中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (11): 1672-1679.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.11.006
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
低能体外冲击波和低剂量间歇甲状旁腺素干预成骨细胞的增殖和分化
刘长剑1,王 李2,罗宗键3
- 1大连医科大学附属第一医院骨科,辽宁省大连市 116001;2大连市友谊医院医学影像科,辽宁省大连市 116001;3长春市中医药大学附属第一医院骨科,吉林省长春市 130011
-
修回日期:2014-01-07出版日期:2014-03-12发布日期:2014-03-12 -
通讯作者:罗宗键,博士,副教授。长春市中医药大学附属第一医院骨科,吉林省长春市 130011 -
作者简介:Liu Chang-jian, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China
Low-density extracorporeal shock wave and low-dose intermittent recombinant human parathyroid hormone 1-34 influence proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts
Liu Chang-jian1, Wang Li2, Luo Zong-jian3
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China; 2 Department of Radiology, Dalian Friendship Hospital, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China ; 3 Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130011, Jilin Province, China
-
Revised:2014-01-07Online:2014-03-12Published:2014-03-12 -
Contact:Luo Zong-jian, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130011, Jilin Province, China -
About author:刘长剑,男,1973年生,辽宁省大连市人,汉族,2008年吉林大学白求恩医学部毕业,博士,副教授。
摘要:
背景:体外冲击波等应力刺激可促进成骨,甲状旁腺激素激素也参与调控骨代谢。
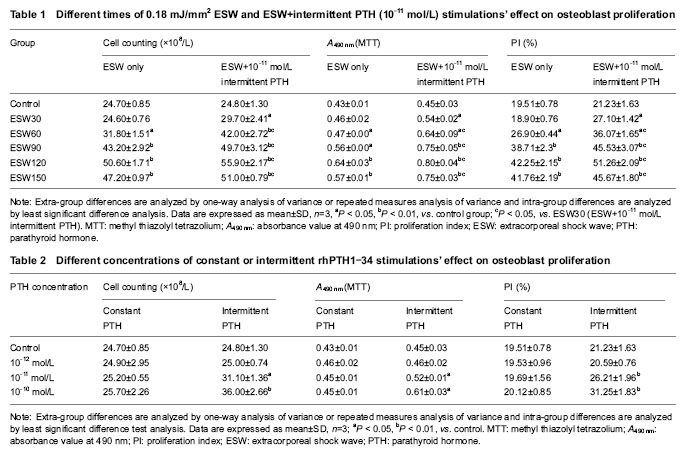
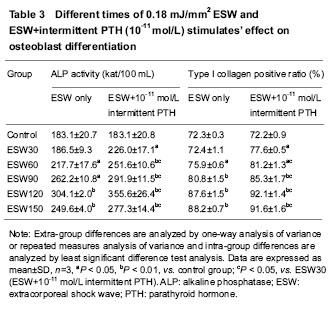
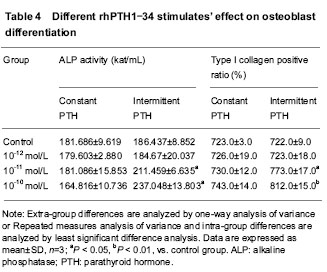
结果与结论:60-150次0.18 mJ/mm2低能体外冲击波刺激、间歇人重组甲状旁腺素1-34 (10-11和10-10 mol/L)刺激以及低能体外冲击波+间歇人重组甲状旁腺素1-34 (10-11 mol/L)刺激均可显著促进体外培养大鼠成骨细胞增殖和成骨分化(P < 0.05),其中60-150次低能体外冲击波刺激+间歇人重组甲状旁腺素1-34刺激各组作用最强(P < 0.05)。结果证实,适当的低能体外冲击波应力刺激和低剂量间歇人重组甲状旁腺素1-34刺激联合应用可显著促进体外培养大鼠成骨细胞的增殖和成骨分化。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘长剑,王 李,罗宗键. 低能体外冲击波和低剂量间歇甲状旁腺素干预成骨细胞的增殖和分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(11): 1672-1679.
Liu Chang-jian, Wang Li, Luo Zong-jian. Low-density extracorporeal shock wave and low-dose intermittent recombinant human parathyroid hormone 1-34 influence proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(11): 1672-1679.
