| [1] Miller DL,Williams AR,Morris JE,et al. Sonoporation of erythrocytes by lithotripter shockwaves in vitro. Ultrasonics.1998;36(9):947-952.
[2] Hynynen K,McDannold N,Vykhodtseva N,et al. Noninvasive MR imaging-guided focal opening of the blood-brain barrier in rabbits.Radiology.2001; 220(3): 640-646.
[3] Meairs S,Alonso A.Ultrasound,microbubbles and the blood-brain barrier.Prog. Biophys Mol Biol.2007;93: 354-362.
[4] Martynov S,Stride E,Saffari N.The natural frequencies of microbubble oscillation in elastic vessels . The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2009; 126(6): 2963.
[5] Stride E,Pancholi K,Edirisinghe MJ,et al.Increasing the nonlinear character of microbubble oscillations at low acoustic pressures.J R Soc Interface.2008;24:807-811.
[6] 郭维,刘光达,焦阳,等.基于脉搏波信号和血管弹性腔模型的动脉血压连续测量方法[J]. 生物医用力学,2012,27(1): 85.
[7] Morgan KE,Allen JS,Dayton PA,et al.Experimental and theoretical evaluation of microbubble behavior: Effect of transmitted phase and bubble size.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control.2000;47(6): 1494-1509.
[8] Allen JS,May DJ,Ferrara KW.Dynamics of therapeutic ultrasound contrast agents. Ultrasound Med Biol.2002;28(6):805-816.
[9] Sassaroli E,Hynynen K.Resonance frequency of microbubbles in small blood vessels: a numerical study.Phys Med Biol.2005;50(22):5293-5305.
[10] Plesset MS,Prosperetti A.Bubble dynamics and cavitation. Ann Rev Fluid Mech.1977;9: 145-185.
[11] Caskey CF,Kruse DE,Dayton PA,et al.Microbubble oscillation in tubes with diameters of 12, 25, and 195 microns.Appl Phys Lett.2006;88(3):033902.
[12] Caskey CF,Kruse DE,Dayton P,et al.On the oscillations of microbubbles in tubes with diameters as small as 12 microns[C]//Ultrasonics Symposium,2005 IEEE.IEEE, 2005; 2: 854-857.
[13] Qin S,Ferrara KW.The natural frequency of nonlinear oscillation of ultrasound contrast agents in microvessels.Ultrasound Med Biol.2007;33:1140-1148.
[14] Martynov S,Stride E,Saffari N.The natural frequencies of microbubble oscillation in elastic vessels.J Acoust Soc Am.2009;126:2963-2972.
[15] Doinikov AA,Aired L,Bouakaz A.Modeling and experiments on the far-field scattering .J Fr Ophtalmol. 2010;36(15):1133-1136.
[16] Doinikov AA,Novell A,Bouakaz A.Dynamics of a Contrast Microbubble Between Two Elastic Walls.2012 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium. 2012;31: 654-662.
[17] Wiedemair W,Tukovi? ?,Jasak H,et al.On ultrasound-induced microbubble oscillation in a capillary blood vessel and its implications for the blood-brain barrier.Phys Med Biol.2012;57(4): 1020-1024.
[18] Hosseinkhah N,Hynynen K.A three-dimensional model of an ultrasound contrast agent gas bubble and its mechanical.Phys Med Biol.2012;57(3):785-808.
[19] de Jong N,Cornet R,Lancee CT.Higher harmonics of vibrating gas-filled microspheres: part 1. Simulation. Ultrasonics.1994;32(6):447-453.
[20] de Jong N,Cornet R,Lancee CT.Higher harmonics of vibrating gas-filled microspheres: part 2: Measurements.Ultrasonics.1994;32(6):455-459.
[21] Paul S,Katiyar A,Sarkar K,et al.Material characterization of the encapsulation of an ultrasound contrast microbubble and its subharmonic response: strain-softening interfacial model.J Acoust Soc Am. 2010;127(6):3846-3850.
[22] Li Q,Matula TJ,Tu J,et al.Modeling complicated rheological behaviors in encapsulating shells of lipid-coated microbubbles accounting for nonlinear changes of both shell viscosity and elasticity.Phys Med Biol.2013;58(4):985-998.
