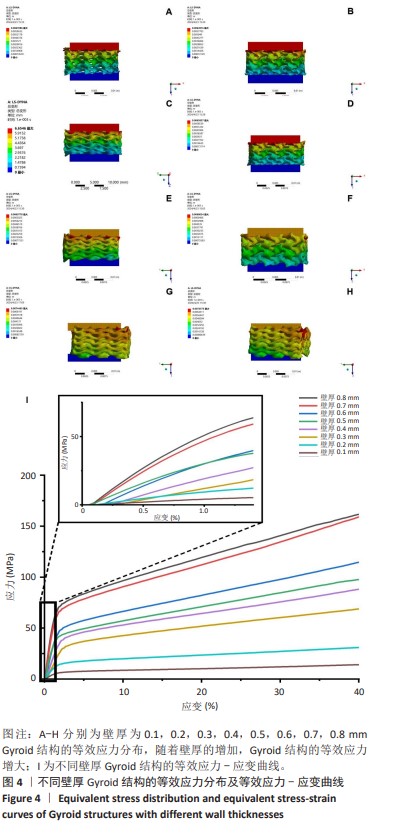
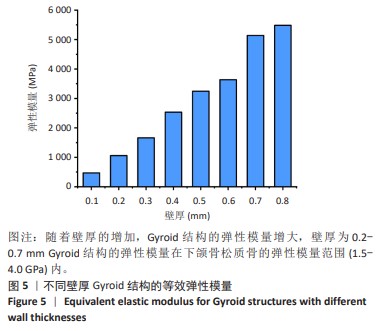
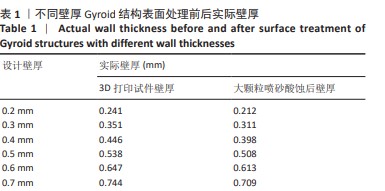
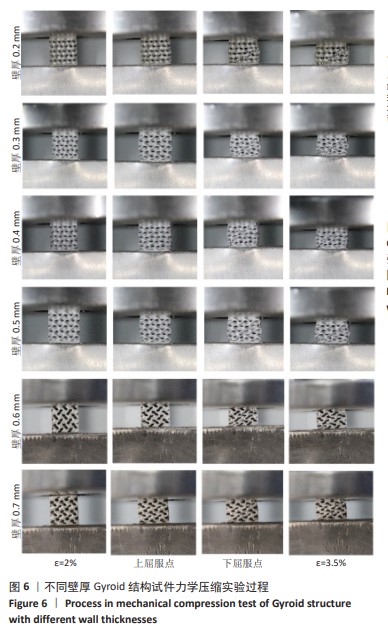
[1] ZHANG M, FUKUSHIMA Y, NOZAKI K, et al. Enhancement of bone regeneration by coadministration of angiogenic and osteogenic factors using messenger RNA Inflamm Regen. 2023;43(1):32.
[2] CHENG C, CHAABAN M, BORN G, et al. Repair of a Rat Mandibular Bone Defect by Hypertrophic Cartilage Grafts Engineered From Human Fractionated Adipose Tissue. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10: 841690.
[3] BEZ M, SHEYN D, TAWACKOLI W, et al. In situ bone tissue engineering via ultrasound-mediated gene delivery to endogenous progenitor cells in mini-pigs. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(390):eaal3128.
[4] KAPLAN J, LEE ZH, GROME L, et al. Sensory Outcomes for Inferior Alveolar Nerve Reconstruction with Allograft following Free Fibula Mandible Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023;152(3): 499e-506e.
[5] BASMA HS, SALEH MHA, GEURS NC, et al. The effect of bone particle size on the histomorphometric and clinical outcomes following lateral ridge augmentation procedures: A randomized double-blinded controlled trial. J Periodontol. 2023;94(2):163-173.
[6] ZHANG Y, WANG H, HUANGFU H, et al. 3D printing of bone scaffolds for treating infected mandible bone defects through adjustable dual-release of chlorhexidine and osteogenic peptide. Mater Design. 2022; 224:111288.
[7] POBLOTH AM, CHECA S, RAZI H, et al. Mechanobiologically optimized 3D titanium-mesh scaffolds enhance bone regeneration in critical segmental defects in sheep. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(423):eaam8828.
[8] BARUI S, PANDA AK, NASKAR S, et al. 3D inkjet printing of biomaterials with strength reliability and cytocompatibility: Quantitative process strategy for Ti-6Al-4V. Biomaterials. 2019;213:119212.
[9] SUMNER DR, TURNER TM, IGLORIA R, et al. Functional adaptation and ingrowth of bone vary as a function of hip implant stiffness. J Biomech. 1998;31(10):909-917.
[10] WONG KK, HSU HC, WU SC, et al. A Review: Design from Beta Titanium Alloys to Medium-Entropy Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2023;16(21):7046.
[11] CHEN SY, HUANG JC, PAN CT, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of open-cell porous Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by selective laser melting.J Alloys Compd. 2017;713:248-254.
[12] MEI S, WANG H, WANG W, et al. Antibacterial effects and biocompatibility of titanium surfaces with graded silver incorporation in titania nanotubes. Biomaterials. 2014;35(14):4255-4265.
[13] LI HF, ZHENG YF. Recent advances in bulk metallic glasses for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:1-20.
[14] SUN X, JIAO X, YANG X, et al. 3D bioprinting of osteon-mimetic scaffolds with hierarchical microchannels for vascularized bone tissue regeneration. Biofabrication. 2022;14(3).doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac6700
[15] BOUAKAZ I, DROUET C, GROSSIN D, et al. Hydroxyapatite 3D-printed scaffolds with Gyroid-Triply periodic minimal surface porous structure: Fabrication and an in vivo pilot study in sheep. Acta Biomater. 2023; 170:580-595.
