中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 120-127.doi: 10.12307/2025.021
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
干细胞在小口径人工血管内皮化中的应用
郑安垲,刘瑞明,向秋玲
- 中山大学中山医学院,广东省广州市 510080
-
收稿日期:2023-11-17接受日期:2023-12-22出版日期:2025-01-08发布日期:2024-05-18 -
通讯作者:向秋玲,女,教授,博士生导师,中山大学中山医学院,广东省广州市 510080 -
作者简介:郑安垲,男,2003年生,广东省东莞市人,汉族,中山大学中山医学院临床医学(本博连读)在读,主要从事小口径人工血管研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(82272164),项目负责人:向秋玲;广东省自然科学基金(2021A1515011648),项目负责人:向秋玲
Application of stem cells in endothelialization of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis
Zheng Ankai, Liu Ruiming, Xiang Qiuling
- Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-11-17Accepted:2023-12-22Online:2025-01-08Published:2024-05-18 -
Contact:Xiang Qiuling, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zheng Ankai, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Xiang Qiuling, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
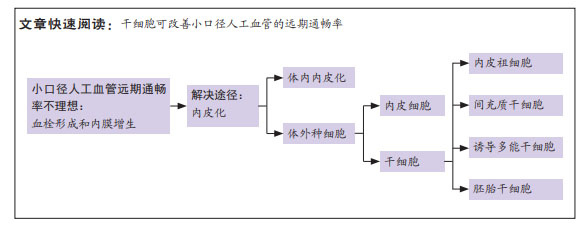
文题释义:
小口径人工血管:是一种直径在6 mm以下的、由人工合成材料或天然材料制备成的、可替代病变血管的管形植入物。
内皮化:通过材料表面改性促进细胞黏附或体外种植细胞等方法,使人工血管内表面覆盖细胞,发挥类似天然内皮的生理功能。
背景:小口径人工血管移植后由于血栓形成和内膜增生等原因造成管腔狭窄甚至闭塞,运用干细胞作为种子细胞实现人工血管的内皮化有助于改善血管移植后的远期通畅率。
目的:总结干细胞在小口径人工血管内皮化中应用的研究进展。
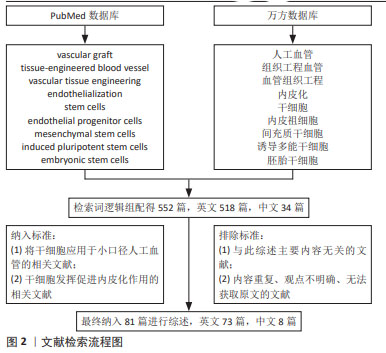
方法:由第一作者检索PubMed和万方数据库2013-2023年发表的相关文献,英文检索词为“vascular graft,tissue-engineered blood vessel/vascular tissue engineering,endothelialization,stem cells,endothelial progenitor cells,mesenchymal stem cells,induced pluripotent stem cells,embryonic stem cells”,中文检索词为“人工血管,组织工程血管/血管组织工程,内皮化,干细胞,内皮祖细胞,间充质干细胞,诱导多能干细胞,胚胎干细胞”,检索近10年国内外关于干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化的相关文献,初检文献552篇,根据纳排标准最终选取81篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①远期通畅率不理想限制了小口径人工血管的临床应用,造成远期通畅率低下的主要原因是血栓形成和内膜增生。天然血管内皮层具有良好的抗血栓及内膜增生性能,内皮化可以模拟天然血管的特性,是提升远期通畅率的有效手段。②小口径人工血管植入体内后会经历体内内皮化过程,但难以形成完整的内皮层。干细胞具有分化为内皮细胞的潜能,体内招募干细胞或将其作为种子细胞种植在人工血管内表面是实现内皮化的研究策略。③将内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞、诱导多能干细胞及胚胎干细胞等作为种子细胞种植均能够一定程度改善小口径人工血管的远期通畅率,且它们各具优势。内皮祖细胞便于获取且可直接用于种植;间充质干细胞来源广泛且具有旁分泌和调节免疫的功能;诱导多能干细胞来源丰富且可消除免疫原性;胚胎干细胞增殖能力强且能多向分化。④将干细胞用于人工血管的研究目前仍未转化至临床,未来需要进一步研究并促进临床转化。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
郑安垲, 刘瑞明, 向秋玲. 干细胞在小口径人工血管内皮化中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(1): 120-127.
Zheng Ankai, Liu Ruiming, Xiang Qiuling. Application of stem cells in endothelialization of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 120-127.