[23] 程茜,钱梦騄.超声微泡造影剂的低频动力学行为[J].声学技术,2006,25(4):292-298.
[24] 邱晓晖,沈圆圆,钱建庭,等.刚性微管内微泡动力学行为的有限元数值分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2011,28(5): 911-915.
[25] Shen YY,Wang TF,Diao X,et al.Numerical analysis of interaction between microbubble and elastic microvessel in low frequency ultrasound field using fluid solid interaction method [C].Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI),2012 IEEE-EMBS International Conference on IEEE,2012:733-736.
[26] VanBavel E.Effects of shear stress on endothelial cells: possible relevance for ultrasound applications.Prog Biophys Mol Biol.2007;93:374-383.
[27] Mukundakrishnan K,Ayyaswamy PS,Eckmann DM.Bubble motion in a blood vessel: shear stress induced endothelial cell injury.Biomech Eng.2009; 131:074516.
[28] Qin S,Ferrara KW.Acoustic response of compliable microvessels containing ultrasound contrast agents. Phys Med Biol.2006;51(20):5065.
[29] Sergey M,Erik K,Nader S,et al.Forced vibration of a bubble in a liquid-filled elastic vessel.J Acoust Soc Am.2012;130(5):2700-2708.
[30] Shen YY,Wang TF,Chin CT,et al.Interaction between microbubble and elastic microvessel in low frequency ultrasound field using finite element method. Chin Sci Bull.2013;58(3):291-298.
[31] Oishi Y,Kakimoto T,Yuan W,et al.Fetal Gene Therapy for Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency by Intrahepatic Plasmid DNA-Micro-Bubble Injection Combined with Hepatic Ultrasound Insonation. Ultrasound Med Biol.2016;42(6):1357-1361.
[32] Wang G,Zhang Q,Zhuo Z,et al.Enhanced Homing of CXCR-4 Modified Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Acute Kidney Injury Tissues by Micro- Bubble-Mediated Ultrasound Exposure. Ultrasound Med Biol.2016;42(2):539-548.
[33] Sajjadi B,Raman AA,Ibrahim S.Influence of ultrasound power on acoustic streaming and micro-bubbles formations in a low frequency sono-reactor: mathematical and 3D computational simulation. Ultrason Sonochem.2015;24:193-203.
[34] Chiu AH,Haluszkiewicz E,McAuliffe W.Micro-bubble transcranial Doppler ultrasound for exclusion of right-to-left circulatory shunts: why should we provide the service?J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol.2014;58(4): 464-468.
[35] Tong J,Ding J,Shen X,et al.Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation enhancement in myocardial infarction rat model under ultrasound combined with nitric oxide microbubbles.PLoS One.2013;8(11):e80186.
[36] Ren ST,Shen S,He XY,et al.The Effect of Docetaxel-Loaded Micro-Bubbles Combined with Low-Frequency Ultrasound in H22 Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Bearing Mice.Ultrasound Med Biol.2016; 42(2):549-560. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
微泡超声对比剂:不仅能增强超声造影,而且也能作为运送基因或药物的载体。在超声作用下, 含基因或药物的微泡能穿透血管内皮,释放基因或药物, 达到靶向治疗目的。 自Gramiak 等将超声微泡对比剂应用于临床以来, 超声微泡的研究得到了很大的发展。特别是第3 代微泡对比剂如Optison®的出现,以白蛋白、非离子表面活性剂、脂质或高分子多聚物为壳膜,内含低弥散度的氟碳气体,使微泡的稳定性显著提高。
微泡振动与外部超声激励、微血管尺寸和管壁弹性间的关系:激励频率增加,微泡的振动幅度减弱,其振动频率增加,而微血管的扩张与收缩幅度减弱,且其能更快地趋于稳定。激励声压变化对微泡与微血管的影响,与激励频率相反;血管的尺寸越小,对微泡振动频率和幅值的限制越强烈,微泡振动频率与振幅均增加,反之亦然;管壁杨氏模量和泊松比增加,微泡的振动幅度降低,但振动频率增加;微泡半径的增加,血管的收缩、扩张幅度和频率均增加。
文题释义:
微泡超声对比剂:不仅能增强超声造影,而且也能作为运送基因或药物的载体。在超声作用下, 含基因或药物的微泡能穿透血管内皮,释放基因或药物, 达到靶向治疗目的。 自Gramiak 等将超声微泡对比剂应用于临床以来, 超声微泡的研究得到了很大的发展。特别是第3 代微泡对比剂如Optison®的出现,以白蛋白、非离子表面活性剂、脂质或高分子多聚物为壳膜,内含低弥散度的氟碳气体,使微泡的稳定性显著提高。
微泡振动与外部超声激励、微血管尺寸和管壁弹性间的关系:激励频率增加,微泡的振动幅度减弱,其振动频率增加,而微血管的扩张与收缩幅度减弱,且其能更快地趋于稳定。激励声压变化对微泡与微血管的影响,与激励频率相反;血管的尺寸越小,对微泡振动频率和幅值的限制越强烈,微泡振动频率与振幅均增加,反之亦然;管壁杨氏模量和泊松比增加,微泡的振动幅度降低,但振动频率增加;微泡半径的增加,血管的收缩、扩张幅度和频率均增加。.jpg) 文题释义:
微泡超声对比剂:不仅能增强超声造影,而且也能作为运送基因或药物的载体。在超声作用下, 含基因或药物的微泡能穿透血管内皮,释放基因或药物, 达到靶向治疗目的。 自Gramiak 等将超声微泡对比剂应用于临床以来, 超声微泡的研究得到了很大的发展。特别是第3 代微泡对比剂如Optison®的出现,以白蛋白、非离子表面活性剂、脂质或高分子多聚物为壳膜,内含低弥散度的氟碳气体,使微泡的稳定性显著提高。
微泡振动与外部超声激励、微血管尺寸和管壁弹性间的关系:激励频率增加,微泡的振动幅度减弱,其振动频率增加,而微血管的扩张与收缩幅度减弱,且其能更快地趋于稳定。激励声压变化对微泡与微血管的影响,与激励频率相反;血管的尺寸越小,对微泡振动频率和幅值的限制越强烈,微泡振动频率与振幅均增加,反之亦然;管壁杨氏模量和泊松比增加,微泡的振动幅度降低,但振动频率增加;微泡半径的增加,血管的收缩、扩张幅度和频率均增加。
文题释义:
微泡超声对比剂:不仅能增强超声造影,而且也能作为运送基因或药物的载体。在超声作用下, 含基因或药物的微泡能穿透血管内皮,释放基因或药物, 达到靶向治疗目的。 自Gramiak 等将超声微泡对比剂应用于临床以来, 超声微泡的研究得到了很大的发展。特别是第3 代微泡对比剂如Optison®的出现,以白蛋白、非离子表面活性剂、脂质或高分子多聚物为壳膜,内含低弥散度的氟碳气体,使微泡的稳定性显著提高。
微泡振动与外部超声激励、微血管尺寸和管壁弹性间的关系:激励频率增加,微泡的振动幅度减弱,其振动频率增加,而微血管的扩张与收缩幅度减弱,且其能更快地趋于稳定。激励声压变化对微泡与微血管的影响,与激励频率相反;血管的尺寸越小,对微泡振动频率和幅值的限制越强烈,微泡振动频率与振幅均增加,反之亦然;管壁杨氏模量和泊松比增加,微泡的振动幅度降低,但振动频率增加;微泡半径的增加,血管的收缩、扩张幅度和频率均增加。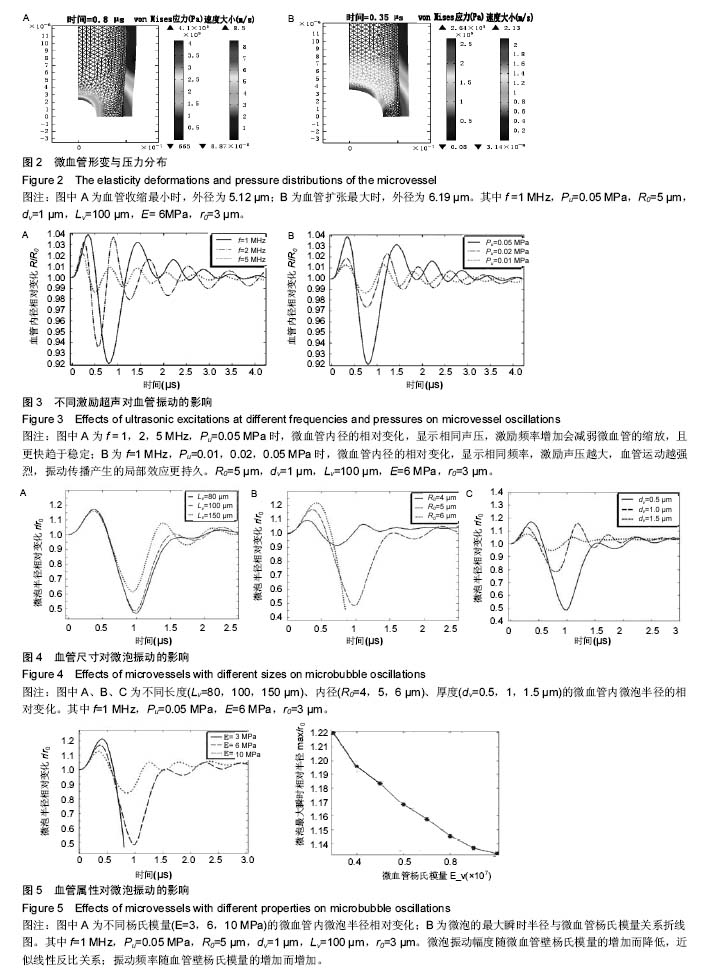
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
微泡超声对比剂:不仅能增强超声造影,而且也能作为运送基因或药物的载体。在超声作用下, 含基因或药物的微泡能穿透血管内皮,释放基因或药物, 达到靶向治疗目的。 自Gramiak 等将超声微泡对比剂应用于临床以来, 超声微泡的研究得到了很大的发展。特别是第3 代微泡对比剂如Optison®的出现,以白蛋白、非离子表面活性剂、脂质或高分子多聚物为壳膜,内含低弥散度的氟碳气体,使微泡的稳定性显著提高。
微泡振动与外部超声激励、微血管尺寸和管壁弹性间的关系:激励频率增加,微泡的振动幅度减弱,其振动频率增加,而微血管的扩张与收缩幅度减弱,且其能更快地趋于稳定。激励声压变化对微泡与微血管的影响,与激励频率相反;血管的尺寸越小,对微泡振动频率和幅值的限制越强烈,微泡振动频率与振幅均增加,反之亦然;管壁杨氏模量和泊松比增加,微泡的振动幅度降低,但振动频率增加;微泡半径的增加,血管的收缩、扩张幅度和频率均增加。
文题释义:
微泡超声对比剂:不仅能增强超声造影,而且也能作为运送基因或药物的载体。在超声作用下, 含基因或药物的微泡能穿透血管内皮,释放基因或药物, 达到靶向治疗目的。 自Gramiak 等将超声微泡对比剂应用于临床以来, 超声微泡的研究得到了很大的发展。特别是第3 代微泡对比剂如Optison®的出现,以白蛋白、非离子表面活性剂、脂质或高分子多聚物为壳膜,内含低弥散度的氟碳气体,使微泡的稳定性显著提高。
微泡振动与外部超声激励、微血管尺寸和管壁弹性间的关系:激励频率增加,微泡的振动幅度减弱,其振动频率增加,而微血管的扩张与收缩幅度减弱,且其能更快地趋于稳定。激励声压变化对微泡与微血管的影响,与激励频率相反;血管的尺寸越小,对微泡振动频率和幅值的限制越强烈,微泡振动频率与振幅均增加,反之亦然;管壁杨氏模量和泊松比增加,微泡的振动幅度降低,但振动频率增加;微泡半径的增加,血管的收缩、扩张幅度和频率均增加。