[1] 周唯敏,万兵.硫酸氢氯吡格雷对老年急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死急诊介入术后患者心功能、血管内皮功能和血脂的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(12):2474-2477.
[2] ANDERSON JL, MORROW DA. Acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(21):2053-2064.
[3] 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告》2021(冠心病部分内容)[J].心肺血管病杂志,2023,42(12):1191-1198.
[4] 吴纲,李雪冬,曹超,等.新活素前置应用对急性心肌梗死急诊PCI病人预后影响的临床研究[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2023,48(9):1211-1214.
[5] PREM PN, SIVAKUMAR B, BOOVARAHAN SR, et al. Recent advances in potential of Fisetin in the management of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury-A systematic review. Phytomedicine. 2022;101: 154123.
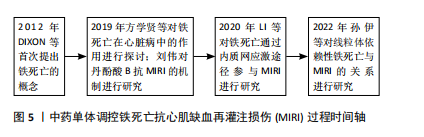
[6] 曹蛟,张杼惠,刘建和.从中医“阳气亏虚,痰瘀内阻”理论探讨中医药防治心肌缺血再灌注损伤的机制[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2021,23(2):510-515.
[7] QIU Y, CAO Y, CAO W, et al. The Application of Ferroptosis in Diseases. Pharmacol Res. 2020;159:104919.
[8] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[9] SU LJ, ZHANG JH, GOMEZ H, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5080843.
[10] 王梅芳,李德冠.铁死亡及其在心脑血管疾病中的研究进展[J].生命科学,2019,31(9):886-893.
[11] SHA W, HU F, XI Y, et al. Mechanism of Ferroptosis and Its Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021:9999612.
[12] LIANG D, FENG Y, ZANDKARIMI F, et al. Ferroptosis surveillance independent of GPX4 and differentially regulated by sex hormones. Cell.2023;186(13):2748-2764.e22.
[13] LIANG C, ZHANG X, YANG M, et al. Recent Progress in Ferroptosis Inducers for Cancer Therapy. Adv Mater. 2019;31(51):e1904197.
[14] URSINI F, MAIORINO M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:175-185.
[15] 张一楠,任彩佩,吴亚俐,等.白藜芦醇通过调节铁死亡通路抑制小鼠溃疡性结肠炎相关性结肠癌实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志, 2023,52(6):671-675+682.
[16] 李浩然,曹策,李磊,等.心肌细胞铁死亡的机制及中药的保护作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(4):260-270.
[17] MARZILLI M, CREA F, MORRONE D, et al. Myocardial ischemia: From disease to syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2020;314:32-35.
[18] MARTINS-MARQUES T, RODRIGUEZ-SINOVAS A, GIRAO H. Cellular crosstalk in cardioprotection: Where and when do reactive oxygen species play a role? Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;169:397-409.
[19] 翟天宇,张灿,赵琳.内质网应激的调节方式及其在脊髓损伤中的靶向作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2023,39(11):1534-1542.
[20] YAO RQ, XIA ZF, YAO YM, et al. Organelle-specific autophagy in inflammatory diseases: a potential therapeutic target underlying the quality control of multiple organelles. Autophagy. 2021;17(2):385-401.
[21] LEI G, KOPPULA P, LIU X, et al. The role of ferroptosis in ionizing radiation-induced cell death and tumor suppression. Cell Res. 2020; 30(2):146-162.
[22] CHU B, CHEN D, LI T, et al. ALOX12 is required for p53-mediated tumour suppression through a distinct ferroptosis pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(5):579-591.
[23] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282.
[24] FUJII J, HOMMA T, KOBAYASHI S. Ferroptosis caused by cysteine insufficiency and oxidative insult. Free Radic Res. 2020;54(11-12): 969-980.
[25] LI J, LU K, SUN F, et al. Panaxydol attenuates ferroptosis against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):96.
[26] WU CT, DENG JS, HUANG WC, et al. Salvianolic Acid C against Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Attenuating Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis through Inhibition of the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:9056845.
[27] MURPHY MP, CHOUCHANI ET. Why succinate? Physiological regulation by a mitochondrial coenzyme Q sentinel. Nat Chem Biol. 2022;18(5): 461-469.
[28] HARGREAVES I, HEATON RA, MANTLE D. Disorders of Human Coenzyme Q10 Metabolism: An Overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6695.
[29] KAWAHARA K, INAZUMI T, SUGIMOTO Y, et al. Prostaglandin E2-induced inflammation: Relevance of prostaglandin E receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1851(4):414-421.
