| [1] Posada-Duque RA, Barreto GE, Cardona-Gomez GP. Protection after stroke: cellular effectors of neurovascular unit integrity. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:231.
[2] Kemp JA, McKernan RM. NMDA receptor pathways as drug targets. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5 Suppl:1039-1042.
[3] Hao L, Zou Z, Tian H, et al. Stem cell-based therapies for ischemic stroke. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:468748.
[4] Durukan A, Tatlisumak T. Acute ischemic stroke: overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2007;87(1):179-197.
[5] Overgaard K. Thrombolytic therapy in experimental embolic stroke. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1994;6(3):257-286.
[6] Shah ZA, Namiranian K, Klaus J, et al. Use of an optimized transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery protocol for the mouse stroke model. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2006; 15(4):133-138.
[7] Tsiminis G, Klari? TS, Schartner EP, et al. Generating and measuring photochemical changes inside the brain using optical fibers: exploring stroke. Biomed Opt Express. 2014; 5(11):3975-3980.
[8] Lozano JD, Abulafia DP, Danton GH, et al. Characterization of a thromboembolic photochemical model of repeated stroke in mice. J Neurosci Methods. 2007;162(1-2):244-254.
[9] Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Busto R, et al. Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol. 1985;17(5):497-504.
[10] Loihl AK, Asensio V, Campbell IL, et al. Expression of nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-2 following permanent focal ischemia and the role of nitric oxide in infarct generation in male, female and NOS-2 gene-deficient mice. Brain Res. 1999;830 (1):155-14.
[11] Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, et al. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(4):355-369.
[12] Ferrer I, Planas AM. Signaling of cell death and cell survival following focal cerebral ischemia: life and death struggle in the penumbra. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003;62(4): 329-339.
[13] Jin Z, Wu J, Oh SY, et al. The effect of stress on stroke recovery in a photothrombotic stroke animal model. Brain Res. 2010;1363:191-197.
[14] Van Winkle JA, Chen B, Lei IF, et al. Concurrent middle cerebral artery occlusion and intra-arterial drug infusion via ipsilateral common carotid artery catheter in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 2013;213(1):63-69.
[15] García-Bonilla L, Rosell A, Torregrosa G, et al. Recommendations guide for experimental animal models in stroke research. Neurologia. 2011;26(2):105-110.
[16] Durukan A, Strbian D, Tatlisumak T. Rodent models of ischemic stroke: a useful tool for stroke drug development. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(4):359-370.
[17] Zhen G, Doré S. Optimized protocol to reduce variable outcomes for the bilateral common carotid artery occlusion model in mice. J Neurosci Methods. 2007;166(1):73-80.
[18] Wu L, Xu L, Xu X, et al. Keep warm and get success: the role of postischemic temperature in the mouse middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Brain Res Bull. 2014;101:12-17.
[19] Richard Green A, Odergren T, Ashwood T. Animal models of stroke: do they have value for discovering neuroprotective agents? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24(8):402-408.
[20] Smith WS. Pathophysiology of focal cerebral ischemia: a therapeutic perspective. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004;15(1 Pt 2):S3-12.
[21] MacManus JP, Buchan AM. Apoptosis after experimental stroke: fact or fashion? J Neurotrauma. 2000;17(10):899-914.
[22] Fisher M, Schaebitz W. An overview of acute stroke therapy: past, present, and future. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(21): 3196-3206.
[23] Mergenthaler P, Dirnagl U, Meisel A. Pathophysiology of stroke: lessons from animal models. Metab Brain Dis. 2004; 19(3-4):151-167.
[24] Sugawara T, Fujimura M, Noshita N, et al. Neuronal death/survival signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. NeuroRx. 2004;1(1):17-25.
[25] Sakata H, Narasimhan P, Niizuma K, et al. Interleukin 6-preconditioned neural stem cells reduce ischaemic injury in stroke mice. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 11):3298-3310.
[26] Garcia JH, Liu KF, Ho KL. Neuronal necrosis after middle cerebral artery occlusion in Wistar rats progresses at different time intervals in the caudoputamen and the cortex. Stroke. 1995;26(4):636-642; discussion 643.
[27] Zhan B, Zhang GW, Chen J, et al.A more consistent intraluminal rhesus monkey model of ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(23): 2087-2094
[28] Takano K, Tatlisumak T, Formato JE, et al. Glycine site antagonist attenuates infarct size in experimental focal ischemia. Postmortem and diffusion mapping studies. Stroke. 1997;28(6):1255-1262; discussion 1263.
[29] Wang J, Feng X, Du Y, et al. Combination treatment with progesterone and rehabilitation training further promotes behavioral recovery after acute ischemic stroke in mice. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2013;31(4):487-499.
[30] Hoffmann S, Beyer C, Zendedel A. Comparative Analysis of Gonadal Steroid-Mediated Neuroprotection after Transient Focal Ischemia in Rats: Route of Application and Substrate Composition. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. in press.
[31] Robertson CL, Fidan E, Stanley RM, et al. Progesterone for neuroprotection in pediatric traumatic brain injury. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2015;16(3):236-244.
[32] dos Santos RL, da Silva FB, Ribeiro RF Jr, et al. Sex hormones in the cardiovascular system. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014;18(2):89-103.
[33] McKay R. Stem cells in the central nervous system. Science. 1997;276(5309):66-71.
[34] Walker MR, Patel KK, Stappenbeck TS. The stem cell niche. J Pathol. 2009;217(2):169-180.
[35] Sawada M, Sawamoto K. Mechanisms of neurogenesis in the normal and injured adult brain. Keio J Med. 2013;62(1):13-28. |
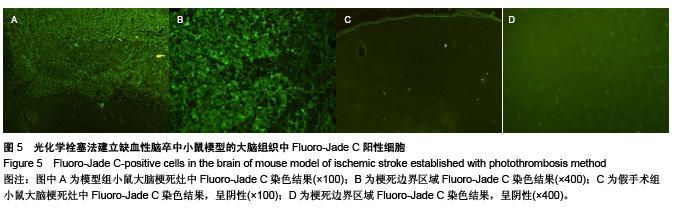
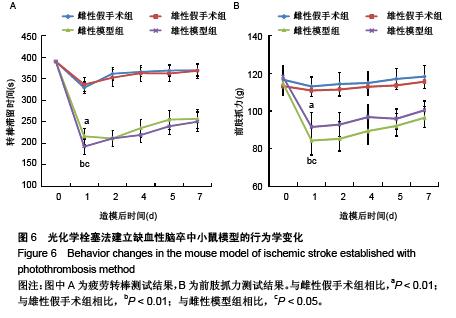
.jpg)