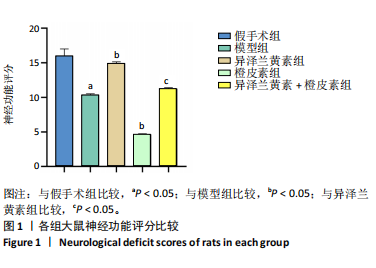
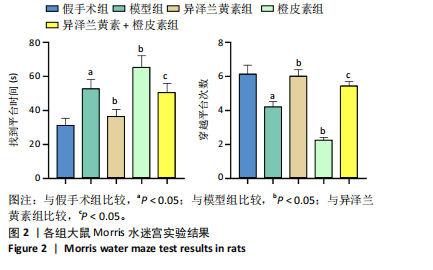
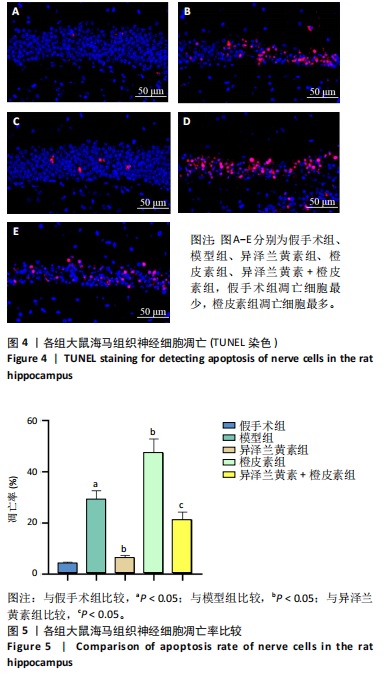
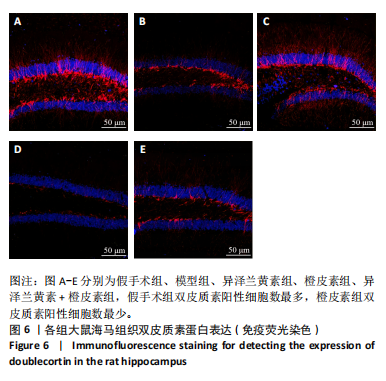
[1] SCHATLO B, FUNG C, STIENEN MN, et al. Incidence and outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the swiss study on subarachnoid hemorrhage (Swiss SOS). Stroke. 2021;52(1):344-347.
[2] LAUZIER DC, JAYARAMAN K, YUAN JY, et al. Early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage: incidence and mechanisms. Stroke. 2023; 54(5):1426-1440.
[3] DENG X, LIANG C, QIAN L, et al. miR-24 targets HMOX1 to regulate inflammation and neurofunction in rats with cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(3):1064-1074.
[4] JUNG H, YOUN DH, PARK JJ, et al. Bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate behavioral and cognitive dysfunction after subarachnoid hemorrhage via HMGB1-RAGE axis mediation. Life (Basel). 2023;13(4):881.
[5] BAI D, SUN T, LU F, et al. Eupatilin suppresses OVA-induced asthma by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK and activating Nrf2 signaling pathways in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1582.
[6] KIM K, HONG HL, KIM GM, et al. Eupatilin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in mice. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023;45(9):7027-7042.
[7] ZHOU Y, ZHANG X, GUO Y, et al. Eupatilin mitigates Gestational diabetes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic pregnant rats through the Regulation of inflammation and oxidative stress. Heliyon. 2024;10(10):e30911.
[8] ROSA A, PIRAS F, POLLASTRO F, et al. Comparative evaluation of anticancer activity of natural methoxylated flavones xanthomicrol and eupatilin in A375 skin melanoma cells. Life (Basel). 2024;14(3):304.
[9] 申友奎,王雁秋,刘飞飞,等.异泽兰黄素对脑出血小鼠的神经保护作用及氧化应激和神经元凋亡的影响[J].中国中医药科技, 2024,31(2):226-230,268.
[10] QIAO HB, LI J, LV LJ, et al. Eupatilin inhibits microglia activation and attenuates brain injury in intracerebral hemorrhage. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(5):4005-4009.
[11] HONG Y, HE S, ZOU Q, et al. Eupatilin alleviates inflammatory response after subarachnoid hemorrhage by inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB axis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023;37(5):e23317.
[12] SUN P, MA F, XU Y, et al. Genetic deletion of endothelial microRNA-15a/16-1 promotes cerebral angiogenesis and neurological recovery in ischemic stroke through Src signaling pathway. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021;41(10):2725-2742.
[13] AMINI H, KNEPP B, RODRIGUEZ F, et al. Early peripheral blood gene expression associated with good and poor 90-day ischemic stroke outcomes. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):13.
[14] LIU M, ZHONG W, LI C, et al. Fluoxetine attenuates apoptosis in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage through Notch1/ASK1/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):8396-8411.
[15] WANG X, ZHANG A, YU Q, et al. Single-cell rna sequencing and spatial transcriptomics reveal pathogenesis of meningeal lymphatic dysfunction after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(21):e2301428.
