• 脊柱损伤基础实验 basic experiments of spinal injury • 下一篇
骨形态发生蛋白2对退变椎间盘组织学和Ⅰ,Ⅱ型胶原的影响
林 曦1,叶君健2
- 福建医科大学附属第一医院,1急诊科,2骨科,福建省福州市 350004
Bone morphogenetic protein-2 gene affects the histology and collagen type Ⅰ and Ⅱ expressions in degenerative intervertebral disc
Lin Xi1, Ye Jun-jian2
- 1Department of Emergency, 2Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350004, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
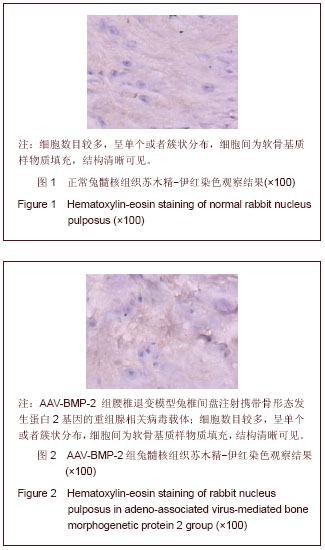
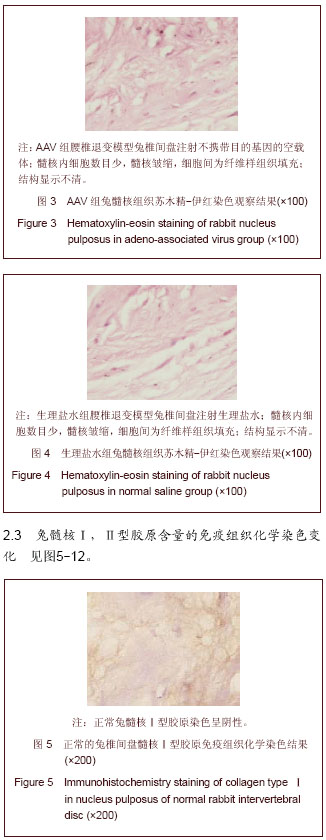
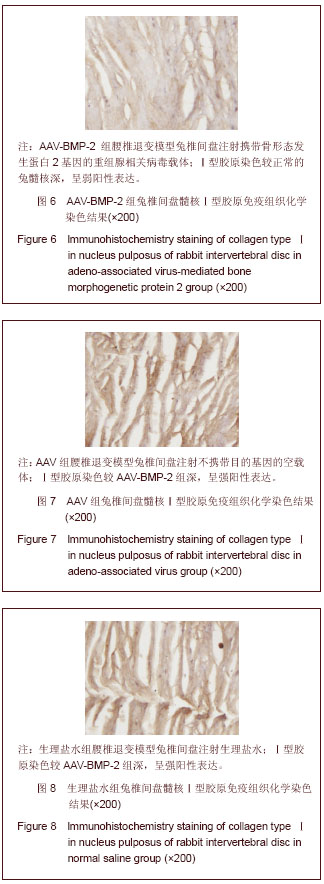
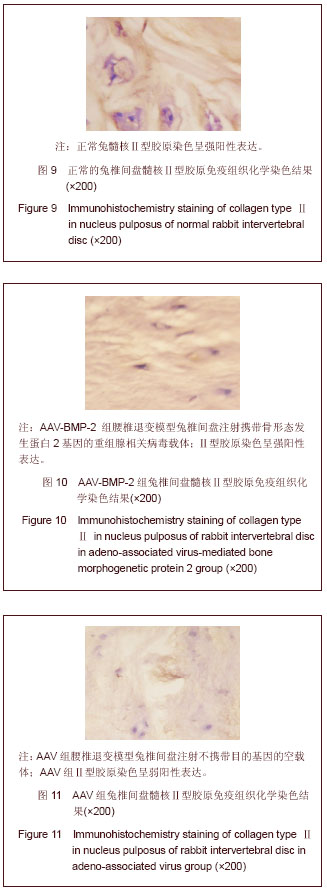
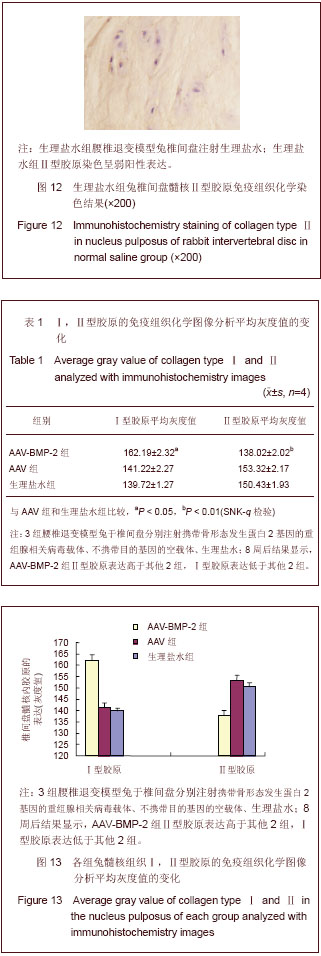
背景:研究表明,退变椎间盘细胞外基质的主要变化是Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白多糖含量的减少和Ⅰ型胶原含量的增加。 目的:观察腺相关病毒介导的骨形态发生蛋白2基因(AAV-BMP-2)对兔退变腰椎间盘内髓核Ⅰ,Ⅱ型胶原的影响。 方法:将12只新西兰大白兔L2-3,L3-4,L4-5,L5-6椎间盘针刺制造退变模型后随机分为3组,每组4只。其中AAV-BMP-2组兔椎间盘注射AAV-BMP-2,AAV组兔椎间盘注射不携带目的基因的空载体,生理盐水组兔椎间盘注射生理盐水,注射后第8周处死动物取其相应的椎间盘常规石蜡包埋,组织切片,以苏木精-伊红染色观察其髓核组织学变化,免疫组织化学法检测髓核组织Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型胶原表达并进行半定量分析。 结果与结论:普通苏木精-伊红染色结果显示AAV-BMP-2组椎间盘内髓核细胞数目较多,呈单个或者簇状分布,髓核结构清晰,无纤维样组织填充。而AAV组和生理盐水组的组织结构相似,髓核内细胞数目少,髓核皱缩干瘪,细胞间为纤维样组织填充且排列紊乱。免疫组织化学染色显示:AAV-BMP-2组椎间盘髓核内Ⅱ型胶原的表达均高于AAV组和生理盐水组(P < 0.05);AAV-BMP-2组椎间盘髓核内Ⅰ型胶原的表达均低于AAV组和生理盐水组(P < 0.05)。结果说明,体内转染AAV-BMP-2能抑制椎间盘髓核细胞表达Ⅰ型胶原,促进椎间盘髓核细胞表达合成Ⅱ型胶原,提示维持椎间盘内胶原的含量、种类,可维持椎间盘内组织学的结构和形态,稳定髓核细胞生长环境,延缓椎间盘的退变。
中图分类号:
.jpg)