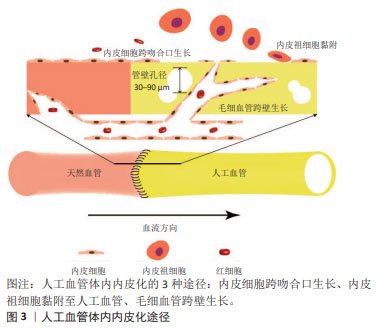
因此,依赖内皮祖细胞黏附而形成的内皮层可能是不连续的。此外,当人工血管管壁孔隙直径达到30-90 μm时,毛细血管通过跨壁生长促进内皮化[10]。文章概括了人工血管体内内皮化的3种途径:内皮细胞经吻合口内皮化、内皮祖细胞迁移黏附和毛细血管跨壁生长,见图3。
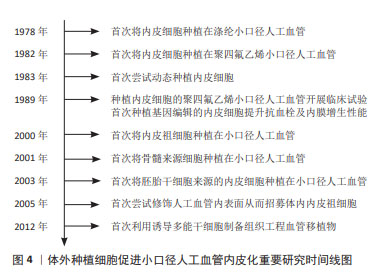
血管移植通常需要移植长度在2 cm以上的血管,移植后如果仅依靠体内内皮化难以形成完整的内皮层。因此,体外种植细胞后再进行移植是一种能够保证人工血管实现完整、均匀内皮化的有效途径。而且,体外种植细胞可以增强人工血管的血液相容性,减少移植后对凝血级联系统的激活,有利于人工血管移植后通畅[16]。图4列举了体外种植细胞促进小口径人工血管内皮化的重要研究。在1978年,研究者首次从血管组织中获取内皮细胞,体外扩增后种植在涤纶人工血管,开创了小口径人工血管体外内皮化的先河。此后20年间,优化内皮细胞成为提升小口径人工血管内皮化的重要研究方向。其中,通过基因编辑技术对内皮细胞进行改造从而提升其抗血栓及内膜增生性能是最为热门的研究策略。随着干细胞研究的发展,内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞、胚胎干细胞、诱导多能干细胞陆续被应用于小口径人工血管内皮化,并逐渐取代了原代内皮细胞。目前,干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化的研究聚焦于招募体内干细胞或体外种植干细胞来源内皮祖细胞或内皮细胞。
2.2 小口径人工血管体外种植内皮细胞 内皮细胞可以来源于患者自体或同种异体,但是获取细胞会带来手术创伤,耗时较长,同种异体的内皮细胞存在免疫原性,而且内皮细胞的增殖能力低且来源有限,质量受生理状态或病理状态的影响[16-20]。脐静脉内皮细胞具有数量多、生长快的特点,从脐带获取血管组织不需要额外的手术创伤,相比于患者或其他供体的内皮细胞更具优势[21]。但是从多种血管细胞中纯化脐静脉内皮细胞比较困难[21]。另有研究发现脐静脉内皮细胞在动态培养之后并没有展现出与流动方向一致的排列方式,不利于防止动脉粥样硬化以及减少炎症信号[22]。此外,脐静脉内皮细胞在人工血管材料上黏附并不牢固,不利于防止血栓形成[21]。因此,直接种植内皮细胞需要面临细胞来源少、细胞质量差、准备时间长以及内皮化效果不理想等问题,而应用干细胞为解决以上问题提供了新的思路。
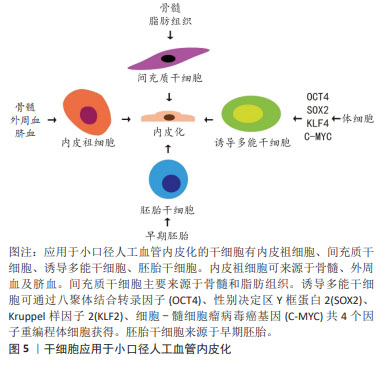
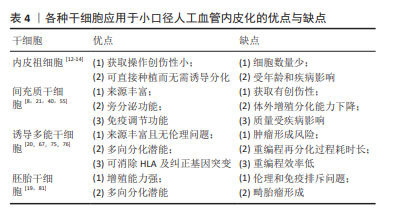
2.3 干细胞与小口径人工血管 干细胞具有自我更新和多向分化能力,应用于小口径人工血管展现出了巨大的潜能。目前,应用于血管组织工程的干细胞有内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞、诱导多能干细胞和胚胎干细胞,见图5。
2.3.1 内皮祖细胞内皮化 内皮祖细胞是内皮细胞的前体细胞,存在于骨髓、外周血和脐血等[19]。根据目前共识,内皮祖细胞主要表面标记为CD34和血管内皮生长因子受体2[23],也有根据CD45,CD14,CD133和CD146等标志物对其进行更细致的分类[24]。内皮祖细胞可通过自身细胞增殖或分泌促血管生成细胞因子及生长因子直接或间接促进内皮形成[25]。MUNISWAMI等[26]发现脐血内皮祖细胞在体外培养时可自发形成管状排列的结构,而且这些内皮祖细胞与成熟内皮细胞具有相似的功能。内皮祖细胞还可以分化出内皮生长细胞,它们也能够抗血栓和抑制内膜增生[27-28]。
内皮祖细胞用于小口径人工血管内皮化主要有两种研究策略:促进人工血管招募体内内皮祖细胞或体外种植内皮祖细胞。体内内皮祖细胞的动员、归巢和分化可以促进血管移植物的体内内皮化,因此借助特异分子招募体内内皮祖细胞或增强其附着从而促进原位内皮化是一种研究策略。常用的表面修饰分子包括多肽、核苷酸及药物等,修饰后的人工血管可以促进内皮祖细胞归巢。在人工血管上种植内皮祖细胞后再移植入体内是另一种人工血管内皮化的研究策略。汪川等[29]将兔骨髓来源的内皮祖细胞种植在脱细胞人脐动脉后移植于兔颈动脉,可以观察到移植术后30 d血管仍保持通畅。内皮祖细胞在体外分化为内皮细胞的功能以及在人工血管上的黏附能力会影响内皮祖细胞体外种植促进内皮化的效果。细胞因子对内皮祖细胞的动员和分化有一定作用,研究发现血管内皮生长因子或基质细胞衍生因子1α等均可以促进体外内皮祖细胞的动员、分化及在人工血管上的生长[25,30-31]。此外,MELCHIORRI等[32]借助管状灌注系统提供类似静脉系统的低水平剪切应力,发现动态培养下内皮祖细胞内皮一氧化氮合酶3的表达上调,有助于抑制血小板黏附聚集从而抑制血栓形成,而且内皮祖细胞在人工血管上增殖、黏附以及分化为内皮细胞的功能增强,分布也比静态培养更为密集。
表2列举了促进人工血管招募体内内皮祖细胞的分子[33-38],它们在动物实验中展现出良好的远期通畅率。
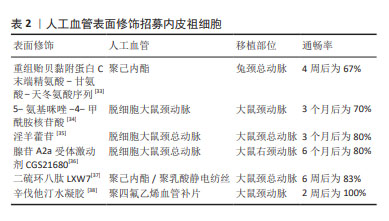
需要指出的是,内皮祖细胞在体外增殖能力弱,培养两三代后细胞活性会下降。因此,相较于体外种植内皮祖细胞,促进人工血管招募体内内皮祖细胞更具有前景。随着材料科学的发展,修饰人工血管促进招募体内内皮祖细胞从而实现内皮化是解决内皮祖细胞体外增殖能力弱的有效手段。涂层技术、水凝胶技术及纳米颗粒技术等均能够应用于人工血管表面修饰从而促进招募外周血内皮祖细胞。
2.3.2 间充质干细胞内皮化 间充质干细胞是一群高表达CD105,CD90,CD73及CD44,低表达CD34,CD45,CD11b,CD19及HLA-DR等标志物的细胞,广泛存在于骨髓及脂肪等组织中,具有强大的增殖能力和分化潜能,适合作为人工血管内皮化的种子细胞。间充质干细胞可以在血管内皮生长因子的诱导下向内皮细胞分化[39]。此外,间充质干细胞具有旁分泌和免疫调节功能,可以分泌抗炎症因子并调控巨噬细胞的极化,保护人工血管免受炎症反应[21,40]。最常用于小口径人工血管的间充质干细胞有骨髓间充质干细胞和脂肪间充质干细胞,胸腺、毛囊和羊膜等来源的间充质干细胞也被用于人工血管研究。
骨髓间充质干细胞:骨髓间充质干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化的研究策略是将其诱导成内皮细胞后种植在人工血管。利用血管内皮生长因子单因子诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向内皮细胞分化是较成熟的方法,而刘明颖[41]发现血管内皮生长因子和成纤维细胞生长因子协同作用比血管内皮生长因子单独诱导效果更佳。艾文佳等[42]通过调节转化生长因子β1主要Ⅰ型受体ALK5的活化水平从而诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为内皮细胞,种植到脱细胞异种动脉支架7 d后观察到较完整的内皮层。此外,作者课题组发现过表达Gremlin1可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞在缺血环境中存活并有助于血管新生[43],提示种植过表达Gremlin1的骨髓间充质干细胞有助于人工血管内皮化。与上述内皮祖细胞作用相似,骨髓间充质干细胞可被招募至人工血管从而促进内皮化。SHAFIQ等[44]发现含有P物质和肝素的人工血管移植到大鼠背部皮下后可以招募骨髓间充质干细胞。他们课题组还发现缓释P物质及基质细胞衍生因子1α的聚己内酯/胶原人工血管可以增强细胞浸润、骨髓间充质干细胞招募和血管形成,移植到兔腹主动脉4周后形成血管性血友病因子阳性的单层细胞层[45]。需要指出的是,骨髓间充质干细胞仅占骨髓单个核细胞约0.01%,且随着年龄的增长,其所占比例以及分化能力会逐渐下降,制约了募集体内骨髓间充质干细胞实现人工血管内皮化的效果,提示外源性补充骨髓间充质干细胞可能是实现内皮化的有效补充。
脂肪间充质干细胞:该细胞存在于人体的脂肪组织当中,脂肪抽吸术常见手术部位为腹股沟皮下,创伤小于骨髓穿刺术。脂肪间充质干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化的策略包括将其诱导为内皮细胞后种植或直接种植在人工血管。脂肪间充质干细胞具有成血管功能,可以分化为内皮细胞。BERTANHA等[46]用人血小板裂解物来源的内皮诱导剂生长因子将脂肪间充质干细胞诱导为功能性内皮细胞,种植到脱细胞血管支架上可形成内皮层以及毛细血管样结构。FERIMAN等[47]发现脂肪间充质干细胞和脂肪来源的微血管内皮细胞共同种植在聚乳酸/聚乳糖基乙醇酸人工血管上有助于血管生成和血管网络形成。LIN等[48]发现1-磷酸-鞘氨醇可以刺激种植的脂肪间充质干细胞发挥内皮样功能并防止syndecan-1脱落,增强了脱细胞人脐动脉的抗血栓性能。此外,POLICHA等[49]利用糖尿病患者来源脂肪间充质干细胞种植在人大隐静脉,发现其血管生成能力与正常间充质干细胞无显著差异,但其向内皮细胞分化的功能下降,提示疾病状态会影响脂肪间充质干细胞的质量。然而,由于获取脂肪间充质干细胞并分化扩增内皮细胞耗时长,有研究直接将脂肪间充质干细胞种植在人工血管并进行移植,一些动物实验证实远期通畅效果良好[50-53],见表3。这些研究提示将脂肪间充质干细胞作为种子细胞直接种植可以发挥类似内皮细胞的功能。
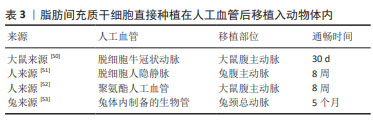
