中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (41): 7255-7264.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.41.011
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
牙周膜牵引成骨快速远中移动尖牙的可行性
麦志辉1,张静兰2,卢红飞1,陈 奇1,梁焕友1,艾 虹1
- 1中山大学第三附属医院口腔科,广东省广州市 510630;2广东省口腔医院儿童牙科,广东省广州市 510280
-
收稿日期:2013-03-30修回日期:2013-05-22出版日期:2013-10-08发布日期:2013-11-01 -
通讯作者:艾虹,硕士,教授,广东省口腔医院儿童牙科,广东省广州市 510280 Aih_zssy09@126.com -
作者简介:麦志辉☆,男,1977年生,广东省番禺市人,汉族,2012年中山大学毕业,博士,主治医师,主要从事口腔正畸学方面的研究。 并列第一作者:张静兰,硕士。 -
基金资助:广东省自然科学基金(s2011010004629)*
Rapid canine distal movement through distraction osteogenesis of the periodontal ligament
Mai Zhi-hui1, Zhang Jing-lan2, Lu Hong-fei1, Chen Qi1, Liang Huang-you1, Ai Hong1
- 1 Department of Stomatology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China;2 Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Guangdong Provincial Stomatological Hospital, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2013-03-30Revised:2013-05-22Online:2013-10-08Published:2013-11-01 -
Contact:Ai Hong, Master, Professor, Department of Stomatology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China Aih_zssy09@126.com -
About author:Mai Zhi-hui☆, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China maiya2007@126.com Zhang Jing-lan, Master, Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Guangdong Provincial Stomatological Hospital, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China Zhang Jing-lan and Mai Zhi-hui contributed equally to this paper. -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. s2011010004629*
摘要:
背景:牵引成骨应用于患者的尖牙远中移动,能大幅度提高牙齿的移动速度,同时保护磨牙支抗。但关于牵引的速率、尖牙的牙髓活力、尖牙的牙周组织改建及该技术的生物学机制目前研究甚少。 目的:在成人患者中,评估使用牙周膜牵张成骨快速远中移动尖牙的可行性,同时监测牙髓活力、牙根吸收及尖牙牙周组织改建情况。 方法:选取9例成年错牙合患者,拔除上颌两侧第一双尖牙,通过改良牵张装置快速远中移动尖牙至预定的位置。利用头颅定位片及根尖片测量尖牙远中移动距离、支抗丧失、根尖吸收及牙槽间隔改建情况;并监测尖牙的牙髓及牙周情况。 结果与结论:通过牙周膜牵张成骨能在12-16 d内快速远中移动上颌尖牙至预定位置,尖牙远中移动7.18 mm 及远中倾斜(13.24±2.87)°;支抗丧失为0.5 mm;未见明显根尖吸收及牙周组织丧失;尖牙的牙髓活力在牵引后迅速下降,但3个月后明显恢复。结果显示牙周膜牵引成骨可显著加快尖牙移动速度,缩短矫治时间,同时保护磨牙支抗;未见牙根明显吸收、牙齿松动、牙髓坏死及牙周组织丧失等不良反应。提示牙周膜牵引成骨能够快速有效移动尖牙。
中图分类号:
引用本文
麦志辉,张静兰,卢红飞,陈 奇,梁焕友,艾 虹. 牙周膜牵引成骨快速远中移动尖牙的可行性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(41): 7255-7264.
Mai Zhi-hui, Zhang Jing-lan, Lu Hong-fei, Chen Qi, Liang Huang-you, Ai Hong. Rapid canine distal movement through distraction osteogenesis of the periodontal ligament[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(41): 7255-7264.