[16] JINNAI H, WATASHIBA H, KAJIHARA T, et al. Surface curvatures of trabecular bone microarchitecture. Bone. 2002;30(1):191-194.
[17] WANG Y, CHEN S, LIANG H, et al. Design and fabrication of biomimicking radially graded scaffolds via digital light processing 3D printing for bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(41):9961-9974.
[18] LI N, XUE C, CHEN S, et al. 3D Printing of Flexible Mechanical Metamaterials: Synergistic Design of Process and Geometric Parameters. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(23):4523.
[19] NAZIR A, GOHAR A, LIN SC, et al. Flexural Properties of Periodic Lattice Structured Lightweight Cantilever Beams Fabricated Using Additive Manufacturing: Experimental and Finite Element Methods. 3D Print Addit Manuf. 2023;10(6):1381-1393.
[20] FAN X, TANG Q, FENG Q, et al. Design, mechanical properties and energy absorption capability of graded-thickness triply periodic minimal surface structures fabricated by selective laser melting. Int J Mech Sci. 2021;204:106586.
[21] LI L, SHI J, ZHANG K, et al. Early osteointegration evaluation of porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds designed based on triply periodic minimal surface models. J Orthop Transl. 2019;19:94-105.
[22] ZHANG L, LEE W, LI X, et al. 3D direct printing of mechanical and biocompatible hydrogel meta-structures. Bioact Mater. 2022;10: 48-55.
[23] MASKERY I, ABOULKHAIR NT, AREMU AO, et al. Compressive failure modes and energy absorption in additively manufactured double gyroid lattices. Add Manufact. 2017;16:24-29.
[24] 张亮,韩泽奎,臧旖欣,等.仿生蛛网孔隙结构3D打印个性化钛网设计及三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30): 4796-4801.
[25] 肖映雄,张平,舒适,等.一种计算复合材料等效弹性性能的有限元方法[J].固体力学学报,2006(1):77-82.
[26] HUISKES R, RUIMERMAN R, VAN LENTHE GH, et al. Effects of mechanical forces on maintenance and adaptation of form in trabecular bone. Nature. 2000;405(6787):704-706.
[27] IVAÑEZ I, FERNANDEZ-CAÑADAS LM, SANCHEZ-SAEZ S. Compressive deformation and energy-absorption capability of aluminium honeycomb core. Compos Struct. 2017;174:123-133.
[28] MASKERY I, ABOULKHAIR NT, AREMU AO, et al. A mechanical property evaluation of graded density Al-Si10-Mg lattice structures manufactured by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A. 2016;670: 264-274.
[29] QIU C, YUE S, ADKINS NJE, et al. Influence of processing conditions on strut structure and compressive properties of cellular lattice structures fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A. 2015;628: 188-197.
[30] NOVAES AB JR, DE SOUZA SLS, DE BARROS RRM, et al. Influence of implant surfaces on osseointegration. Braz Dent J. 2010;21(6):471-481.
[31] LI Y, YANG C, ZHAO H, et al. New Developments of Ti-Based Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Materials (Basel). 2014;7(3):1709-1800.
[32] 陈新民,王劲茗,赵云凤,等.人体下颌骨强度研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2002,3(2):113-115.
[33] NIE R, SUN Y, LV H, et al. 3D printing of MXene composite hydrogel scaffolds for photothermal antibacterial activity and bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Nanoscale. 2022;14(22): 8112-8129.
[34] ZHANG B, YIN X, ZHANG F, et al. Customized bioceramic scaffolds and metal meshes for challenging large-size mandibular bone defect regeneration and repair. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad057.
[35] PARK SJ, RAHMAN MM, LEE J, et al. Investigation of Bone Regeneration Efficacy of New Bovine Bone Minerals in a Canine Mandibular Critical Defect Model. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(22):e2202942.
[36] GUO Y, WU J, XIE K, et al. Study of Bone Regeneration and Osteointegration Effect of a Novel Selective Laser-Melted Titanium-Tantalum-Niobium-Zirconium Alloy Scaffold. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(12):6463-6473.
[37] BOSE S, ROY M, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10):546-554.
[38] REZWAN K, CHEN QZ, BLAKER JJ, et al. Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27(18):3413-3431.
[39] CASTRO APG, RUBEN RB, GONÇALVES SB, et al. Numerical and experimental evaluation of TPMS Gyroid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(6): 567-573.
[40] DALLAGO M, FONTANARI V, TORRESANI E, et al. Fatigue and biological properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI cellular structures with variously arranged cubic cells made by selective laser melting. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;78:381-394.
[41] LIANG B, SADEGHIAN DEHKORD E, VAN HEDE D, et al. Model-Based Design to Enhance Neotissue Formation in Additively Manufactured Calcium-Phosphate-Based Scaffolds. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(12):563.
[42] LU Y, CUI Z, CHENG L, et al. Quantifying the discrepancies in the geometric and mechanical properties of the theoretically designed and additively manufactured scaffolds. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;112:104080.
[43] 柏龙,熊飞,陈晓红,等. SLM制备的Ti6Al4V轻质点阵结构多目标结构优化设计研究[J].机械工程学报,2018,54(5):156-165.
[44] PENG X, HUANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Elastic response of anisotropic Gyroid cellular structures under compression: Parametric analysis. Mater Design. 2021;205:109706. |