其他类型间充质干细胞:胸腺间充质干细胞存在于胸腺的小叶间小梁,在免疫系统的发育和功能执行中发挥重要作用,作为种子细胞的优势是免疫反应调节能 力[54]。毛囊间充质干细胞可以分化为平滑肌细胞,但是目前还没有发现可以直接诱导获得内皮细胞,有研究也尝试将毛囊间充质干细胞重编程为诱导多能干细胞后再分化为内皮细胞[55-56]。羊膜间充质干细胞存在于人类胎盘,它们分泌旁分泌因子从而调节内皮功能,在体外可以增强内皮细胞的活力并促进内皮细胞网络的形成,在体内可诱导血管生成[57]。除了上述组织来源的间充质干细胞以外,以往还有研究聚焦于脐带、脐血、羊水和心包积液等来源的间充质干细胞[58-60]。
除了不同间充质干细胞来源之外,间充质干细胞亚群、氧化应激、生物力学环境等因素也会影响内皮化效果。选择促血管新生能力强的间充质干细胞亚群作为种子细胞可以有效促进内皮化。间充质干细胞在体外扩增过程中会差异性表达醛脱氢酶,醛脱氢酶可以在细胞受到氧化应激时起保护作用。SHERMAN等[61]发现高表达醛脱氢酶的间充质干细胞是促血管生成的亚群,适用于治疗性血管重建。人工血管移植过程中吻合口附近的天然内皮损伤会引起氧化应激,从而导致间充质干细胞的功能活性下降及凋亡增加。BAI等[62]利用肿瘤坏死因子α预处理静脉移植物,改善间充质干细胞在氧化应激下的存活和迁移,移植后间充质干细胞可以分泌血管内皮生长因子及肝细胞生长因子保护吻合口附近内皮细胞,同时抑制内膜增生,提示可以预处理内皮化的人工血管从而促进移植后适应局部氧化应激环境。此外,特定的生物力学环境作为一种物理信号,对间充质干细胞发挥内皮化功能有重要作用。LI等[39]发现机械力在血管内皮生长因子诱导间充质干细胞向内皮细胞的分化中起促进作用。LA等[63]对种植脂肪间充质干细胞的血管施加适当的动态剪切应力后发现其抗血小板黏附能力有所提升,而且脂肪间充质干细胞在人工血管上沿着特定方向有序排布,这种排列方式有利于人工血管移植后适应血流动力学环境。JIAO等[64]通过增加生物反应器的搏动刺激频率增强骨髓间充质干细胞在脱细胞人工血管上的黏附、增殖和分化能力。但是,ZHAO等[65]发现施加过高和过长时间的剪切应力会导致间充质干细胞的凋亡和死亡,而内源性的细胞凋亡抑制蛋白1是保护间充质干细胞在过度剪切应力下生存的重要分子。
尽管间充质干细胞在人体内分布广泛,但其在体外培养条件下易衰老,增殖和分化潜能在8-10代之后有所下降,种植后可能难以发挥令人满意的生理功能。而且,对于糖尿病患者,高血糖状态导致间充质干细胞修复和再生血管组织的能力受损,严重时间充质干细胞的免疫调节和抗炎症功能也会受到影响[40]。值得一提的是,在上述众多间充质干细胞中,脂肪间充质干细胞具有获取创伤性小、可以直接用于种植的优势,更适合作为小口径人工血管的种子细胞。
2.3.3 诱导多能干细胞内皮化 在2006年,Yamanaka在成纤维细胞利用反转录病毒诱导生成多能干细胞。这种诱导形成的干细胞在形态、增殖分化潜力、细胞表面抗原、类胚体和畸胎瘤生成能力等方面与胚胎干细胞极为相似。诱导多能干细胞来源广泛且易于获得,可来自皮肤、外周血和尿液等[8,66]。将患者来源的细胞重编程为诱导多能干细胞可以避免伦理及免疫排斥问题。此外,如果患者的血管细胞因衰老、血管疾病或基因突变等受到损害,可通过细胞重编程或基因编辑等方式纠正[8,67]。
诱导多能干细胞用于人工血管内皮化最常见思路是将其分化为内皮细胞后种植在人工血管。目前将诱导多能干细胞分化为内皮细胞主要有4种方法:与基质细胞共培养、类胚体途径、添加细胞因子的二维培养和三维培养[17]。近年来,上述方法也在不断改进与完善。有研究将分化培养基中所有动物来源的试剂更换为人来源的试剂并分化无异基因条件的内皮细胞,种植在脱细胞人脐动脉后发现它们能发挥类似于一般内皮细胞的功能[68]。然而,有学者认为诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞的功能不如人体内源性内皮细胞。BEZENAH等[69]将脐静脉内皮细胞和诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞分别与成纤维细胞进行三维共培养,发现二者均能形成成熟的血管样网络,但是诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞形成的毛细血管芽更少。LUO等[18]将种植诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞的人工血管移植到裸鼠主动脉,发现7 d后人工血管上存在诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞和大鼠内皮细胞,而30 d时只存在大鼠内皮细胞,说明宿主体内内皮细胞可能会更新体外种植的诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞。尽管诱导多能干细胞可以分化为内皮细胞,但人体内皮细胞在不同的血管类别和组织类型之间表现出高度的异质性[70]。SIVARAPATNA等[71]利用生物反应器为诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞提供生理水平的剪切应力,发现内皮细胞动脉样表型相关的标志物表达上调。但是目前尚无将诱导多能干细胞分化为各器官特异性内皮细胞亚型的方法,未来的研究可以针对特定器官诱导内皮细胞并种植在人工血管用于特定部位病变血管移植。此外,诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞还可用于构建人工血管疾病模型,ATCHISON等[72]利用Hutchinson-Gilford早衰综合征患者诱导多能干细胞来源的内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞制备人工血管,发现其表达与内皮相关的心血管疾病的标志物。
除了将诱导多能干细胞分化为内皮细胞,还可以将诱导多能干细胞分化为内皮祖细胞或间充质干细胞,直接作为种子细胞或进一步分化为内皮细胞。作者课题组发现Gremlin1会抑制诱导多能干细胞向中胚层分化而促进内皮祖细胞的分化与扩增,提示可以在内皮祖细胞体外扩增阶段外源性添加重组的Gremlin1从而获得充足的内皮祖细胞作为种子细胞[66]。SAMUEL等[73]在人包皮成纤维细胞来源的诱导多能干细胞所分化的细胞中选择出CD34+/KDR+/NRP1+的内皮祖细胞,并利用二维的培养系统扩增并分化内皮细胞,联合同一诱导多能干细胞来源的间充质干细胞构建组织工程血管移植物。SUNDARAM等[74]利用无血清的化学诱导分化方法,经过神经嵴中间体将诱导多能干细胞分化为间充质干细胞用于构建组织工程血管移植物。
将诱导多能干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化也需要一定的考量,潜在的畸胎瘤形成风险是主要顾虑之一。细胞重编程技术的发展很大程度上解决了诱导多能干细胞的成瘤性问题,已有的非整合性重编程方法可以保证其安全性[75]。临床上利用患者细胞构建诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞需要耗费大量时间,而预先大规模生产和冷冻保存患者诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞可用于构建组织工程血管移植物[67]。若需要应用同种异体来源的诱导多能干细胞,可以通过消除人类白细胞抗原的表达来建立“通用的”诱导多能干细胞,从而降低免疫原性[20]。另外,诱导多能干细胞的重编程效率低是需要关注的问题[76]。尽管如此,诱导多能干细胞为内皮细胞、内皮祖细胞提供无创且可大量扩增的来源,能够有效解决原代内皮细胞及内皮祖细胞数量有限、质量受年龄和疾病状态影响以及体外增殖能力弱的问题,因此应用诱导多能干细胞仍然是一种很有前景的人工血管内皮化策略,其研究热度将持续上升。未来的研究需要关注诱导多能干细胞来源内皮细胞及内皮祖细胞与原代细胞之间存在的功能差异,确保诱导多能干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化能够达到理想的远期通畅率。
2.3.4 胚胎干细胞内皮化 胚胎干细胞来源于早期胚胎或原始性腺,具有自我更新和多向分化的潜能,它们表达AKP,SSEA-3和SSEA-4等表面分子。理论上,胚胎干细胞可以被诱导为内皮细胞、内皮祖细胞及间充质干细胞。夏振伟等[77]发现血管内皮生长因子联合低氧的培养条件可以促进H9细胞向内皮细胞分化,而且这种内皮细胞能够摄取低密度脂蛋白并形成类似微血管的结构。CAMPAGNOLO等[78]发现胚胎干细胞来源的c-Kit+/Sca-1-血管祖细胞可以通过Klf4/β-catenin依赖的途径诱导向内皮细胞的分化而抑制向平滑肌细胞的分化,而将c-Kit+细胞来源的内皮细胞种植在脱细胞小鼠降主动脉并置换小鼠颈动脉4周后可保持100%的通畅率。SUNDARAM等[79]认为人胚胎干细胞来源的间充质干细胞也可以作为种子细胞。此外,ZHAO等[80]利用A549细胞的条件培养基对脱细胞大鼠腹主动脉进行预处理后,发现小鼠胚胎干细胞在人工血管上的黏附效果有所提升,分布也更均匀。
然而,胚胎干细胞的伦理及免疫排斥问题限制其应用[19,81]。胚胎干细胞具有多向分化的潜能,存在形成畸胎瘤的风险[19],以往的研究也发现胚胎干细胞应用于人工血管可检测到软骨和骨组织的标志物[81]。因此,胚胎干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化的研究向临床转化仍面临较大挑战。见表4。