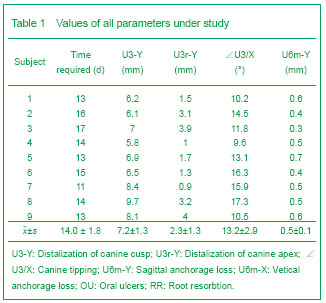
Root resorption
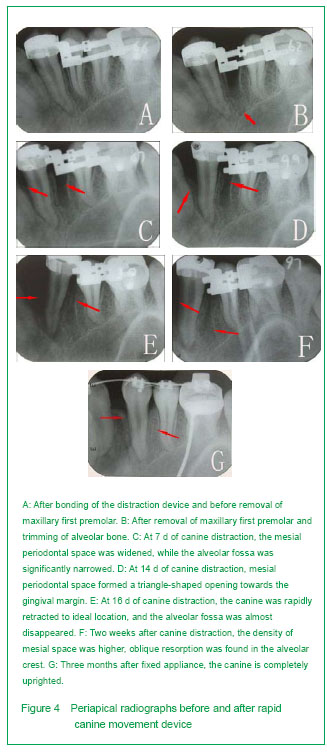
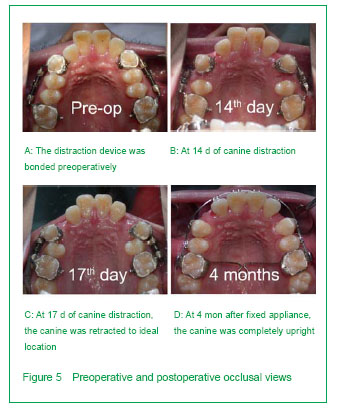
Pulp vitality of maxillary canines, second premolar and first molar
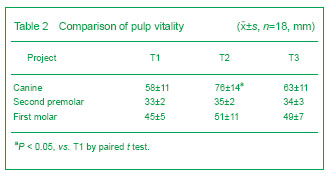
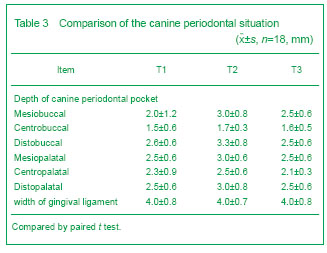
Canine periodontal situation There were significant differences in canine periodontal probing depth and mucogingianl junction width between T1, T2 and T3. During canine distration, the periodontal tissue was healthy without edema and inflammation. Oral ulcers were found in three patients because of the oppression on the mucosa by the distraction device (Table 3).
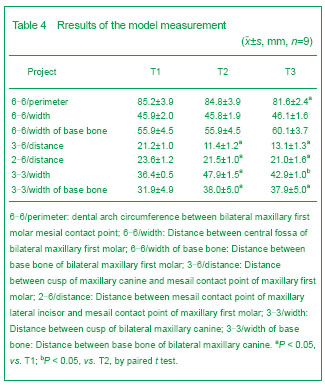
Model measurement
| [1] Codivilla A. The classic: On the means of lengthening, in the lower limbs, the muscles and tissues which are shortened through deformity. 1905. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(12):2903-2909.
[2] Ilizarov GA. The principles of the Ilizarov method. Bull Hosp Jt Dis Orthop Inst. 1988;48(1):1-11.
[3] McCarthy JG. The role of distraction osteogenesis in the reconstruction of the mandible in unilateral craniofacial microsomia. Clin Plast Surg. 1994;21(4):625-631.
[4] Liou EJ, Huang CS. Rapid canine retraction through distraction of the periodontal ligament. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1998;114(4):372-382.
[5] Sharpe W, Reed B, Subtelny JD, et al. Orthodontic relapse, apical root resorption, and crestal alveolar bone levels. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1987;91(3):252-258.
[6] von Böhl M, Maltha JC, Von Den Hoff JW, et al. Focal hyalinization during experimental tooth movement in beagle dogs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004;125(5): 615-623.
[7] von Böhl M, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. Hyalinization during orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review on tissue reactions. Eur J Orthod. 2009;31(1):30-36.
[8] Kim SJ, Park YG, Kang SG. Effects of Corticision on paradental remodeling in orthodontic tooth movement. Angle Orthod. 2009;79(2):284-291.
[9] Chung KR, Mitsugi M, Lee BS, et al. Speedy surgical orthodontic treatment with skeletal anchorage in adults--sagittal correction and open bite correction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67(10):2130-2148.
