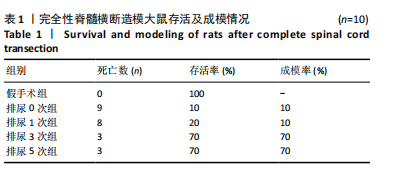
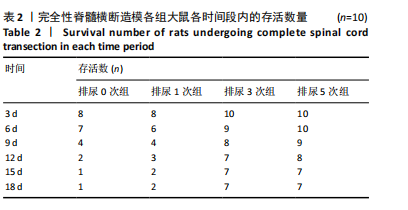
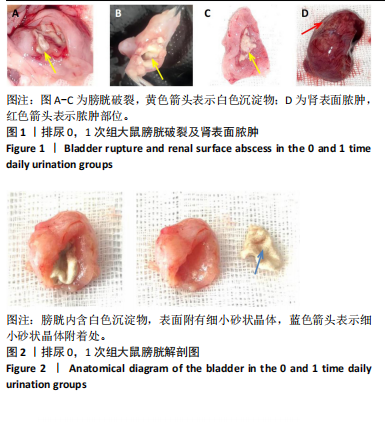
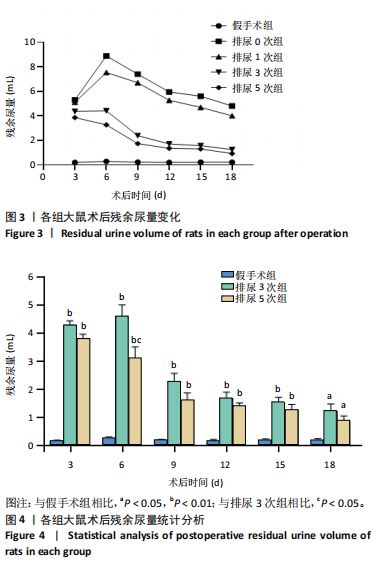
[1] 蔡文智,孟玲,李秀云.神经源性膀胱护理实践指南(2017年版)[J].护理学杂志,2017,32(24):1-7.
[2] CHEN PC, LEE KH, LEE WC, et al. Treating Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Chronic Spinal Cord Injury Patients-When Intravesical Botox Injection or Urethral Botox Injection Are Indicated. Toxins (Basel). 2023;15(4):288.
[3] LEILAZ A, JOUSSAIN C, DENYS P, et al. Concomitant Botulinum Toxin Injections for Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity and Spasticity-A Retrospective Analysis of Practice and Safety. Toxins (Basel). 2024; 16(6):252.
[4] LOGHMARI A, MTIRAOUI A, AHMED KB, et al. Assessment of sexual function and quality of life of patients with spinal cord injury. Eur Psychiat. 2023; 66(S1): S1095.
[5] DOELMAN AW, STREIJGER F, MAJERUS SJA, et al. Assessing Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction after Spinal Cord Injury: Animal Models in Preclinical Neuro-Urology Research. Biomedicines. 2023;11(6):1539.
[6] 杜凯然,邓强,郭铁峰,等.改良椎板切除法构建脊髓损伤模型大鼠[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(32):5173-5177.
[7] 何星艳,罗维,蒋理,等.针刺治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱动物实验研究进展[J].世界中医药,2023,18(11):1635-1639+1644.
[8] FERREIRA A, NASCIMENTO D, CRUZ CD. Molecular Mechanism Operating in Animal Models of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity: A Systematic Review Focusing on Bladder Dysfunction of Neurogenic Origin. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4):3273.
[9] KURIS EO, ALSOOF D, OSORIO C, et al. Bowel and Bladder Care in Patients With Spinal Cord Injury. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022;30(6): 263-272.
[10] AKKOÇ Y, ERSÖZ M, ÇINAR E, et al. Evaluation and management of neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury: Current practice among physical medicine and rehabilitation specialists in Turkey. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;67(2):225-232.
[11] ROMO PGB, SMITH CP, COX A, et al. Non-surgical urologic management of neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury. World J Urol. 2018; 36(10):1555-1568.
[12] 罗静,邓石峰,余雨荷,等.完全性骶髓损伤后大鼠神经源性膀胱模型的制备与观察[J].中国康复,2022,37(7):387-391.