| [1] AFRA S, MATIN MM. Potential of mesenchymal stem cells for bioengineered blood vessels in comparison with other eligible cell sources. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;380(1):1-13. [2] BIAN Q, CHEN J, WENG Y, et al. Endothelialization strategy of implant materials surface: the newest research in recent 5 years. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2022;20:22808000221105332. [3] ASLANI S, KABIRI M, HOSSEINZADEH S, et al. The applications of heparin in vascular tissue engineering. Microvasc Res. 2020;131:104027. [4] CHEN SG, UGWU F, LI WC, et al. Vascular Tissue Engineering: advanced Techniques and Gene Editing in Stem Cells for Graft Generation. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021;27(1):14-28. [5] NIKLASON LE, LAWSON JH. Bioengineered human blood vessels. Science. 2020; 370(6513):eaaw8682. [6] ARUTYUNYAN I, FATKHUDINOV T, SUKHIKH G. Umbilical cord tissue cryopreservation: a short review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):236. [7] KIRKTON RD, PRICHARD HL, SANTIAGO-MAYSONET M, et al. Susceptibility of ePTFE vascular grafts and bioengineered human acellular vessels to infection. J Surg Res. 2018;221:143-151. [8] JOUDA H, LARREA MURILLO L, WANG T. Current progress in vascular engineering and its clinical applications. Cells. 2022;11(3):493. [9] NAEGELI KM, KURAL MH, LI Y, et al. Bioengineering human tissues and the future of vascular replacement. Circ Res. 2022;131(1):109-126. [10] SÁNCHEZ PF, BREY EM, BRICEÑO JC. Endothelialization mechanisms in vascular grafts. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(11):2164-2178. [11] TALACUA H, SMITS AI, MUYLAERT DE, et al. In situ tissue engineering of functional small-diameter blood vessels by host circulating cells only. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(19-20):2583-2594. [12] JANA S. Endothelialization of cardiovascular devices. Acta Biomater. 2019;99: 53-71. [13] FALAY M, AKTAS S. Endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) count by multicolor flow cytometry in healthy individuals and diabetes mellitus (DM) patients. Clin Lab. 2016;62(11):2161-2166. [14] 田玲,周诺.内皮祖细胞生物学特性的研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2019,29(10):112-116,130. [15] SU LC, XU H, TRAN RT, et al. In situ re-endothelialization via multifunctional nanoscaffolds. ACS Nano. 2014;8(10):10826-10836. [16] DAHAN N, SARIG U, BRONSHTEIN T, et al. Dynamic autologous reendothelialization of small-caliber arterial extracellular matrix: a preclinical large animal study. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(1-2):69-79. [17] JANG S, COLLIN DE L’HORTET A, SOTO-GUTIERREZ A. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells: overview, current advances, applications, and future directions. Am J Pathol. 2019;189(3):502-512. [18] LUO J, QIN L, PARK J, et al. Readily available tissue-engineered vascular grafts derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Circ Res. 2022;130(6): 925-927. [19] ZOU T, FAN J, FARTASH A, et al. Cell-based strategies for vascular regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(5):1297-1314. [20] SHI X, HE L, ZHANG SM, et al. Human iPS cell-derived tissue engineered vascular graft: recent advances and future directions. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(3): 862-877. [21] CAI Q, LIAO W, XUE F, et al. Selection of different endothelialization modes and different seed cells for tissue-engineered vascular graft. Bioact Mater. 2021; 6(8):2557-2568. [22] KRAUS X, VAN DE FLIERDT E, RENZELMANN J, et al. Peripheral blood derived endothelial colony forming cells as suitable cell source for pre-endothelialization of arterial vascular grafts under dynamic flow conditions. Microvasc Res. 2022; 143(1095-9319 (Electronic)):104402. [23] MEDINA RJ, BARBER CL, SABATIER F, et al. Endothelial progenitors: a consensus statement on nomenclature. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(5):1316-1320. [24] CHOPRA H, HUNG MK, KWONG DL, et al. Insights into endothelial progenitor cells: origin, classification, potentials, and prospects. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018: 9847015. [25] BRAGHIROLLI DI, HELFER VE, CHAGASTELLES PC, et al. Electrospun scaffolds functionalized with heparin and vascular endothelial growth factor increase the proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells. Biomed Mater. 2017;12(2):025003. [26] MUNISWAMI DM, REDDY LVK, AMIRTHAM SM, et al. Endothelial progenitor/stem cells in engineered vessels for vascular transplantation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(12):119. [27] GLYNN JJ, HINDS MT. Endothelial outgrowth cells regulate coagulation, platelet accumulation, and respond to tumor necrosis factor similar to carotid endothelial cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(1-2):174-182. [28] GLYNN JJ, HINDS MT. Endothelial outgrowth cells: function and performance in vascular grafts. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(4):294-303. [29] 汪川,李京倖,辛毅,等.人脱细胞脐动脉支架与兔骨髓内皮祖细胞构建组织工程血管的实验研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2014,33(4):586-591. [30] GUO HF, DAI WW, QIAN DH, et al. A simply prepared small-diameter artificial blood vessel that promotes in situ endothelialization. Acta Biomater. 2017;54: 107-116. [31] CHEN X, WANG J, AN Q, et al. Electrospun poly (L-lactic acid-co-varepsilon-caprolactone) fibers loaded with heparin and vascular endothelial growth factor to improve blood compatibility and endothelial progenitor cell proliferation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;128:106-114. [32] MELCHIORRI AJ, BRACAGLIA LG, KIMERER LK, et al. In vitro endothelialization of biodegradable vascular grafts via endothelial progenitor cell seeding and maturation in a tubular perfusion system bioreactor. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(7):663-670. [33] KANG TY, LEE JH, KIM BJ, et al. In vivo endothelization of tubular vascular grafts through in situ recruitment of endothelial and endothelial progenitor cells by RGD-fused mussel adhesive proteins. Biofabrication. 2015;7(1):015007. [34] 吴杨霄.调控干细胞能量代谢在体构建小口径组织工程血管[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2015. [35] 杨婧媛. 表面修饰诱导原位抗凝及促内皮化的组织工程血管构建[D].重庆:陆军军医大学,2019. [36] CHEN W, XIAO L, BAI J, et al. The promotion of tissue engineering blood vessel patency by CGS21680 through regulating pro-inflammatory activities of endothelial progenitor cell. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(10):2634-2642. [37] HAO D, FAN Y, XIAO W, et al. Rapid endothelialization of small diameter vascular grafts by a bioactive integrin-binding ligand specifically targeting endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial cells. Acta Biomater. 2020;108(1878-7568 (Electronic)):178-193. [38] THITIWUTHIKIAT P, II M, SAITO T, et al. A vascular patch prepared from Thai silk fibroin and gelatin hydrogel incorporating simvastatin-micelles to recruit endothelial progenitor cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(7-8):1309-1319. [39] LI N, RICKEL AP, HONG Z. On-site differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into vascular cells on extracellular matrix scaffold under mechanical stimulations for vascular tissue engineering. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2375 (1940-6029 (Electronic)):35-46. [40] DHULEKAR J, SIMIONESCU A. Challenges in vascular tissue engineering for diabetic patients. Acta Biomater. 2018;70:25-34. [41] 刘明颖. 海藻酸钙微纤维中包封的骨髓间充质干细胞被诱导向血管内皮分化的研究[D]. 重庆:重庆大学,2018. [42] 艾文佳,李杰,李雯,等.调节ALK5受体活化水平优化间充质干细胞的内皮分化及组织工程血管的应用[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版),2013,34(2): 207-214. [43] XIANG Q, HONG D, LIAO Y, et al. Overexpression of gremlin1 in mesenchymal stem cells improves hindlimb ischemia in mice by enhancing cell survival. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(5):996-1007. [44] SHAFIQ M, JUNG Y, KIM SH. Covalent immobilization of stem cell inducing/recruiting factor and heparin on cell-free small-diameter vascular graft for accelerated in situ tissue regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(6): 1352-1371. [45] SHAFIQ M, ZHANG Q, ZHI D, et al. In Situ blood vessel regeneration using SP (Substance P) and SDF (Stromal cell-derived factor)-1alpha peptide eluting vascular grafts. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(7):e117-e134. [46] BERTANHA M, MOROZ A, ALMEIDA R, et al. Tissue-engineered blood vessel substitute by reconstruction of endothelium using mesenchymal stem cells induced by platelet growth factors. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59(6):1677-1685. [47] FREIMAN A, SHANDALOV Y, ROZENFELD D, et al. Adipose-derived endothelial and mesenchymal stem cells enhance vascular network formation on three-dimensional constructs in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:5. [48] LIN CH, LU JH, HSIA K, et al. The antithrombotic function of sphingosine-1-phosphate on human adipose-stem-cell-recellularized tissue engineered vascular graft in vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5218. [49] POLICHA A, ZHANG P, CHANG L, et al. Endothelial differentiation of diabetic adipose-derived stem cells. J Surg Res. 2014;192(2):656-663. [50] LIN CH, HSIA K, TSAI CH, et al. Decellularized porcine coronary artery with adipose stem cells for vascular tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2019;14(4):045014. [51] MCILHENNY S, ZHANG P, TULENKO T, et al. eNOS transfection of adipose-derived stem cells yields bioactive nitric oxide production and improved results in vascular tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(11):1277-1285. [52] HASKETT DG, SALEH KS, LORENTZ KL, et al. An exploratory study on the preparation and evaluation of a “same-day” adipose stem cell-based tissue-engineered vascular graft. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;156(5):1814-1822 e1813. [53] TSENG YC, ROAN JN, HO YC, et al. An in vivo study on endothelialized vascular grafts produced by autologous biotubes and adipose stem cells (ADSCs). J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(10):166. [54] IACOBAZZI D, SWIM MM, ALBERTARIO A, et al. Thymus-derived mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering clinical-grade cardiovascular grafts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(9-10):794-808. [55] KOOBATIAN MT, LIANG MS, SWARTZ DD, et al. Differential effects of culture senescence and mechanical stimulation on the proliferation and leiomyogenic differentiation of MSC from different sources: implications for engineering vascular grafts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(7-8):1364-1375. [56] GAO Y, LIU F, ZHANG L, et al. Acellular blood vessels combined human hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells for engineering of functional arterial grafts. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(10):2177-2189. [57] PFEIFFER D, WANKHAMMER K, STEFANITSCH C, et al. Amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve viability of endothelial cells exposed to shear stress in ePTFE grafts. Int J Artif Organs. 2019;42(2):80-87. [58] 王俊力,许慧芳,冯莉,等.不同组织来源间充质干细胞向血管内皮细胞诱导分化的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(36):5466-5472. [59] WEBER B, KEHL D, BLEUL U, et al. In vitro fabrication of autologous living tissue-engineered vascular grafts based on prenatally harvested ovine amniotic fluid-derived stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(1):52-70. [60] WANG JN, KAN CD, LIN SH, et al. Potential of autologous progenitor cells and decellularized porcine artery matrix in construction of tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Organogenesis. 2021;17(3-4):72-84. [61] SHERMAN SE, KULJANIN M, COOPER TT, et al. High aldehyde dehydrogenase activity identifies a subset of human mesenchymal stromal cells with vascular regenerative potential. Stem Cells. 2017;35(6):1542-1553. [62] BAI X, XI J, BI Y, et al. TNF-alpha promotes survival and migration of MSCs under oxidative stress via NF-kappaB pathway to attenuate intimal hyperplasia in vein grafts. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(9):2077-2091. [63] LA A, TRANQUILLO RT. Shear conditioning of adipose stem cells for reduced platelet binding to engineered vascular grafts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(15-16): 1242-1250. [64] JIAO Y, ZHANG Y, XIAO Y, et al. The crescendo pulse frequency of shear stress stimulates the endothelialization of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on the luminal surface of decellularized scaffold in the bioreactor. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):7925-7938. [65] ZHAO D, SUN Y, WEI X, et al. cIAP1 attenuates shear stress-induced hBMSC apoptosis for tissue-engineered blood vessels through the inhibition of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Life Sci. 2015;137:81-88. [66] CHEN H, ZHANG Z, WANG Z, et al. Stage-specific regulation of Gremlin1 on the differentiation and expansion of human urinary induced pluripotent stem cells into endothelial progenitors. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(14):8018-8030. [67] CONG X, ZHANG SM, BATTY L, et al. Application of human induced pluripotent stem cells in generating tissue-engineered blood vessels as vascular grafts. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(24):1581-1594. [68] LUO J, SHI X, LIN Y, et al. Efficient differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into endothelial cells under xenogeneic-free conditions for vascular tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021;119:184-196. [69] BEZENAH JR, KONG YP, PUTNAM AJ. Evaluating the potential of endothelial cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells to form microvascular networks in 3D cultures. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2671. [70] KLEIN D. iPSCs-based generation of vascular cells: reprogramming approaches and applications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(8):1411-1433. [71] SIVARAPATNA A, GHAEDI M, LE AV, et al. Arterial specification of endothelial cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells in a biomimetic flow bioreactor. Biomaterials. 2015;53:621-633. [72] ATCHISON L, ABUTALEB NO, SNYDER-MOUNTS E, et al. iPSC-derived endothelial cells affect vascular function in a tissue-engineered blood vessel model of hutchinson-gilford progeria syndrome. Stem Cell Reports. 2020;14(2):325-337. [73] SAMUEL R, DAHERON L, LIAO S, et al. Generation of functionally competent and durable engineered blood vessels from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(31):12774-12779. [74] SUNDARAM S, ONE J, SIEWERT J, et al. Tissue-engineered vascular grafts created from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(12):1535-1543. [75] JI J, XU H, LI C, et al. Small-caliber tissue-engineered vascular grafts based on human-induced pluripotent stem cells: progress and challenges. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2023;29(4):441-455. [76] GENERALI M, CASANOVA EA, KEHL D, et al. Autologous endothelialized small-caliber vascular grafts engineered from blood-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019;97:333-343. [77] 夏振伟,王纪文,李向东,等.低氧条件下诱导人胚胎干细胞向血管内皮前体细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(45):7255-7259. [78] CAMPAGNOLO P, TSAI TN, HONG X, et al. c-Kit+ progenitors generate vascular cells for tissue-engineered grafts through modulation of the Wnt/Klf4 pathway. Biomaterials. 2015;60:53-61. [79] SUNDARAM S, ECHTER A, SIVARAPATNA A, et al. Small-diameter vascular graft engineered using human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(3-4):740-750. [80] ZHAO L, CHEN HL, XIE LQ, et al. Modification of decellularized vascular scaffold with conditioned medium to enhance cell reseeding. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2016;27(11):1115-1125. [81] WANG L, HU J, SOREK CE, et al. Fabrication of tissue-engineered vascular grafts with stem cells and stem cell-derived vascular cells. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016; 16(3):317-330. |