Detection of PI value by flow cytometry
Different patterns of rhPTH1-34 stimulations’ effect on ALP activity
Cooperation of 30-150 times of ESW and 10-11 mol/L intermittent rhPTH1-34 stimulations’ effect on ALP activity

| [1] Saussine C. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Prog Urol. 2013;23(14):1168-1171. [2] Kolk A, Auw Yang KG, Tamminga R, et al. Radial extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in patients with chronic rotator cuff tendinitis: a prospective randomised double-blind placebo-controlled multicentre trial. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11):1521-1526. [3] Hausner T, Nógrádi A.The use of shock waves in peripheral nerve regeneration: new perspectives? Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013;109:85-98. [4] Tailly GG. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy today. Indian J Urol. 2013;29(3):200-207.[5] Liu J, Zang YJ. Comparative study between three analgesic agents for the pain management during extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Urol J. 2013;26; 10(3):942-945.[6] Mikami Y, Matsumoto T, Kano K, et al. Current status of drug therapies for osteoporosis and the search for stem cells adapted for bone regenerative medicine. Anat Sci Int. 2014;89(1):1-10.[7] Teotia PK, Hussein KE, Park KM, et al. Mouse adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells expressed osteogenic specific transcripts of osteocalcin and parathyroid hormone receptor during osteogenesis. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(8): 3102-3107. [8] Sheyn D, Cohn Yakubovich D, Kallai I, et al. PTH promotes allograft integration in a calvarial bone defect. Mol Pharm. 2013;10(12):4462-4471. [9] Smith BJ, Bu SY, Wang Y, et al. Comparative study of the bone metabolic response to dried plum supplementation and PTH treatment in adult, osteopenic ovariectomized rat. Bone. 2013;58C:151-159. [10] Zhong G, Pei FX, Li SF, et al. Experimental study on the proliferation and function of osteoblast cell induced by pBLAST49-mVEGF gene transfection. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006;37(1):44-47.[11] Ejersted C, Andreassen TT, Nilsson MHL, et al. Human parathyroid hormone(1-34) increases bone formation and strength of cortical bone in aged rats. Europe J Endocrinol. 1994;130(2):201-207.[12] Xu J, Rong H, Ji H, et al. Effects of different dosages of parathyroid hormone-related protein 1-34 on the bone metabolism of the ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;93(3):276-287.[13] Chen YJ, Kuo YR, Yang KD, et al. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and p38 kinase in shock wave-promoted bone formation of segmental defect in rats. Bone. 2004;34(3):466-477.[14] Wang FS, Yang KD, Kuo YR, et al. Temporal and spatial expression of bone morphogenetic proteins in extracorporeal shock wave-promoted healing of segmental defect. Bone. 2003;32(4):387-396.[15] 15 Ishizuya T, Yokose S, Hori M, et al. Parathyroid hormone exerts disparate effects on osteoblast differentiation depending on exposure time in rat osteoblastic cells. J Clin Invest. 1997;99(12):2961-2970.[16] UzawaT, HoriM, Ejiri S, et al. Comparison of the effects of intermittent and continuous administration of human Parathyroid hormone (1-34) on rat bone. Bone. 1995;16(4): 477-484.[17] Wang YH, Qiu Y, Han XD, et al. Haploinsufficiency of endogenous parathyroid hormone-related peptide impairs bone fracture healing. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013; 40(11):715-723. [18] Khan MP, Mishra JS, Sharan K, et al. A novel flavonoid C-glucoside from Ulmus wallichiana preserves bone mineral density, microarchitecture and biomechanical properties in the presence of glucocorticoid by promoting osteoblast survival: a comparative study with human parathyroid hormone. Phytomedicine. 2013;20(14):1256-1266. [19] Hamedifar H, Salamat F, Saffarion M, et al. a novel approach for high level expression of soluble recombinant human parathyroid hormone (rhPTH 1-34) in Escherichia coli. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2013;5(3):193-201.[20] Pereira Vasconcelos DF, Marques MR, Benatti BB, et al. Intermittent PTH administration improves periodontal healing in rats. J Periodontol. 2013.[21] Klein-Nulend J, Semeins CM, Burger EH. Metabolism in primary mouse osteoblastic Prostaglandin mediated modulation of transforming growth factor-β metabolism in primary mouse osteoblastic cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1996;168:1-7.[22] Reich KM, Mcallister TN, Gudi S. Activation of G protein mediates flow-induced prostaglandin E2 production in osteoblast. Eradocranology. 