中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 111-119.doi: 10.12307/2024.137
• 细胞相关实验/试验研究Cell related experimental/trial studies • 上一篇 下一篇
基于活产建立体外受精-胚胎移植精子DNA碎片指数的参考阈值及子代短期安全性
周 超1,王淑娴2,于春梅2,庾广聿1,蒋月园1
- 1广西壮族自治区南溪山医院生殖中心,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541000;2常州市妇幼保健院,江苏省常州市 213000
Reference threshold and offspring short-term security of in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer sperm DNA fragmentation index based on live birth
Zhou Chao1, Wang Shuxian2, Yu Chunmei2, Yu Guangyu1, Jiang Yueyuan1
- 1Reproductive Center, Nanxishan Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Guilin 541000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Changzhou Maternal and Child Health Area Hospital, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
精子DNA碎片指数:通过反映精子DNA单、双链断裂及碎片化程度,进而从基因层面反映男性精子核遗传物质完整性与损伤程度,现已作为一种风险分层指标,对不明原因不育、精索静脉曲张、反复妊娠丢失、危险生活及环境暴露的评估具有重要意义。
男性不育:是指育龄夫妇有规律性生活且未采取避孕措施,由男方因素导致女方在一年内未能自然受孕的状态。男性不育分为原发性不育和继发性不育。据世界卫生组织数据显示,全球育龄人口中有15%夫妇存在生育问题,其中男性因素约占所有不孕因素的50%。
背景:精子DNA碎片指数与受精、胚胎发育潜能、胚胎植入、流产及子代安全性等存在显著的相关性。然而,其临床参考值受多种因素的影响,导致临床意义极其有限,该研究以活产为结局,通过倾向评分匹配校正其他混杂因素后,构建精子DNA碎片指数与活产的最佳临床截断值,并对其进行内外部验证,具有较好的预测价值及临床应用效能。
目的:探讨基于活产建立体外受精-胚胎移植精子DNA碎片指数的参考阈值及子代短期安全性。
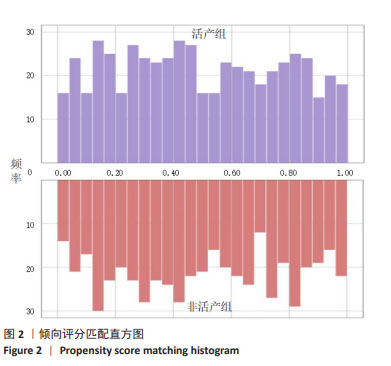
