中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (12): 1853-1858.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1123
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印点接触导板在胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体成形治疗中的应用
张佳园,周 全,赵加力,张 明,方 涛,王新宏,潘 伟
- 徐州医科大学附属淮安医院骨科,江苏省淮安市 223002
Application of three-dimensional printing point-contact guide template in percutaneous vertebroplasty for thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Zhang Jiayuan, Zhou Quan, Zhao Jiali, Zhang Ming, Fang Tao, Wang Xinhong, Pan Wei
- Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Huai’an Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Huai’an 223002, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
3D打印点接触导板:试验利用3个不在一条直线上的点确定一个平面的原理,设计出一种3D打印点接触导板,利用3D打印点接触导板与皮肤进行3点接触,以期避免“面接触导板”与皮肤不能完全接触吻合对穿刺定位定向的干扰,用于辅助经皮椎体成形术中椎弓根穿刺定位。
经皮椎体成形术:是指经皮通过椎弓根或椎弓根外向椎体内注入骨水泥以达到增加椎体强度和稳定性,防止塌陷,缓解疼痛,甚至部分恢复椎体高度为目的一种微创脊椎外科技术。因其具有创伤小、疼痛缓解率高、起效快等优点,已成为目前治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折、椎体转移瘤、血管瘤、骨髓瘤等疾病的主要微创方法。
摘要
背景:有些学者利用3D打印技术设计制作经皮导板辅助椎弓根穿刺,减少了经皮椎体(后凸)成形中透视次数及手术时间,增加了手术安全性。但此类导板均为“面接触导板”,应用时需导板与皮肤完全贴合,患者体位变化常导致导板与皮肤不容易完全贴合,需要多次调整甚至失去导引作用。而用于经皮椎弓根定位的3D打印点接触导板研究较少。
目的:探讨3D打印点接触导板应用于经皮椎体成形术治疗胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床效果。
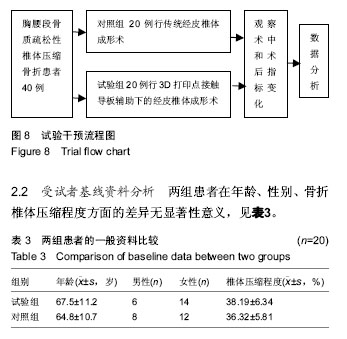
方法:2017年1月至2018年4月共纳入徐州医科大学附属淮安医院40例单节段骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折拟行经皮椎体成形术患者,将其随机分成2组,对照组20例行传统经皮椎体成形术,试验组20例行3D打印点接触导板辅助下的经皮椎体成形术。记录每次手术穿刺针到达理想穿刺位置前的透视次数以及时间、术中透视总次数、手术时间、术前及术后1 d疼痛目测类比评分等指标。
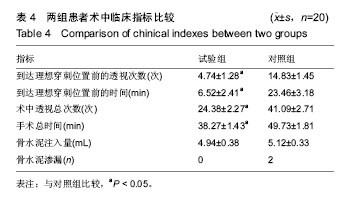
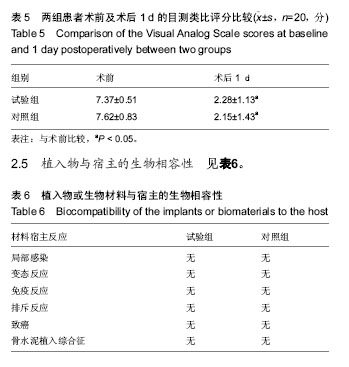
结果与结论:两组患者均顺利完成手术。试验组术中获得理想穿刺位置前的透视次数以及时间、术中透视总次数、手术时间均显著少于对照组(P < 0.05);两组患者术后疼痛目测类比评分均较术前明显降低(P < 0.05)。结果证实,3D打印点接触导板辅助胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术,有利于穿刺针精准置入,减少穿刺过程的透视次数,缩短手术时间。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-9619-2187(周全)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)