| [1] Cajal SR. El plexo de Auerbach de los batracios. Nota sobre el plexo de Auerbach de la rana. Trab Lab Histol Fac Med. (Barc). 1892:23-28. [2] Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM. Interstitial Cajal‐like cells (ICLC) in human resting mammary gland stroma. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) identification. J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9(4):893-910. [3] Pieri L, Vannucchi MG, Faussonepellegrini MS. Histochemical and ultrastructural characteristics of an interstitial cell type different from ICC and resident in the muscle coat of human gut. J Cell Mol Med. 2008; 12(5b):1944-1955. [4] Popescu LM, Faussone-Pellegrini MS. TELOCYTES-a case of serendipity: the winding way from Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC), via Interstitial Cajal-Like Cells (ICLC) to TELOCYTES. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(4):729-740. [5] Hinescu ME, Popescu LM. Interstitial Cajal‐like cells (ICLC) in human atrial myocardium. J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9(4):972-975. [6] Formey A, Buscemi L, Boittin FX, et al. Identification and functional response of interstitial Cajal-like cells from rat mesenteric artery. Cell Tissue Res. 2011;343(3):509. [7] Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Popescu LM. Telocytes. Biomol Concepts. 2011;2(6):481. [8] Cismasiu VB, Radu E, Popescu LM. miR-193 expression differentiates Telocytes from other stromal cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(5): 1071-1074. [9] Zhao B, Chen S, Liu J, et al. Cardiac Telocytes were decreased during myocardial infarction and their therapeutic effects for ischaemic heart in rat. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(1):123-133. [10] Shim W. Myocardial Telocytes: A new player in electric circuitry of the heart. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;913:241-251. [11] Mandache E, Gherghiceanu M, Macarie C, et al. Telocytes in human isolated atrial amyloidosis: ultrastructural remodelling. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(12):2739-2747. [12] Kucybala I, Janas P, Ciuk S, et al. A comprehensive guide to Telocytes and their great potential in cardiovascular system. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2017;118(5):302. [13] Hostiuc S, Marinescu M, Costescu M, et al. Cardiac Telocytes. From basic science to cardiac diseases. II. Acute myocardial infarction. Ann Anat. 2018;2018:18-27. [14] Hostiuc S, Negoi I, Dogaroiu C, et al. Cardiac Telocytes. From basic science to cardiac diseases. I. Atrial fibrillation. Ann Anat. 2018;218: 83-87. [15] Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM. Electron microscope tomography: further demonstration of nanocontacts between caveolae and smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Mol Med. 2007;11(6):1416-1418. [16] Popescu LM, Manole CG, Gherghiceanu M, et al. Telocytes in human epicardium. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(8):2085-2093. [17] 徐莎莎,廖肇福,蔡冬青.心脏Telocytes在年老大鼠心脏的分布[J].解剖学报,2016,47(6):802-806.[18] Gherghiceanu M, Manole CG, Popescu LM. TELOCYTES in endocardium: electron microscope evidence. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14(9):2330-2334. [19] Wang J, Jin M, Ma W H, et al. The History of Telocyte Discovery and Understanding. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;913:1-21. [20] Aleksandrovych V, Pasternak A, Basta P, et al. Telocytes: facts, speculations and myths. Folia Med Cracov. 2017;57(1):5-22. [21] Mihaela G, Popescu L M. Heterocellular communication in the heart. Electron tomography of Telocyte-myocyte junctions. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(4):1005-1011. [22] Zhang HQ, Lu SS, Xu T, et al. Morphological evidence of Telocytes in mice aorta. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(3):348-352. [23] Cretoiu D, Hummel E, Zimmermann H, et al. Human cardiac Telocytes: 3D imaging by FIB-SEM tomography. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18(11): 2157-2164. [24] Varga I, Kyselovi? J, Galfiova P, et al. The non-cardiomyocyte cells of the heart. Their possible roles in exercise-induced cardiac regeneration and remodeling. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;999:117-136. [25] Xiao J, Chen P, Qu Y, et al. Telocytes in exercise-induced cardiac growth. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20(5):973-979. [26] Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM. Cardiomyocyte precursors and Telocytes in epicardial stem cell niche: electron microscope images. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(4):871-877. [27] Mandache E, Popescu L M, Gherghiceanu M. Myocardial interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) and their nanostructural relationships with intercalated discs: shed vesicles as intermediates. J Cell Mol Med. 2007;11(5):1175-1184. [28] Kostin S. Cardiac Telocytes in normal and diseased hearts. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016;55:22-30. [29] Cantarero I, Luesma M J, Junquera C. The primary cilium of Telocytes in the vasculature: electron microscope imaging. J Cell Mol Med. 2011; 15(12):2594-2600. [30] Vandecasteele T, Cornillie P, Vandevelde K, et al. Presence of ganglia and Telocytes in proximity to myocardial sleeve tissue in the porcine pulmonary veins wall. Anat Histol Embryol. 2017;46(4):325-333. |
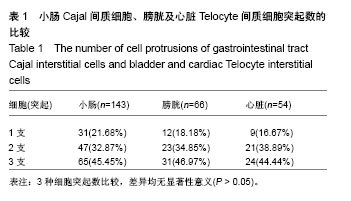
.jpg)
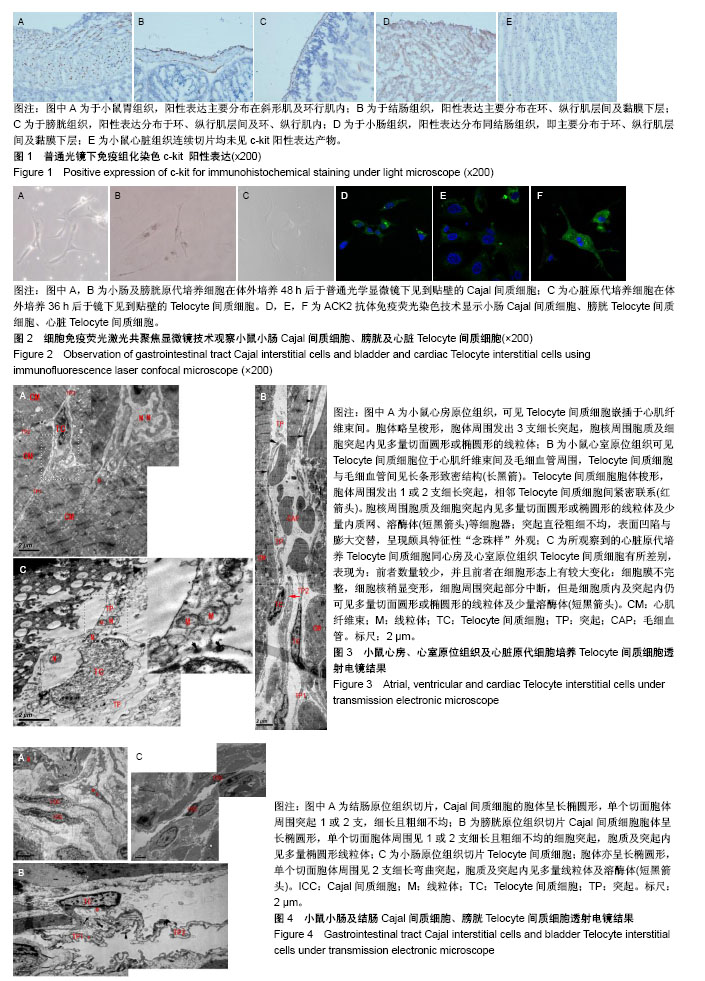
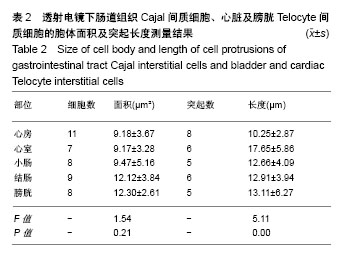
.jpg)