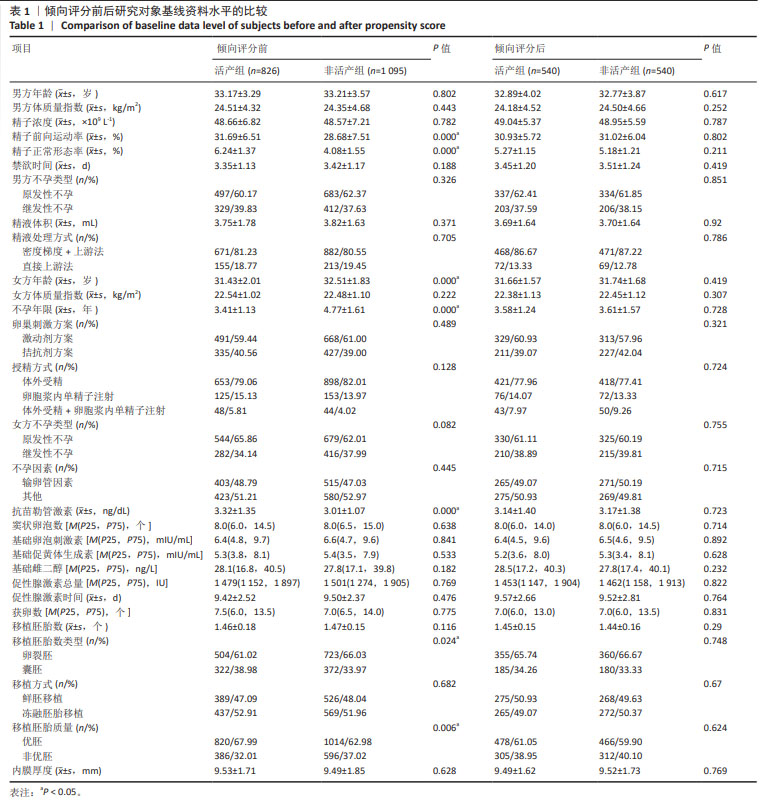
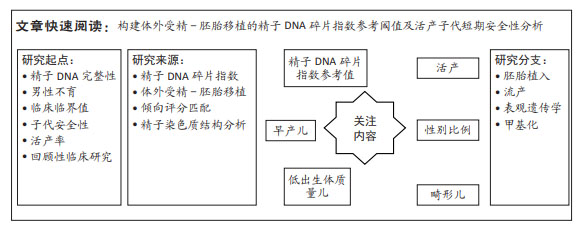
方法:选取2019年5月至2021年5月于常州市妇幼保健院接受体外受精-胚胎移植患者1 921例,以倾向匹配容差0.02为标准,1∶1进行倾向评分匹配,结果活产组与非活产组各成功匹配540例,以此建立模型组;通过选取同时期广西壮族自治区南溪山医院接受体外受精-胚胎移植患者135例作为外部验证组;采用受试者工作曲线探求精子DNA碎片指数对活产的临床最佳截断值,分别采用限制性立方样条曲线、标准曲线、临床决策曲线、临床影响曲线及内外部验证等方法,对该截断值的准确性及临床应用效能进行评估。
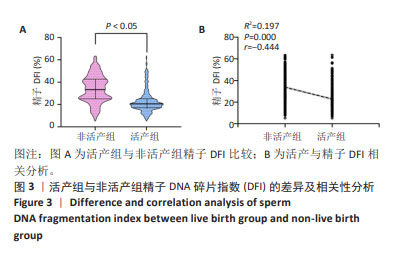
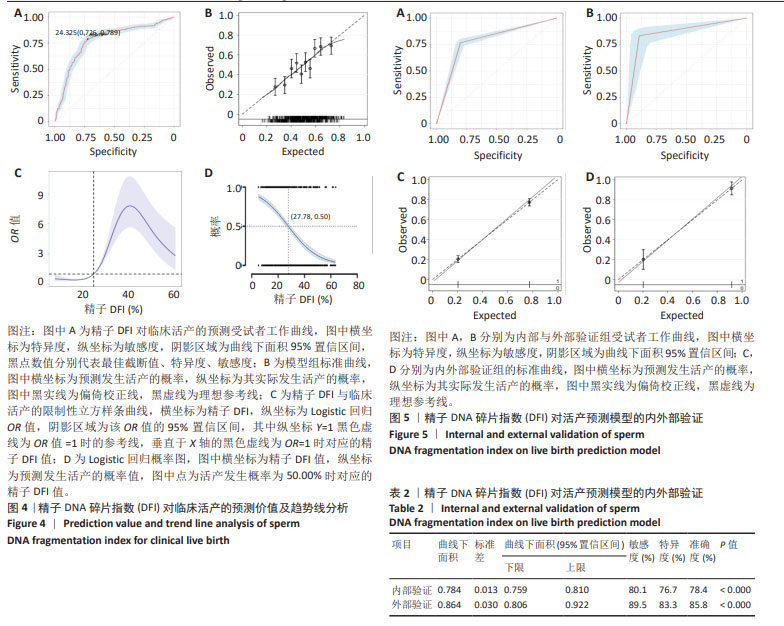
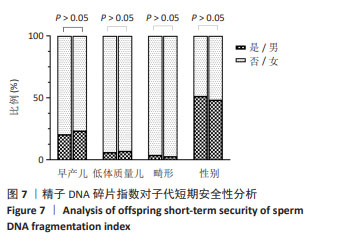
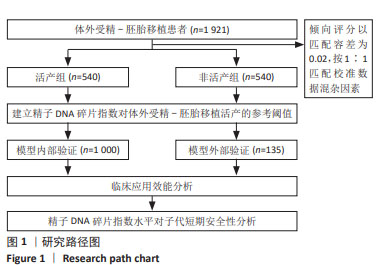
结果与结论:①非活产组精子DNA碎片指数显著高于活产组且与活产存在显著的负相关性(r=-0.444,P < 0.001);②受试者工作曲线结果显示,DNA碎片指数对活产的最佳截断值为24.33%,曲线下面积为0.775(0.746,0.804),特异度为72.60%,敏感度为78.90%,准确度为75.70%;③限制性立方样条曲线拟合Logistic回归结果显示,当精子DNA碎片指数大于24.57%时,临床非活产的风险呈趋势性增涨;④Logistic回归概率分析结果显示,精子DNA碎片指数为活产的危险因素[OR(95%CI)=0.916(0.904,0.928),P < 0.001],且当精子DNA碎片指数大于27.78%时,临床活产发生的概率将小于50%,随着精子DNA碎片指数每增高1个单位,活产的概率下降8.4%;⑤内外部对该临床截断值的验证均显示,该截点具有一定的临床预测价值及准确性;⑥临床决策曲线与临床影响曲线显示,以该临床截断值建立的预测模型在阈概率为0.22-0.73时具有临床最大净获益值,且在该阈概率范围内损失与获益的比值始终小于1,证实该预测模型具有较好的临床应用效能;⑦精子DNA碎片指数与子代短期安全性分析结果显示,精子DNA碎片指数与出生儿早产、体质量、畸形、性别差异无显著性;⑧结果表明,精子DNA碎片指数对体外受精-胚胎移植活产的最佳临床截断值为24.33%,以此建立的临床预测模型具有较好的区分度、准确度与临床应用效能,精子DNA碎片指数对子代短期安全性影响并不显著,但仍需大样本及长期的追踪评估。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9843-6731 (周超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: