中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 236-241.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.02.015
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
人天然型和诱导型CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127-Treg细胞表型多样性的比较
王海灏1,朱 莉2,仰霈雯3,郭倩男1
- 华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院,1心脏大血管外科、同济医院心肺移植研究所;2血液内科,湖北省武汉市 430030,3华中科技大学同济医学院,湖北省武汉市 430030
Phenotypic diversity of human nature and induced CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127- regulatory T cells
Wang Hai-hao1, Zhu Li2, Yang Pei-wen3, Guo Qian-nan1
- 1Cardiopulmonary Transplantation Institute of Tongji Hospital, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Hematology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China; 3Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
调节性T细胞:调节性T细胞是一类控制体内自身免疫反应性的T细胞亚群,分为天然产生的自然调节性T细胞和诱导产生的适应性调节性T细胞,如Th3、Tr1,CD8 Treg、NKT细胞等,与自身免疫性疾病的发生关系密切,其异常表达可导致自身免疫性疾病。
细胞表型:细胞表型是细胞的表现形式。遗传后染色体自有重组会产生新的“基因型”,但不同的基因型不一定都有不同的表现,而生物体外在表现出来的就是所谓“表型”。比如隐形是a,显性是A,基因型Aa和AA表现出来的样子可以是一样的(完全显性状况下),即为他们的表型相同。
背景:人调节性T细胞(Treg)分为天然型Treg(nTreg)和诱导型Treg(iTreg)。虽然CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127-是目前最公认的Treg细胞表型,但是nTreg与iTreg的细胞表型多样性,尤其是其共表达细胞因子的情况仍不清楚。
目的:了解并比较nTreg与iTreg的细胞表型多样性,并通过分析其表达细胞因子的情况以推测可能的作用途径。
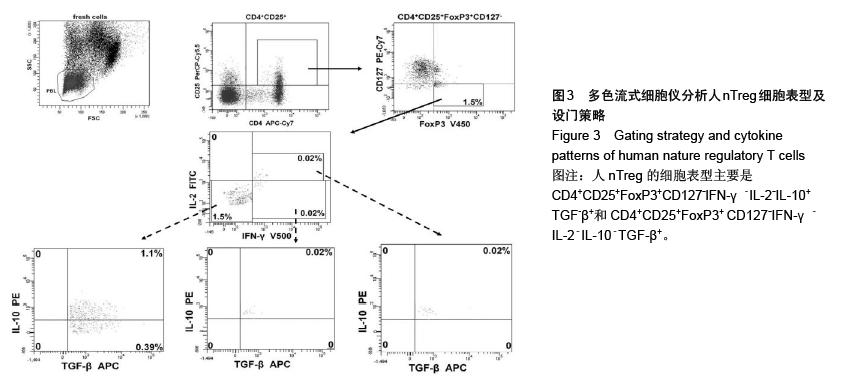
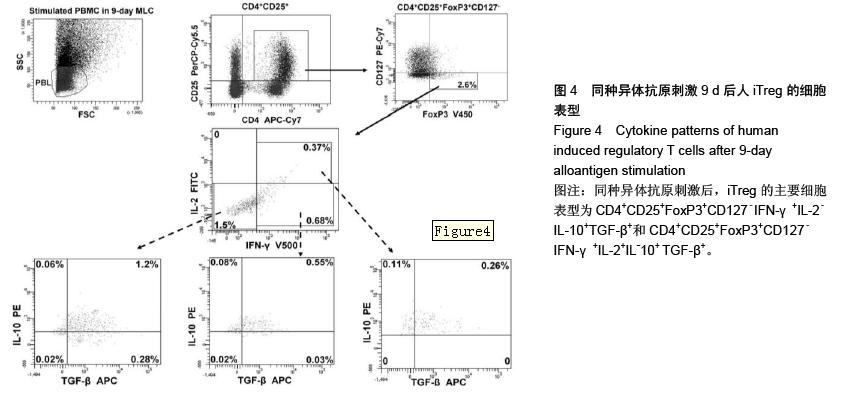
方法:从5例健康受试者的外周血中分离得到外周血单个核细胞,以8色流式细胞仪检测(FACSCanto II)并分析CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127-nTreg的细胞表型和其共表达细胞因子的情况;将外周血单个核细胞在体外接受同种异体抗原刺激,进行混合淋巴细胞培养,9 d后以8色流式细胞仪检测并分析CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127- iTreg的细胞表型和其共表达细胞因子的情况。
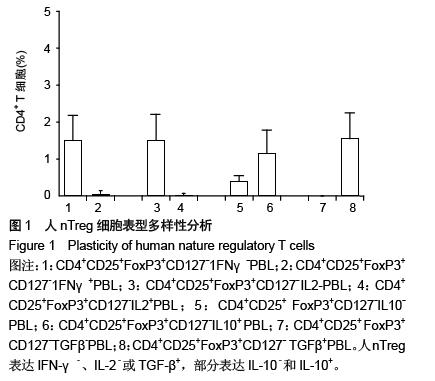
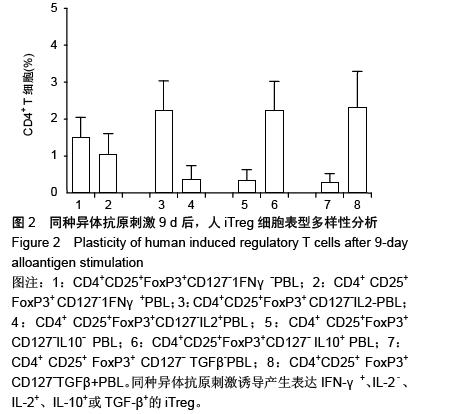
结果与结论:CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127-nTreg占全部CD4+ T细胞的比例为(1.5±0.70)%,且几乎所有的nTreg细胞均表达IFN-γ-、IL-2-或TGF-β+,部分表达IL-10-和IL-10+;同种异体抗原刺激诱导产生表达IFN-γ+、IL-2-、IL-2+、IL-10+或TGF-β+的CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127-iTreg;人nTreg的细胞表型主要是CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127-IFN-γ-IL-2-IL-10+TGF-β+和CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127-IFN-γ-IL-2-IL-10-TGF-β+,其占全部CD4+ T细胞的比例分别为(1.1±0.59)%和(0.39±0.16)%;iTreg的主要细胞表型为CD4+CD25+ FoxP3+ CD127-IFN-γ+IL-2-IL-10+TGF-β+和CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127-IFN-γ+IL-2+IL-10+TGF-β+。结果说明,CD4+ CD25+FoxP3+CD127-nTreg的特征是IFN-γ-IL-2-,同时产生白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β,或者只产生转化生长因子β而不产生白细胞介素10,且nTreg在体外通过混合淋巴细胞培养是不会被增殖的。混合淋巴细胞培养刺激后,IFN-γ+iTreg增殖明显,其中约1/3的IFN-γ+iTreg表达IL-2+,而2/3的IFN-γ+iTreg表达IL-2-,且这两组IFN-γ+iTreg均同时分泌白细胞介素10和转化生长因子TGF-β。产生细胞因子转化生长因子β和白细胞介素10可能是CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127- Treg具有免疫抑制功能的原因。
ORCID: 0000-0002-9717-6461(王海灏)