[10] Ghoneima AA, Allam ES, Zunt SL, et al. Bisphosphonates treatment and orthodontic considerations. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2010;13(1):1-10.
[11] Ahn JJ, Shin HI. Bone tissue formation in extraction sockets from sites with advanced periodontal disease: a histomorphometric study in humans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(6):1133-1138.
[12] Prabhakar AR, Tauro DP, Shubha AB. Management of an unusual maxillary dentoalveolar fracture: a case report. J Dent Child (Chic). 2006;73(2):112-115.
[13] Brusveen EM, Brudvik P, Bøe OE, et al. Apical root resorption of incisors after orthodontic treatment of impacted maxillary canines: a radiographic study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012;141(4):427-435.
[14] Weltman B, Vig KW, Fields HW, et al. Root resorption associated with orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010;137(4):462-476; discussion 12A.
[15] Cope JB, Harper RP, Samchukov ML. Experimental tooth movement through regenerate alveolar bone: A pilot study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1999;116(5):501-505.
[16] Nakamoto N, Nagasaka H, Daimaruya T, et al. Experimental tooth movement through mature and immature bone regenerates after distraction osteogenesis in dogs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;121(4):385-395.
[17] Kharkar VR, Kotrashetti SM. Transport dentoalveolar distraction osteogenesis-assisted rapid orthodontic canine retraction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(5):687-693.
[18] Kumar PS, Saxena R, Patil S, et al. Clinical investigation of periodontal ligament distraction osteogenesis for rapid orthodontic canine retraction. Aust Orthod J. 2009;25(2):147-152.
[19] Gürgan CA, I?eri H, Ki?ni?ci R. Alterations in gingival dimensions following rapid canine retraction using dentoalveolar distraction osteogenesis. Eur J Orthod. 2005;27(4):324-332.
[20] Ren Y, Maltha JC, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. Optimum force magnitude for orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic literature review. Angle Orthod. 2003;73(1):86-92.
[21] Alkumru P, Erdem D, Altug-Atac AT. Evaluation of changes in the vertical facial dimension with different anchorage systems in extraction and non-extraction subjects treated by Begg fixed appliances: A retrospective study. Eur J Orthod. 2007;29(5):508-516.
[22] Sayin S, Bengi AO, Gürton AU, et al. Rapid canine distalization using distraction of the periodontal ligament: a preliminary clinical validation of the original technique. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(3):304-315.
[23] Tanne K, Yoshida S, Kawata T, et al. An evaluation of the biomechanical response of the tooth and periodontium to orthodontic forces in adolescent and adult subjects. Br J Orthod. 1998;25(2):109-115.
[24] Yoshihara T, Matsumoto Y, Suzuki J, et al. Effect of serial extraction alone on crowding: spontaneous changes in dentition after serial extraction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000;118(6):611-616.
[25] Wei S, Fu MK. Posttreatment stability of four first bicuspid extraction cases treated with the Alexander technique--model analysis. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005;40(4):271-274.
[26] Miyajima K, Nakamura S. Distalization with 'driftodontics'. J Clin Orthod. 1994;28(7):393-394.
[27] Miura H, Hasegawa S, Okada D, et al. The measurement of physiological tooth displacement in function. J Med Dent Sci. 1998;45(2):103-115.
[28] Gritsch K, Laroche N, Morgon L, et al. A systematic review of methods for tissue analysis in animal studies on orthodontic mini-implants. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2012; 15(3):135-147.
[29] Ai H, Xu QF, Lu HF, et al. Rapid tooth movement through distraction osteogenesis of the periodontal ligament in dogs. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008;121(5):455-462.
[30] Kharkar VR, Kotrashetti SM. Transport dentoalveolar distraction osteogenesis-assisted rapid orthodontic canine retraction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(5):687-693.
[31] Kurt G, I?eri H, Ki?ni?ci R. Rapid tooth movement and orthodontic treatment using dentoalveolar distraction (DAD). Long-term (5 years) follow-up of a Class II case. Angle Orthod. 2010;80(3):597-606.