[30] 亓燕,方芸,王峰,等.COX-2/PGE2在肿瘤发生发展中的研究进展[J].药学与临床研究,2023,31(4):342-346.
[31] CHEN B, CHEN Z, LIU M, et al. Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis in the acute phase of intracerebral hemorrhage shows long-term cerebroprotective effects. Brain Res Bull. 2019;153:122-132.
[32] LI Y, WANG J, CHEN S, et al. miR-137 boosts the neuroprotective effect of endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes in oxyhemoglobin-treated SH-SY5Y cells partially via COX2/PGE2 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):330.
[33] 黄海燕,翁嘉灏,陆萍,等.参附汤抑制铁死亡缓解化疗药物心脏毒性研究[J].世界中医药,2024,5(19):1-11.
[34] 王锋,秦文秀,王琪,等.AMPK调控铁死亡相关信号通路的研究现状[J].中国药理学通报,2023,39(10):1801-1805.
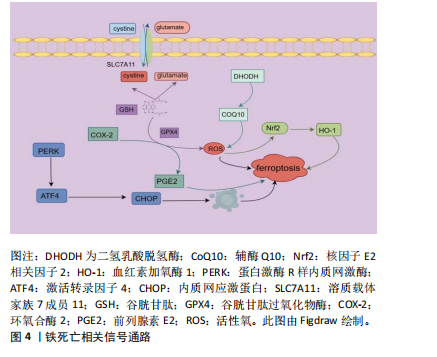
[35] 洪莉莉,吴玲娟,何海刚.青蒿琥酯调节PERK/ATF4/CHOP信号通路对OGD/R诱导的心肌细胞铁死亡的影响[J].微循环学杂志, 2023,33(1):24-32.
[36] BABA Y, HIGA JK, SHIMADA BK, et al. Protective effects of the mechanistic target of rapamycin against excess iron and ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;314(3): H659-H668.
[37] ZHAO WK, ZHOU Y, XU TT, et al. Ferroptosis: Opportunities and Challenges in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:9929687.
[38] SHENG H, XIONG J, YANG D. Protective Effect of Sevoflurane Preconditioning on Cardiomyocytes Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury by Modulating Iron Homeostasis and Ferroptosis. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2023;23(2):86-92.
[39] YAN HF, ZOU T, TUO QZ, et al. Ferroptosis: mechanisms and links with diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):49.
[40] BILLINGHAM LK, STOOLMAN JS, VASAN K, et al. Mitochondrial electron transport chain is necessary for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. 2022;23(5):692-704.
[41] 李云曌,吴辉,刘滴.内质网应激与心肌缺血再灌注损伤的研究进展[J].生命的化学,2020,40(6):919-924.
[42] ZHANG XJ, CHENG X, YAN ZZ, et al. An ALOX12-12-HETE-GPR31 signaling axis is a key mediator of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nat Med. 2018;24(1):73-83.
[43] LIN Y, CHEN F, ZHANG J, et al.Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol on ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through TRPC6/CREB pathways. J Mol Neurosci. 2013;50(3):504-513.
[44] FAN Z, CAI L, WANG S, et al. Baicalin Prevents Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibiting ACSL4 Mediated Ferroptosis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:628988.
[45] 李兰,杨一秋,解继胜,等.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的葛根素对骨质疏松症作用的研究进展[J].解剖科学进展,2024,6(7):1-6.
[46] DING Y, LI W, PENG S, et al. Puerarin Protects against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Biol Pharm Bull. 2023;46(4):524-532.
[47] 于欢,马晓昀.黄芩苷和黄芩素干预眼部疾病的基础研究进展[J].中国中医眼科杂志,2024,34(6):581-584+596.
[48] FAN Z, CAI L, WANG S, et al. Baicalin Prevents Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibiting ACSL4 Mediated Ferroptosis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:628988.
[49] 刘海平,康敏,申娜.丹参素介导Wnt-β-catenin通路增强丙泊酚对小鼠缺血再灌注肾组织损伤的保护作用机制[J].特产研究,2024, 46(2):93-98.
[50] ZHANG Y, ZHANG G, LIANG Y, et al. Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Hepatic-Protective Effects of Danshensu on Iron Overload Mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020;43(6):968-975.
[51] 盛亚男,王长远.牡荆素预防和治疗疾病作用机制研究进展[J].中国现代应用药学,2021,38(17):2156-2161.
[52] XUE W, TANG H, ZHU H, et al. Vitexin attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by regulating mitochondrial dysfunction induced by mitochondrial dynamics imbalance. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;124:109849.