[13] SHAKER H, MOURAD MS, ELBIALY MH, et al. Urinary bladder hyperreflexia: a rat animal model. Neurourol Urodyn. 2003;22(7):693-698.
[14] 展立芬,曾学究,梁柔筠,等.电针通过TGF-β1/Smad2信号通路调控神经源性膀胱大鼠膀胱纤维化趋势的研究[J].中华中医药杂志, 2024,39(5):2423-2429.
[15] INSKIP JA, RAMER LM, RAMER MS, et al. Autonomic assessment of animals with spinal cord injury: tools, techniques and translation. Spinal Cord. 2009;47(1):2-35.
[16] 张莉莉,全玮琳.Crede手法及清洁间歇导尿对宫颈癌术后尿潴留患者自主排尿功能恢复的影响[J].中国肿瘤临床与康复,2021, 28(6):737-740.
[17] 周贤锋,施静,骆乐.独立通气笼饲养大鼠的进食量及饮水量生理值测定[J].实用医院临床杂志,2015,12(5):72-74.
[18] BASSO DM, BEATTIE MS, BRESNAHAN JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1):1-21.
[19] MA L, MU Y, LI X, et al. Expression of transforming growth factor-β1 and autophagy markers in the bladder of rats with neurogenic lower urinary tract injury. Spinal Cord. 2023;61(2):154-159.
[20] 廖宇翔,刘璐,付渊博,等.隔姜隔盐灸“神阙”法对逼尿肌过度活动大鼠膀胱ATP敏感性钾离子通道的影响[J].针刺研究,2024, 49(8):814-820.
[21] FITZPATRICK MA, NWAFO N. Urinary Tract Infection Diagnostic and Management Considerations in People with Spinal Cord Injury and Neurogenic Bladder. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2024;38(2):381-393.
[22] KOZOMARA M, BIRKHÄUSER V, ANDERSON CE, et al. Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in the First Year After Spinal Cord Injury: A Descriptive Study of Urodynamic Findings. J Urol. 2023;209(1):225-232.
[23] YEH SD, KHASANAH N, GUSTAFSON KJ, et al. Beneficial carry-over effects of chronic at-home genital nerve stimulation on incontinence in individuals with spinal cord injury: A pragmatic trial. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2024;67(2):101799.
[24] DIOKNO AC. A 50-Year Review of Lapides’ Clean Intermittent Catheterization: A Revolutionary, Life-Saving, Quality-of-Life Improving Technique For Bladder Management. Urologic Nursing. 2019; 39(5): 229.
[25] IKEFUAMA EC, KENDZIORSKI GE, ANDERSON K, et al. Improved Locomotor Recovery in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury by BioLuminescent-OptoGenetic (BL-OG) Stimulation with an Enhanced Luminopsin. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):12994.
[26] ZHU Y, CHENG J, YIN J, et al. Effects of sacral nerve electrical stimulation on 5‑HT and 5‑HT3AR/5‑HT4R levels in the colon and sacral cord of acute spinal cord injury rat models. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(2):763-773.
[27] 展立芬,卓越,艾坤,等.超声观察神经源性膀胱大鼠膀胱形态学变化及其与尿流动力学的相关性研究[J].临床超声医学杂志, 2024,26(1): 9-14.
[28] YOSHIMURA N, OGAWA T, MIYAZATO M, et al. Neural mechanisms underlying lower urinary tract dysfunction. Korean J Urol. 2014; 55(2):81-90.
[29] PANICKER JN, FOWLER CJ, KESSLER TM. Lower urinary tract dysfunction in the neurological patient: clinical assessment and management. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(7):720-732.
[30] KINNEAR N, BARNETT D, O’CALLAGHAN M, et al. The impact of catheter-based bladder drainage method on urinary tract infection risk in spinal cord injury and neurogenic bladder: A systematic review. Neurourol Urodyn. 2020;39(2):854-862.
[31] 许明,张泓,刘继生,等.完全性骶上脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱大鼠模型的建立及尿流动力学分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2016, 22(8):869-875.
[32] 焦子远,卓越,梁柔筠,等.电针改善脊髓损伤大鼠逼尿肌的形态结构和膀胱功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(28):4484-4490.
[33] GE Q, XU H, FAN Z, et al. Efficacy of peripheral electrical nerve stimulation on improvements of urodynamics and voiding diary in patients with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2023;109(5):1342-1349. |