[16] LIU Z, WANG B, GUO Q. MiR-26b-5p-modified hUB-MSCs derived exosomes attenuate early brain injury during subarachnoid hemorrhage via MAT2A-mediated the p38 MAPK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull. 2021;175:107-115.
[17] DUAN H, LI L, SHEN S, et al. Hydrogen sulfide reduces cognitive impairment in rats after subarachnoid hemorrhage by ameliorating neuroinflammation mediated by the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in microglia. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:210.
[18] 孙林林,张兴祥,李建民,等.法舒地尔对大鼠蛛网膜下腔出血早期脑损伤的行为能力及海马区神经细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(10):2481-2484.
[19] 刘振刚,高建亮,孙林林,等.颈内动脉刺破法制作大鼠蛛网膜下腔出血模型[J].中国比较医学杂志,2017,27(6):37-45.
[20] GARCIA JH, WAGNER S, LIU KF, et al. Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical validation. Stroke. 1995;26(4):627-634.
[21] EL AMKI M, DUBOIS M, LEFEVRE-SCELLES A, et al. Long-Lasting Cerebral Vasospasm, Microthrombosis, Apoptosis and Paravascular Alterations Associated with Neurological Deficits in a Mouse Model of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(4):2763-2779.
[22] LIU C, YAO K, TIAN Q, et al. CXCR4-BTK axis mediate pyroptosis and lipid peroxidation in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage via NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB pathway. Redox Biol. 2023;68:102960.
[23] ANDERSEN CR, PRESSEAU J, SAIGLE V, et al. Core outcomes for subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(12):1075-1076.
[24] JUNG H, YOUN DH, PARK JJ, et al. Bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate behavioral and cognitive dysfunction after subarachnoid hemorrhage via HMGB1-RAGE axis mediationv. Life (Basel). 2023;13(4):881.
[25] ZHANG Y, QIN L, XIE J, et al. Eupatilin prevents behavioral deficits and dopaminergic neuron degeneration in a Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Life Sci. 2020;253(1):117745-117756.
[26] FEI X, CHEN C, KAI S, et al. Eupatilin attenuates the inflammatory response induced by intracerebral hemorrhage through the TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;76(1):105837-105846.
[27] CAO Y, WANG Y, LI X, et al. MCC950 ameliorates cognitive function by reducing white matter microstructure damage in rats after SAH. Brain Res Bull. 2023;202:110743.
[28] VERON AD, BIENBOIRE-FROSINI C, GIRARD SD, et al. Syngeneic transplantation of olfactory ectomesenchymal stem cells restores learning and memory abilities in a rat model of global cerebral ischemia. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018(1):2683969-2683978.
[29] JEON J, MONY TJ, CHO E, et al. Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rubrofusarin-enhanced cognitive functions and neurite outgrowth. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;147:112663.
[30] ZUO Y, WANG J, ENKHJARGAL B, et al. Neurogenesis changes and the fate of progenitor cells after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Exp Neurol. 2019;311(1):274-284.
[31] KUIL LE, SEIGERS R, LOOS M, et al. Fractionated brain X-irradiation profoundly reduces hippocampal immature neuron numbers without affecting spontaneous behavior in mice. Heliyon. 2024;10(9):e29947.
[32] LEE S, LEE W, YANG S, et al. Di-n-butyl phthalate disrupts neuron maturation in primary rat embryo neurons and male C57BL/6 mice. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2022;85(2):56-70.
[33] ZUO Y, WANG J, LIAO F, et al. Inhibition of heat shock protein 90 by 17-AAG reduces inflammation via P2X7 receptor/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and increases neurogenesis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11(1):401-416.
[34] WAN T, WANG Z, LUO Y, et al. FA-97, a new synthetic caffeic acid phenethyl ester derivative, protects against oxidative stress-mediated neuronal cell apoptosis and scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019(1): 8239642-8239663.
[35] OU S, KIM TY, JUNG E, et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase contributes to TNFα-induced endothelial tube formation of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by activating the JAK/STAT/TIE2 signaling axis. BMB Rep. 2024;57(5):238-243.
[36] HUANG C, DONG J, CHENG L, et al. Alkaloids from aconitum carmichaelii alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice via MAPK/NF-κB/STAT3 signaling inhibition. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:6257778.
[37] Choi JY, Yun J, Hwang CJ, et al. (E)-2-methoxy-4-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl) prop-1-en-1-yl) phenol Ameliorates MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration by inhibiting the STAT3 pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2632-2647.
[38] CHEN CM, YEN CY, CHEN WL, et al. Pathomechanism characterization and potential therapeutics identification for Parkinson’s Disease targeting neuroinflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1062.
[39] WU CR, YANG QY, CHEN QW, et al. Ghrelin attenuate cerebral microvascular leakage by regulating inflammation and apoptosis potentially via a p38 MAPK-JNK dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;552:37-43. |