[53] INCHINGOLO AD, INCHINGOLO AM, MALCANGI G, et al. Effects of Resveratrol, Curcumin and Quercetin Supplementation on Bone Metabolism-A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2022;14(17):3519.
[54] LI T, TAN Y, OUYANG S, et al. Resveratrol protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via attenuating ferroptosis. Gene. 2022; 808:145968.
[55] 汪丽娜,任若瑜,何富乐.白皮杉醇对卵巢癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭的影响及其诱导凋亡作用的实验研究[J].中国中医药科技, 2023,30(5):866-870.
[56] 赵天昊.白皮杉醇通过Nrf-2信号介导铁代谢抑制铁死亡保护心肌缺血/再灌注损伤[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2024.
[57] 白心语,王显鹤.槲皮素治疗新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病中的研究进展[J].广东工业大学学报,2024,51(12):88-90.
[58] 宣学习,张宇,张华,等.槲皮素对心肌缺血再灌注大鼠氧化应激反应及心电图的影响[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2022, 20(5):848-853.
[59] 张维书,李强,王洪权.中药川芎嗪在阿尔茨海默病中的神经保护作用机制研究进展[J/OL].中药药理与临床,1-10[2024-10-12].https://doi.org/10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20240412.010.
[60] QIAN W, XIONG X, FANG Z, et al. Protective effect of tetramethylpyrazine on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2014:107501.
[61] 韩明磊,刘振,侯永兰,等.石蒜碱对缺氧条件下心肌细胞损伤和心肌成纤维细胞活化与胶原合成的影响及其生物学机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2024,44(5):1165-1172.
[62] 陈文明,陈嘉敏,蹇明辉.石蒜碱上调Notch1信号通路并减轻心肌细胞缺氧/复氧诱导的损伤[J].心脏杂志,2023,35(6):637-642.
[63] ZHANG J, WU C, GAO L, et al. Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: A research review on the pharmacological effects.Adv Pharmacol. 2020;87:89-112.
[64] Jiang M, Ni J, Cao Y, et al. Astragaloside IV Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury from Oxidative Stress by Regulating Succinate, Lysophospholipid Metabolism, and ROS Scavenging System. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:9137654.
[65] 刘艳,尧俊涵,梅瑀,等.红景天化学成分研究[J].中草药,2024, 55(9):2875-2886.
[66] 王明燕,宣清清,许玲.红景天苷介导p38 MAPK信号通路抑制脂多糖诱导的心肌细胞焦亡及氧化损伤[J].广东医学,2023,44(10):1216-1222.
[67] 冯科冉,李伟霞,王晓艳,等.丹参化学成分、药理作用及其质量标志物(Q-Marker)的预测分析[J].中草药,2022,53(2):609-618.
[68] JIANG L, ZENG H, NI L, et al. HIF-1α Preconditioning Potentiates Antioxidant Activity in Ischemic Injury: The Role of Sequential Administration of Dihydrotanshinone I and Protocatechuic Aldehyde in Cardioprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019;31(3):227-242.
[69] 杨妞妞,邵海峰,邓嘉林,等.白鲜皮主要药效成分白鲜碱、黄柏酮、梣酮的抗皮炎作用比较及机制研究[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2023,43(12):1636-1642+1649.
[70] 范志能,周厚清.黄柏酮通过调控铁死亡途径对心肌缺血/再灌注大鼠心肌损伤的保护作用研究[J].中国医院药学杂志,2023,43(17): 1932-1938.
[71] 张小妮,陈由强,陈建楠.芦荟苷及其水解产物芦荟大黄素的研究进展[J].生物技术通讯, 2020,31(2):227-231.
[72] 王哲.芦荟苷在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中的保护作用及机制研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2023.
[73] 尚玉杰,张强,韩彦斌,等.天麻化学成分、药理作用及其产品开发分析[J].中医药学报,2024,52(8):115-121.
[74] CHEN Q, ZHOU B, XIONG X. Neutral polysaccharide from Gastrodia elata alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis-mediated neuroinflammation via the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024;30(3):e14456.
[75] 杜国丰,陈红漫,刘凤翊,等.海藻多糖的提取、生物活性及其应用研究进展[J].食品科技,2023,48(2):188-195.
[76] 张联标,杨荧,王东升.海藻多糖调节Nrf2通路对过氧化氢诱导的心肌细胞损伤及铁死亡的抑制作用[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2023,15(6):712-715+720.
|