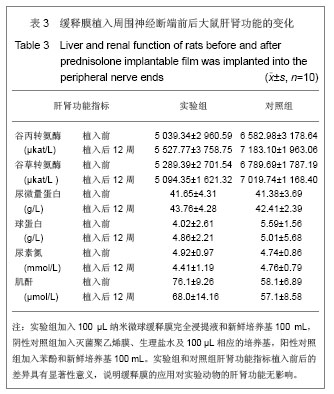
| [1]Cui F, Shi K, Zhang L, et al. Biodegradable nanoparticles loaded with insulin-phospholipid complex for oral delivery: preparation, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release. 2006;114(2):242-250.[2]Deumens R, Bozkurt A, Meek MF, Marcus MA, Joosten EA, Weis J, et al. Repairing injured peripheral nerves: bridging the gap. Prog Neurobiol. 2010;92(3):245-276.[3]IJpma FF, Van De Graaf RC, Meek MF. The early history of tubulation in nerve repair. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2008;33(5): 581-586.[4]Yates JM, Smith KG, Robinson PP. The effect of triamcinolone hexacetonide on the spontaneous and mechanically-induced ectopicdischarge following lingual nerve injury in the ferret. Pain. 2004;111(3):261-269.[5]Azuma C, Tohyama H, Nakamura H, et al. Antibody neutralization of TGF-beta enhances the deterioration of collagen fascicles in a tissue-cultured tendon matrix with ex vivo fibroblast infiltration. J Biomech. 2007;40(10):2184-2190.[6]赵永青,苏衍萍,韩凤岳.甲基强的松龙对急性脊髓损伤神经元保护作用的实验研究[J].中华神经外科杂志,2005,21(6):367-370. [7]张海英,李玉珍.糖皮质激素类药物的药理特性及合理应用[J].临床药物治疗杂志,2004,2(3):36-42.[8]王晓波.药物运释系统[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2007.[9]Takezawa T, T akeuchi T, Nitani A, et al. Collagen vitr igel membrane useful for parac-rine assays in vit ro and drug delivery systems in vivo. J Biotechnol. 2007;131(1):76-83.[10]Bellamkonda RV. Peripheral nerve regeneration: an opinion on channels, scaffolds and anisotropy. Biomaterials. 2006; 27(19):3515-3518.[11]Navarro X, Vivo M, Valero-Cabre A. Neural plasticity after peripheral nerve injury and regeneration. Prog Neurobiol. 2007;82(4):163-201.[12]The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [13]Fournier C, Hecquet B, Bouffard R, et al. Experimental studies and preliminary clinical trial of vinorelbine-loaded polymeric bioresorbable implants for the local treatment of solid tumors. Cancer Res. 1991;51(19):5384-5391.[14]Wang J, Ng CW, Win KY, et al. Release of paclitaxel from polylactide-co-glycolide (PLGA) microparticles and discs under irradiation. J Microencapsulation. 2003;20(3):317-327.[15]Shameem M, Lee H, Burton K, et al. Effect of γ-irradiation on peptide-containing hydrophilic poly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J Pharm Sci Technol. 1999;53(6):309-315.[16]林晓艳,唐敏,张兴栋.γ射线低温辐照对胶原膜体外稳定性和细胞相容性的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2006,23(4):822-825.[17]杨飞,杨吟野,李训虎,等.γ射线辐照对壳聚糖薄膜的改性研究[J].透析与人工器官,2003,2(14):14-19.[18]Ruiter GC, Onyeneho IA, Liang ET, et al. Methods for in vitro characterization of multichannel nerve tubes. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;84(3):643-651.[19]Graham WP 3rd, Davis TS, Miller SH, et al. Efficacy of triamcinolone acetonide following neurorrhaphy-an electroneuromy ographic evaluation. Ann Plast Surg. 1982; 9(3):230-237.[20]Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, et al. Toxic potential ofmateri-als at the nanolevel. Science. 2006;311(5761):622-627.[21]陆兵,袁本利,徐国杰,等.纳曲酮植入剂不同动物体内的组织相容性和生物可降解性[J].中国药学杂志,2000,35(6):391-393.[22]Lee SH, Park M, Park CG, et al. Microchip for sustained drug delivery by diffusion through microchannels. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2012;13(1):211-217.[23]Ni S, Lin K, Chang J, et al. β-CaSiO3/β-Ca3(PO4)2 composite materials for hard tissue repair:In vitro studies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;85(1):72-82.[24]Sclapp M, Friess W. Collagen/PLGA microparticle composites for local controlled delivery of gentamicin. J Pharm Sci. 2003; 92(11):2145-2151.[25]Jeong B, Bae YH, Kim SK, et al. Drug release from biodegradable injectable thermosensitive hydrogel of PEG-PLGA-PEG triblock copolymers. J Control Release. 2000;63(1-2):155-163.[26]Bini TB, Gao S, Xu X, et al. Peripheral nerve re-generation by microbraided poly (L-lactide-co-glycol-ide)biodegradable polymer fibers. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;68(2):286-295.[27]Chang CJ, Hsu. The effect of high outflow permeability in asymmetric poly(dl-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) conduits for peripheralnerve regeneration. Biomaterials. 2006;27(7): 1035-1042.[28]叶震海,顾立强.雪旺细胞和聚乳酸材料的体外相容性研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2000,2(4):306-307.[29]Liu P, Sun Y, Wang Q, et al. Intracellular trafficking and cellular uptake mechanism of mPEG-PLGA-PLL and mPEG-PLGA-PLL-Gal nanoparticles for targeted delivery to hepatomas. Biomaterials. 2014;35(2):760-770.[30]张文元,杨亚冬,张科技,等.蚕丝-聚乳酸-聚羟基乙酸纤维混合编织绳状支架的生物学性能[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(5): 931-933. |
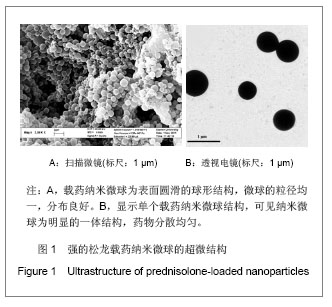
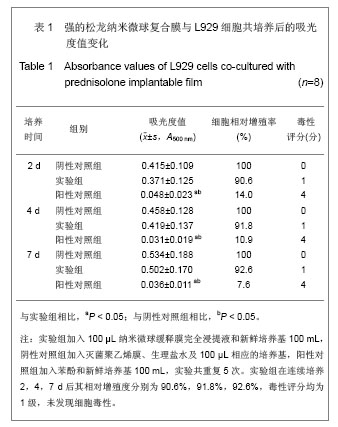
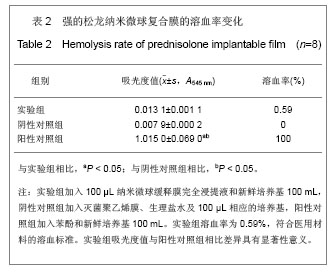
.jpg)
.jpg)