| [1]Mrosek EH,Chung HW,Fitzsimmons JS,et al.Porous tantalum biocomposites for osteochondral defect repair.Bone Joint Res.2016;5(9):403-411.[2]Whitehouse MR,Masri BA,Duncan CP,et al.Continued Good Results With Modular Trabecular Metal Augments for Acetabular Defects in Hip Arthroplasty at 7 to 11 Years. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2015;473(2):521-527.[3]Clementini M,Morlupi A,Canullo L,et al.Success rate of dental implants inserted in horizontal and vertical guided bone regenerated areas: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2012;41(7):847-852.[4]Hui C,Nizhou L,Xinchen X,et al. Smoking, radiotherapy, diabetes and osteoporosis as risk factors for dental implant failure: a meta-analysis.PloS One.2013;8(8):e71955.[5]Monje A,Alcoforado G,Padialmolina M,et al.Generalized aggressive periodontitis as a risk factor for dental implant failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Periodontol. 2014;85(10):1398-407.[6]Sanz-Sánchez I,Sanz-Martín I,Figuero E,et al.Clinical efficacy of immediate implant loading protocols compared to conventional loading depending on the type of the restoration: a systematic review.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(8): 964-982.[7]Lin MH,Mau LP,Cochran DL,et al.Risk assessment of inferior alveolar nerve injury for immediate implant placement in the posterior mandible: a virtual implant placement study.J Dent. 2014;42(3):263-270.[8]Peñarrocha-Oltra D,Aloy-Prósper A,Cervera-Ballester J,et al.Implant treatment in atrophic posterior mandibles: vertical regeneration with block bone grafts versus implants with 5.5-mm intrabony length.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2014; 29(3):659-666.[9]Schwartzarad D,Ofec R,Eliyahu G,et al.Long Term Follow-Up of Dental Implants Placed in Autologous Onlay Bone Graft.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2015;18(3):449-461.[10]Bencharit S,Byrd WC,Altarawneh S,et al.Development and Applications of Porous Tantalum TrabecularMetal‐Enhanced Titanium Dental Implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2014; 16(6):817-826.[11]叶宁.“骨小梁”金属:一种新型的牙种植体[J].中国医疗设备, 2013,28(9):174-175.[12]Nasser S,Poggie RA.Revision and salvage patellar arthroplasty using a porous tantalum implant.J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(5):562-572.[13]Brown NM,Bell JA,Jung EK,et al.The Use of Trabecular Metal Cones in Complex Primary and Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2015;30(9 Suppl):90-93.[14]Kim DG,Huja SS,Tee BC,et al.Bone ingrowth and initial stability of titanium and porous tantalum dental implants: a pilot canine study. Implant Dent.2013;22(4):399-405.