| [1] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | 于经邦, 吴亚云. 非编码RNA在肺纤维化过程中的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [3] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [4] | 袁维勃, 刘 婵, 余丽梅. 肝脏类器官在肝脏疾病模型与移植治疗中的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [5] | 喻 婷, 吕冬梅, 邓 浩, 孙 涛, 程 钎. 淫羊藿苷预处理增强人牙周膜干细胞对M1型巨噬细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [6] | 杨治航, 孙祖延, 黄文良, 万 喻, 陈仕达, 邓 江. 神经生长因子促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化并抑制肥大分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [7] | 胡涛涛, 刘 兵, 陈 诚, 殷宗银, 阚道洪, 倪 杰, 叶凌霄, 郑祥兵, 严 敏, 邹 勇. 过表达神经调节蛋白1的人羊膜间充质干细胞促进小鼠皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [8] | 金 凯, 唐 婷, 李美乐, 谢裕安. 人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基及外泌体对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [9] | 李帝均, 酒精卫, 刘海峰, 闫 磊, 李松岩, 王 斌. 明胶三维微球装载人脐带间充质干细胞修复慢性肌腱病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [10] | 娄 国, 张 敏, 付常喜. 8周运动预适应增强脂肪干细胞治疗心肌梗死大鼠的效果[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [11] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [12] | 艾克帕尔·艾尔肯, 陈晓涛, 吾凡别克·巴合提. 成骨诱导人牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体促进炎症微环境下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [13] | 章镇宇, 梁秋健, 杨 军, 韦相宇, 蒋 捷, 黄林科, 谭 桢. 新橙皮苷治疗骨质疏松症的靶点及对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [14] | 谢刘刚, 崔书克, 郭楠楠, 李遨宇, 张菁瑞. 干细胞治疗阿尔茨海默病的研究热点与前沿[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [15] | 彭洪成, 彭国璇, 雷安毅, 林 圆, 孙 红, 宁 旭, 尚显文, 邓 进, 黄明智. 血小板衍生生长因子BB参与生长板损伤修复的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
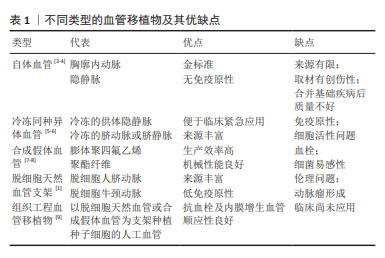 相较于大口径的血管移植物,小口径(内径≤6 mm)的血管移植物由于急性血栓形成和慢性内膜增生等原因,存在远期通畅率低的问题,制约其临床应用。天然血管内皮层具有良好的抗凝血能力和抗内膜增生能力,促进小口径人工血管内皮化可以提升远期通畅率[2]。近年来,将干细胞诱导获得内皮细胞或内皮祖细胞的研究成为热点,为干细胞作为种子细胞种植,从而实现小口径人工血管内皮化提供了坚实的研究基础[3-9]。
文章将总结近10年来国内外将内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞、诱导多能干细胞和胚胎干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化的最新研究进展,并总结上述干细胞的优劣之处。
相较于大口径的血管移植物,小口径(内径≤6 mm)的血管移植物由于急性血栓形成和慢性内膜增生等原因,存在远期通畅率低的问题,制约其临床应用。天然血管内皮层具有良好的抗凝血能力和抗内膜增生能力,促进小口径人工血管内皮化可以提升远期通畅率[2]。近年来,将干细胞诱导获得内皮细胞或内皮祖细胞的研究成为热点,为干细胞作为种子细胞种植,从而实现小口径人工血管内皮化提供了坚实的研究基础[3-9]。
文章将总结近10年来国内外将内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞、诱导多能干细胞和胚胎干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化的最新研究进展,并总结上述干细胞的优劣之处。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2023年10月进行文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索文献发表于2013年1月至2023年10月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed和万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“vascular graft,tissue-engineered blood vessel/vascular tissue engineering,endothelialization,stem cells,endothelial progenitor cells,mesenchymal stem cells,induced pluripotent stem cells,embryonic stem cells”。中文检索词为“人工血管,组织工程血管/血管组织工程,内皮化,干细胞,内皮祖细胞,间充质干细胞,诱导多能干细胞,胚胎干细胞”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 期刊论文及学位论文。
1.1.6 检索策略 包括英文及中文检索词,检索词逻辑组配见图1。
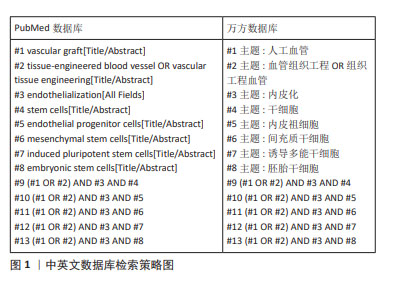
1.1.7 检索文献量 初检文献552篇,其中PubMed数据库518篇,万方数据库34篇。
1.2 入组标准1.2.1 纳入标准 ①将干细胞应用于小口径人工血管研究的相关文献;②干细胞发挥促进内皮化作用的相关文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与此综述主要内容无关的文献;②内容重复、观点不明确及无法获取全文的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 共检索到相关文献552篇,排除471篇,最终纳入81篇,其中PubMed数据库73篇,万方数据库8篇。文献检索流程见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该综述总结了近10年来将干细胞应用于小口径人工血管最新研究进展,它们的目的都是为了抑制血栓形成和内膜增生从而提升小口径人工血管的远期通畅率。在阐述体外种植内皮细胞不足之处的基础上,文章主要展示了内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞、诱导多能干细胞、胚胎干细胞促进小口径人工血管内皮化的方式。综合上述论述,文章在此对干细胞应用于人工血管内皮化的优点予以总结:①细胞来源丰富;②取材创伤性小;③有方法减少患者或供者生理、病理状态对细胞质量的影响;④动物实验证实小口径人工血管的远期通畅率良好。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①文章侧重于干细胞在小口径人工血管内皮化的应用,但小口径人工血管的物理性能对其发挥正常生理功能也具有重要作用;②由于篇幅所限,文章未对人工血管材料制备以及干细胞其他方面作用进行论述。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章较为完整地介绍了各种干细胞在小口径人工血管内皮化的研究进展,总结了干细胞应用于人工血管内皮化的条件,并提出今后研究需要解决的问题,为感兴趣的读者展现了干细胞应用于小口径人工血管内皮化的广阔前景与未来挑战。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 近年来,在人工血管领域促进生命科学与材料科学的交叉融合成为研究热点。目前关于干细胞促进小口径人工血管内皮化的研究主要聚焦于体内招募内皮祖细胞或体外种植种子细胞,而缺乏联合体外种植与体内招募从而促进小口径人工血管内皮化的文献。在体外种植细胞的基础上,联合材料表面改性促进招募外周血内皮祖细胞是否可以进一步提升小口径人工血管的内皮化效果,值得深入研究探讨。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
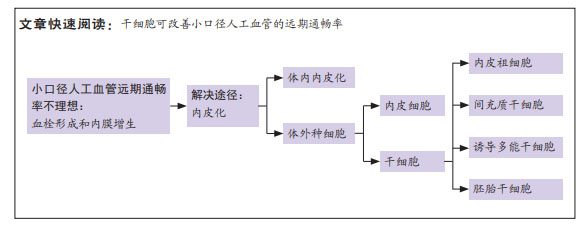
文题释义:
小口径人工血管:是一种直径在6 mm以下的、由人工合成材料或天然材料制备成的、可替代病变血管的管形植入物。
内皮化:通过材料表面改性促进细胞黏附或体外种植细胞等方法,使人工血管内表面覆盖细胞,发挥类似天然内皮的生理功能。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
相较于大口径的血管移植物,小口径(内径≤6 mm)的血管移植物由于急性血栓形成和慢性内膜增生等原因,存在远期通畅率低的问题,制约其临床应用。天然血管内皮层具有良好的抗凝血能力和抗内膜增生能力,促进小口径人工血管内皮化可以提升远期通畅率。近年来,将干细胞诱导获得内皮细胞(endothelial cells,内皮细胞)或内皮祖细胞(endothelial progenitor cells,EPCs)的研究成为热点,为干细胞作为种子细胞种植,从而实现小口径人工血管内皮化提供了坚实的研究基础。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||