中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (13): 2661-2668.doi: 10.12307/2024.148
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
基于中医证候与精液质量相关参数构建精子DNA碎片预测模型与验证
周 超1,庾广聿1,阳绍华1,高磊磊2,金 珍2,蒋月园1,李 欢3
- 1广西壮族自治区南溪山医院生殖中心,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541000;2浙江省人民医院生殖中心,浙江省杭州市 310000;3中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九二四医院检验科,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541000
Prediction model and verification of sperm DNA fragments based on traditional Chinese medicine syndrome and semen quality-related parameters
Zhou Chao1, Yu Guangyu1, Yang Shaohua1, Gao Leilei2, Jin Zhen2, Jiang Yueyuan1, Li Huan3
- 1Reproductive Center, Nanxishan Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Guilin 541000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Reproductive Center of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, Hangzhou 310000, Zhejiang Province, China; 3Laboratory Department of 924 Hospital of the Joint Logistics Support Force of the People’s Liberation Army of China, Guilin 541000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
精子DNA碎片指数:通过反映男方精子核遗传物质的完整性与损伤程度,从基因层面为全面评估精液质量再增一个独立的生物学临床指标。研究证实,精子DNA碎片指数与男性不育、植入失败、妊娠丢失存在显著的相关性。中医证候:通过反映疾病发生和演变过程中某阶段的本质特征,能多维度获取关于该疾病的病因、病机、病位、病势等丰富信息。但因中医证候缺乏定量指标与科学的统计学方法,因而其具有多变性、复杂性、模糊性、隐匿性。
摘要
背景:中医证候与精液质量相关参数相结合,共同预测精子DNA碎片指数(DNA fragmentation index,DFI)异常增高的发生并绘制列线图,能显著提高临床的实操性与应用效能,为临床全面评估精液质量,采取积极干预措施以改善临床结局及制定个体化医疗方案提供依据。
目的:探讨基于中医证候与精液质量相关参数构建精子DNA碎片的预测模型与验证。
方法:回顾性分析2019年7月至2021年7月在广西壮族自治区南溪山医院中医男科接受中医证候诊断及精子DNA碎片率检查的不育患者共420例,据《人类精液检查与处理实验室手册》(第6版),将其中137例精子DFI > 30%患者纳入精子DFI异常增高组,将283例精子DFI≤30%作为对照组;首先采用单因素分析筛选精子DFI异常增高的影响因素,然后采用套索算法(LASSO)校正因子共线性问题并筛选出最佳匹配因子后,将其纳入多因素向前逐步Logistic回归找出其独立影响因素并绘制列线图,最后采用受试者工作曲线、校准曲线、临床决策曲线、临床影响曲线对该预测模型进行区分度与准确度及临床应用效能验证。
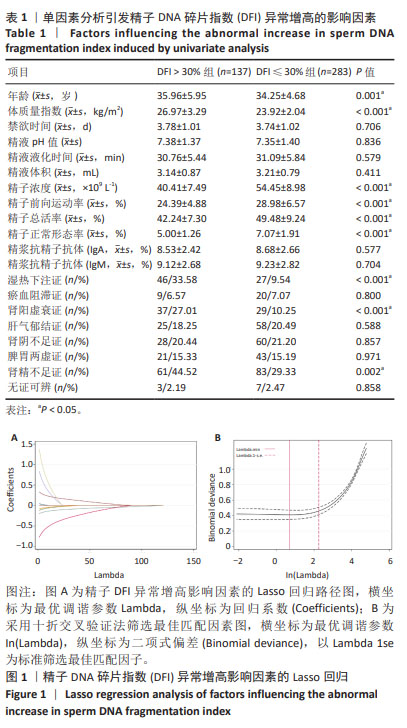
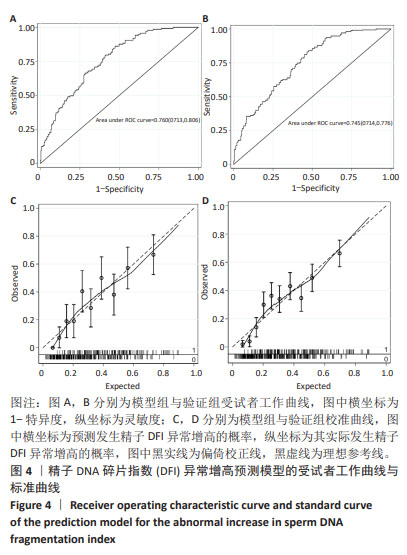
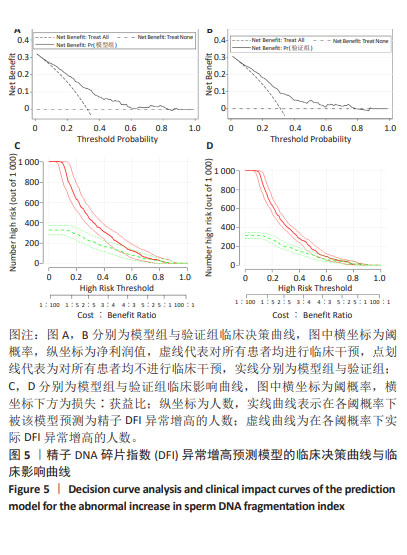
结果与结论:①单因素分析结果显示,年龄、体质量指数、前向运动率、精子总活率、精子浓度、精子形态学、肾阳虚衰证、湿热下注证、肾精不足证为引发精子DFI异常增高的影响因子(P < 0.05);②通过LASSO回归进一步筛选出的最佳匹配因素为年龄、体质量指数、精子总活率、精子浓度、精子形态学、肾阳虚衰证、湿热下注证、肾精不足证(P < 0.05);③多因素向前逐步Logistic回归结果显示年龄、体质量指数、精子浓度、精子总活率、湿热下注证、肾阳虚衰证共6项为引发精子DFI异常增高的独立影响因素;④受试者工作曲线显示,模型组曲线下面积为0.760(0.713,0.806),验证组曲线下面积为0.745(0.714,0.776),说明该预测模型具有较好的区分度;⑤校准曲线平均绝对误差0.040,Hosmer-Lemeshow检验P > 0.05,表明该模型预测发生精子DFI异常增高的概率与实际发生精子DFI异常增高的概率无显著统计学差异,证实该模型具有较好的准确度;⑥临床决策曲线与临床影响曲线显示,模型组与验证组分别在阈概率值为0.08-0.84与0.09-0.78时具有临床最大净获益,且在该阈概率范围内具有较好的临床应用效能;⑦结果表明,年龄、体质量指数、精子浓度、精子总活率、湿热下注证、肾阳虚衰证为引发精子DFI异常增高的独立影响因素,通过其构建的临床预测模型列线图具有较好的临床预测价值与临床应用效能,可为临床全面评估精液质量、预后与干预及个体化医疗服务提供依据。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9843-6731 (周超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: