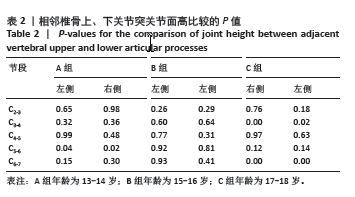
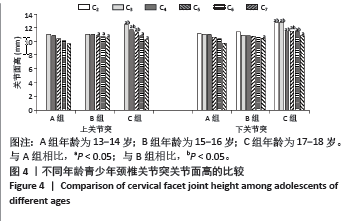
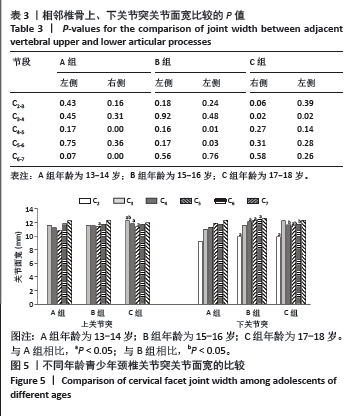
[1] DAVID D, GIANNINI C, CHIARELLI F, et al. Text Neck Syndrome in Children and Adolescents. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4): 1565-1579.
[2] ZIREK E, MUSTAFAOGLU R, YASACI Z, et al. A systematic review of musculoskeletal complaints, symptoms, and pathologies related to mobile phone usage. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;10(49):102-112.
[3] YONGJUN Z, TINGJIE Z, XIAOQIU Y, et al. A survey of chronic pain in China. Libyan J Med. 2020;15(1):1-5.
[4] 武宇轩,郑殿芳,云文科,等.“解痉”针法干预颈椎小关节紊乱症100例[J].武警医学,2022,33(11):990-992.
[5] 王宝剑,李俊海,黄沪,等.北京市某三甲医院2018-2020年颈椎病门诊患者临床流行病学特征分析[J].中国病案,2022,23(12):40-43.
[6] O’LEARY SA, PASCHOS NK, LINK JM, et al. Facet Joints of the Spine: Structure-Function Relationships, Problems and Treatments, and the Potential for Regeneration. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2018;4(20):145-170.
[7] SHANG Q, WANG D, WANG D, et al. Facet joint degeneration-An initial procedure of the cervical spine degeneration. JOR Spine. 2023;6(1): e1241-1251.
[8] TAKESHIMA Y, OKAMOTO A, YOKOYAMA S, et al. Facet Articular Irregularity Is the Most Relevant Risk Factor for Rapidly Progressive Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy. Neurospine. 2023;20(1):365-373.
[9] BÜSKEN F, LATASTER A, HERRLER A. The innervation of the cervical facet joints-an anatomical and histological approach. Clin Anat. 2022;35(6):780-788.
[10] 李志军,丁韶龙,周强.关节突关节横截面积与退行性颈椎滑脱的关系[J].颈腰痛杂志,2022,43(6):794-797.
[11] 徐聪,徐庆平,艾雯,等.颈椎关节突关节矢状位角的不对称性和关节突关节退变关系的影像学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2021, 39(5):535-545.
[12] 和雨洁,张少杰,李志军,等.4-6岁儿童下颈椎关节突关节的三位数字化形态特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4558-4563.
[13] 刘路.7-12岁儿童颈椎关节突关节数字化三维形态研究及其有限元分析[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古医科大学,2016.
[14] DENIS F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries.Spine. 1983;8(8):817-831.
[15] ELFIKY T, BESSADA B, STIENEN MN, et al. Endplate and Facet Joint Changes in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. World Neurosurg. 2023;7:361-366.
[16] BISSON DG, SHENG K, KOCABAS S, et al. Axial rotation and pain are associated with facet joint osteoarthritis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023;31(8):1101-1110.
[17] 田杰,刘慧.颈椎小关节源性疼痛治疗进展及超声应用价值[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2019,25(8):618-623.
[18] 徐庆平.颈椎小关节矢状化与颈椎小关节退变和椎间盘退变的相关性研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2019.
[19] 楚加胜.关节突关节角与退变性下颈椎不稳的相关性分析[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2020.
[20] 文传兵,刘柳,林涛,等.超声横截面扫描探测颈椎关节突关节的可行性及准确性研究[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2021,27(11):825-828.
[21] 张俊麒,王型金,刘浩,等.颈椎关节突关节倾斜角及其不对称的临床意义[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(7):481-485.
[22] 王琪,郭明明,徐森,等.应用影像归档和通信系统测量成人下颈椎关节突关节的临床意义[J].脊柱外科杂志,2017,15(3):171-176.
[23] PAL GP, ROUTAL RV, SAGGU SK, et al. The orientation of the articular facets of the zygapophyseal joints at the cervical and upper thoracic region. J Anat. 2001;4(4):431-441.
[24] 孟庆兰.颈椎间关节面的形态和面积与颈椎病的关系[J].中国康复理论与实践,2002,8(3):134-135.
[25] 卢海波.成人下颈椎关节突关节螺旋CT测量及临床意义[D].汕头:汕头大学,2010.
[26] 刘观燚,徐荣明,马维虎,等.下颈椎关节突关节的解剖学测量与经关节螺钉固定的关系[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(2):140-144.
[27] 赵卫东,徐波,张美超,等.颈椎三维运动对关节突关节压力的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(22):3996-3999.
[28] 赵刘军,徐荣明.中下颈椎经关节螺钉的基础与临床研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2007,20(6):430-432.
[29] 颜滨,李振宇,闫洪印,等.经关节螺钉固定在下颈椎骨折脱位中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(6):447-449.
[30] 周雷杰,陆继业,梁彪,等.下颈椎经关节螺钉钉棒系统形式固定的临床研究[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(7):538-540.
[31] JAUMARD NV, WELCH WC, WINKELSTEIN BA. Spinal facet joint biomechanics and mechanotransduction in normal, injury and degenerative conditions. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(7):1-31.
[32] KULKARNI AG, SAGANE SS. Cervical facet joint effusion: A sign of instability in cervical degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2022;13(1):38-41.
[33] PARK MS, LEE YB, MOON SH, et al. Facet joint degeneration of the cervical spine: a computed tomographic analysis of 320 patients. Spine. 2014;39(12):E713-E718.
[34] WANG QA, GUO C, SUN MJ, et al. Three-dimensional spiral CT observation of the facet joints of the lower cervical spine and its clinical significance. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(6):1536-1541. |