[32] Ding Y, Liu Y, Cao M, et al. Periodontal tissues changes in tooth-borne distraction osteogenesis: an experimental study of closure of wide alveolar bone defects in dogs. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;47(2):111-115.
[33] Thiruvenkatachari B, Pavithranand A, Rajasigamani K, et al. Comparison and measurement of the amount of anchorage loss of the molars with and without the use of implant anchorage during canine retraction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;129(4):551-554. |
| [1] | 麻海亮,于新波,刘梦东,贾 婧,符大勇. 恒牙牙体硬组织钙磷成分的检测:分光光度法与EDTA滴定法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(46): 7432-7436. |
| [2] | 栗炳南,李卫东,林俊堂,丰慧根. 人胶质细胞源性神经营养因子和血管内皮生长因子165双基因真核表达载体的构建与鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(29): 4675-4682. |
| [3] | 刘长剑,王 李,罗宗键. 低能体外冲击波和低剂量间歇甲状旁腺素干预成骨细胞的增殖和分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(11): 1672-1679. |
When the tooth is gradually distalized into the extraction socket, the periodontal ligament generates new bone in a direction parallel to the tooth movement, which is similar to the tooth movement. But little is known about canine pulp vitality, and periodontal tissue reconstruction, as well as the biological mechanism in adult patients. This study is to address these questions, aiming at providing further reference for clinical application of this technique.
Design
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
All data were analyzed using the software SPSS 11.0, paired t test was used for comparison between two groups, and analysis of variance, least significant difference, and Student-Newman-Keuls analysis were used for comparison among multiple groups.
1通过改良的牵引装置,快速远中移动上颌尖牙,同时监测牙髓活力、牙根吸收及尖牙牙周组织改建情况,为临床推广该技术提供依据。 2国内首次应用牙周膜牵引成骨技术移动尖牙,较为系统评估牙周膜牵引成骨技术快速远中移动尖牙的临床可行性,评估手段较为全面,临床意义较大。
牵引成骨是一项通过将骨切开后应用牵引装置缓慢牵拉,使截骨间隙中形成新骨,从而达到骨骼延长目的的技术。该项技术由前苏联著名骨科教授Ilizarov发明,最初被用于矫正肢体长度不等,文献上也称骨牵引、骨痂成形、骨痂牵引、骨延长等。虽然这一技术最初应用于下肢骨,但这些来自肢骨牵引的许多经验如今已被成功地用于颅面骨畸形的矫治,对患者开始治疗的时间也可提前至幼儿时期。与传统的治疗方法如骨切开自体骨移植、异体骨移植、生物材料种植等相比,具有手术创伤小、继发病变少、无需植骨、牵引骨周围软组织可以同时得到扩张等优点,因而该项技术对颅面畸形的矫治具有很大的潜力和广阔的应用前景。牵引成骨通常分为4个阶段:①骨切开。②间歇期。③牵引期和④固定期。影响牵引成骨期间牵引区新骨形成的质量取决于骨段固定的坚固程度、骨髓及骨周软组织和血供受损伤的程度、牵引的速度和频率、新骨负重前适当钙化改建期,而截骨线和牵引力的方向,决定了新骨形成的方向和形态。
牵引成骨在颅颌面外科应用的适应证:半侧颜面发育不全畸形,颞下颌关节强直引起的小下颌畸形,小下颌畸形伴阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征、颌骨缺失的牵引成骨重建,颌骨部分缺损或牙槽骨缺损的垂直向牵引成骨,移植骨的牵引成骨,上下牙弓狭窄的扩弓治疗,腭裂继发重度上颌后缩畸形牵引成骨矫治和颅面部重度发育不全的牵引成骨前徙,如Crouzon综合征、Apert综合征等。另外,利用该技术,还可以修复外伤或肿瘤术后的颌骨缺损,恢复牙槽骨高度,为牙种植手术创造条件。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||