[15]Lekholm U,Zarb GA.Patient selection and preparation// Branemark PI, Zarb GA,Albrek tsson T.Tissue-integrated prostheses : osseointe gration in clinical dentistry. Chicago: Quintessence,1987:199-209.[16]Premnath K,Sridevi J,Kalavathy N,et al.Evaluation of stress distribution in bone of different densities using different implant designs: a three-dimensional finite element analysis.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2013;13(4):555-559.[17]李岩峰,吴子恒,刘洪臣.下颌骨弹性模量研究现状[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2006, 4(4):241-244.[18]Schlee M,Schoor WP,Schoor ARM.Immediate Loading of Trabecular Metal-Enhanced Titanium Dental Implants: Interim Results from an International Proof-of-Principle Study.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2013;17(S1):e308-e320.[19]吴磊,谈珺,彭天洲,等.种植体骨结合强度生物力学测量方法的研究进展[J].广东牙病防治, 2016,24(4):254-256.[20]Javed F,Ahmed HB,Crespi R,et al.Role of primary stability for successful osseointegration of dental implants: Factors of influence and evaluation.Int Med Appl Sci.2013;5(4):162-167. [21]伍颖颖,宫苹.种植体初期稳定性的研究现状与进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2009, 36(6):726-728.[22]李洪友,石茂林,彭云峰.种植牙组件材料力学参数对骨组织接触应力的影响[J].厦门大学学报(自然版),2015,54(3):409-415.[23]刘学军,李智勇,夏海斌.种植体-基台连接形式对种植体周围骨组织应力分布的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2008,43(1):50-53.[24]童乘皓,吕晓飞,彭诚.种植体结构改变对种植体-骨界面皮质骨区应力影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(47): 7597-7602.[25]赵峰,韩彦峰,胡江峰.弹性模量和初始应力对种植体骨界面应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2006, 11(2):55-58.[26]Premnath K,Sridevi J,Kalavathy N,et al.Evaluation of stress distribution in bone of different densities using different implant designs: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Indian Prosthodont Soc.2013;13(4):555-559.[27]Matteo,Capelli,张玺,等.影响种植体周围骨改建的手术、生物学和种植体相关因素[J]. 中国口腔医学继续教育杂志, 2016, 8(5):238-254.[28]Levine BR,Sporer S,Poggie RA,et al.Experimental and clinical performance of porous tantalum in orthopedic surgery. Biomaterials.2006;27(27):4671-4681.[29]卿茂盛,李全.骨科应力遮挡的研究进展[J].中国骨伤, 2003, 16(1):57-58.[30]Chang YY,Huang HL,Chen HJ,et al.Antibacterial properties and cytocompatibility of tantalum oxide coatings.Surf Coat Tech.2014;259:193-198.[31]Shin SY,Han DH.Influence of a microgrooved collar design on soft and hard tissue healing of immediate implantation in fresh extraction sites in dogs.Clin Oral Implants Res.2010;21: 804-814. |
.jpg)

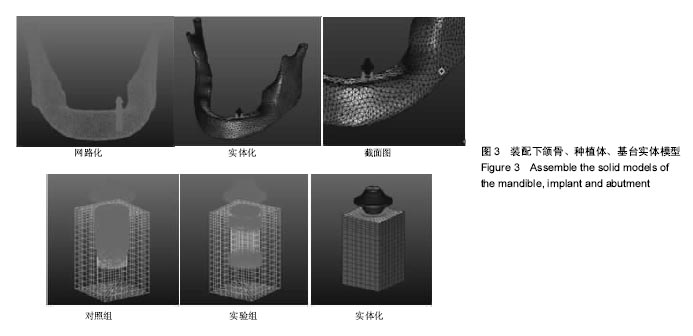
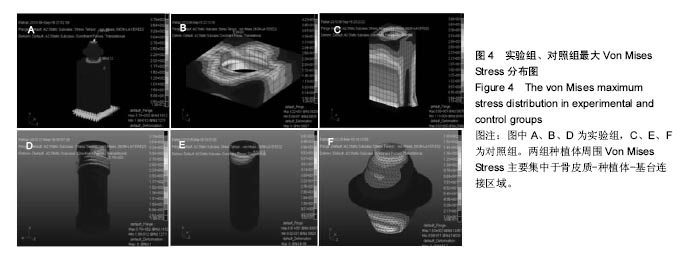
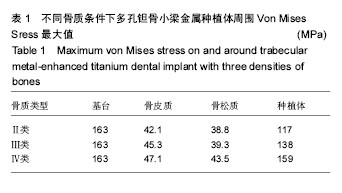
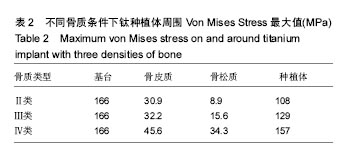
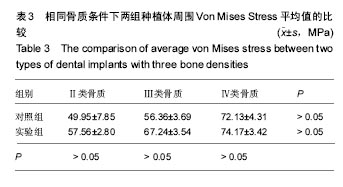
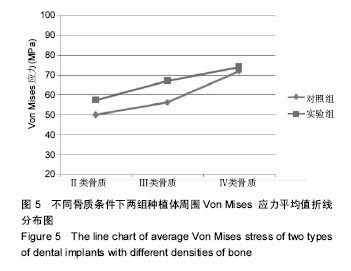
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)