1997;138:1014-1018.[23] Ajubi NE, Klein-Nulend J, Nijweide PJ, et al. Pulsatile fluid flow increases prostaglandin production by cultured chicken osteocytes--a cytoskeleton-dependent process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;225:62-68.[24] Ueberle F, Rad AJ. Characterization of unfocused/weakly focused pressure pulse sources for extracorporeal pain therapy (“Radial Shock Wave Therapy” Sources). Biomed Tech (Berl). 2013. [25] Zhang X, Yan X, Wang C, et al. The dose-effect relationship in extracorporeal shock wave therapy: the optimal parameter for extracorporeal shock wave therapy. J Surg Res. 2014;186(1):484-492. [26] Moon SW, Kim JH, Jung MJ, et al. The effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on lower limb spasticity in subacute stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013;37(4): 461-470. [27] Schmitz C, Császár NB, Rompe JD, et al. Treatment of chronic plantar fasciopathy with extracorporeal shock waves (review). J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8(1):31. [28] Troncati F, Paci M, Myftari T, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy reduces upper limb spasticity and improves motricity in patients with chronic hemiplegia: a case series. NeuroRehabilitation. 2013;33(3):399-405.[29] Qin L, Fok P, Lu H, et al. Low intensity pulsed ultrasound increases the matrix hardness of the healing tissues at bone-tendon insertion-a partial patellectomy model in rabbits. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006;21(4):387-394.[30] Vulpiani MC, Vetrano M, Conforti F, et al. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on fracture nonunions. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2012;41(9):E122-E127.[31] Fovargue DE, Mitran S, Smith NB, et al. Experimentally validated multiphysics computational model of focusing and shock wave formation in an electromagnetic lithotripter. J Acoust Soc Am. 2013;134(2):1598-609. [32] Speed C. A systematic review of shockwave therapies in soft tissue conditions: focusing on the evidence. Br J Sports Med. 2013. [33] Ha CH, Kim S, Chung J, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave stimulates expression of the angiogenic genes via mechanosensory complex in endothelial cells: mimetic effect of fluid shear stress in endothelial cells. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(4):4168-4177. [34] Császár NB, Schmitz C. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8:22. [35] Suhr F, Delhasse Y, Bungartz G, et al. Cell biological effects of mechanical stimulations generated by focused extracorporeal shock wave applications on cultured human bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(2): 951-964. [36] Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/ osteogenesis inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Nad Acad Sci USA. 1998;95: 3597-3602.[37] Saini V, Marengi DA, Barry KJ, et al. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide type 1 receptor (PPR) signaling in osteocytes regulates anabolic and catabolic skeletal responses to PTH. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(28): 20122-20134. [38] Dossing DA, Radeff JM, Sanders J, et al. Parathyroid hormone stimulates translocation of protein kinase C isozymes in UMR-106 osteoblastic osteosarcoma cells. Bone. 2001;29(3):223-230.[39] Lee SJ, Kang JH, Kim JY, et al. Dose-related effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciitis. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013;37(3):379-388. [40] Raabe O, Shell K, Goessl A, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave on proliferation and differentiation of equine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Am J Stem Cells. 2013;2(1):62-73. [41] Rao DS, Parikh N, Palnitkar S, et al. The effect of endogenous parathyroid hormone in iliac bone structure and turnover in healthy postmenopausal women. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;93(3):288-295.[42] Tamura Y, Kaji H. Parathyroid hormone and Wnt signaling. Clin Calcium. 2013;23(6):847-852. |
| [1] | 麻海亮,于新波,刘梦东,贾 婧,符大勇. 恒牙牙体硬组织钙磷成分的检测:分光光度法与EDTA滴定法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(46): 7432-7436. |
| [2] | 栗炳南,李卫东,林俊堂,丰慧根. 人胶质细胞源性神经营养因子和血管内皮生长因子165双基因真核表达载体的构建与鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(29): 4675-4682. |
| [3] | 麦志辉,张静兰,卢红飞,陈 奇,梁焕友,艾 虹. 牙周膜牵引成骨快速远中移动尖牙的可行性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(41): 7255-7264. |
Design
.jpg)
.jpg)
1大量研究证明,频率、能量强度适合的体外冲击波能促进骨愈合,而周期性低剂量给予甲状旁腺素可使动物活体成骨作用增加。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||