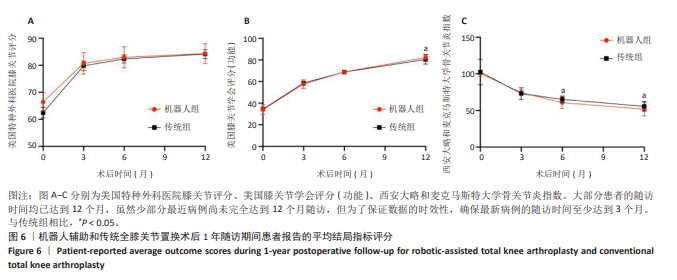
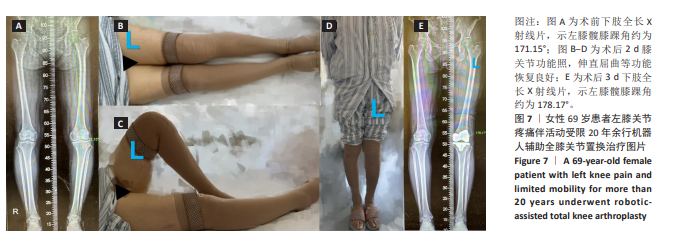
[1] KAHLENBERG CA, NWACHUKWU BU, MCLAWHORN AS, et al. Patient Satisfaction After Total Knee Replacement: A Systematic Review. HSS J. 2018;14(2):192-201.
[2] BAUTISTA M, MANRIQUE J, HOZACK WJ. Robotics in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(7):600-606.
[3] KHATRI C, METCALFE A, WALL P, et al. Robotic trials in arthroplasty surgery. Bone Joint J. 2024;106-b(2):114-120.
[4] BANERJEE S, CHERIAN JJ, ELMALLAH RK, et al. Robotic-Assisted Knee Arthroplasty. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2015;12(6):727-735.
[5] SONG EK, SEON JK, YIM JH, et al. Robotic-Assisted TKA Reduces Postoperative Alignment Outliers and Improves Gap Balance Compared to Conventional TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):118-126.
[6] JAKOPEC M, HARRIS SJ, RODRIGUEZ Y, et al. The First Clinical Application of a “Hands-On” Robotic Knee Surgery System. Comput Aided Surg. 2001;6(6):329-339.
[7] PARRATTE S, PAGNANO MW, TROUSDALE RT, et al. Effect of Postoperative Mechanical Axis Alignment on the Fifteen-Year Survival of Modern, Cemented Total Knee Replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(12):2143-2149.
[8] REED SC, GOLLISH J. The Accuracy of Femoral Intramedullary Guides in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12(6):677-682.
[9] RITTER MA, DAVIS KE, MEDING JB, et al. The Effect of Alignment and BMI on Failure of Total Knee Replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93(17):1588-1596.
[10] GOH GS, LIOW MHL, ABD RAZAK HR, et al. Patient-Reported Outcomes, Quality of Life, and Satisfaction Rates in Young Patients Aged 50 Years or Younger After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(2): 419-425.
[11] HELD MB, GROSSO MJ, GAZGALIS A, et al. Improved Compartment Balancing Using a Robot-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. Arthroplast Today. 2021;7:130-134.
[12] RAJGOR HD, MAYNE A, MUNASINGHE C, et al. Mako Versus ROSA: Comparing Surgical Accuracy in Robotic Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Robot Surg. 2024;18(1):33.
[13] WU XD, ZHOU Y, SHAO H, et al. Robotic-Assisted Revision Total Joint Arthroplasty: A State-of-the-Art Scoping Review. EFORT Open Rev. 2023;8(1):18-25.
[14] SEO SS, KIM CW, SEO JH, et al. Effects of Resection of Posterior Condyles of Femur on Extension Gap of Knee Joint in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(6):1819-1823.
[15] MA N, SUN P, XIN P, et al. Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of MAKO Robot-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Versus Conventional Manual Total Knee Arthroplasty in Uncomplicated Unilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty a Single-Centre Retrospective Analysis. Int Orthop. 2024;48(9):2351-2358.
[16] XU JZ, LI LL, FU J, et al. Comparison of Serum Inflammatory Indicators and Radiographic Results in MAKO Robotic-Assisted Versus Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Retrospective Study of Chinese Patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):418.
[17] SIRES JD, WILSON CJ. Accuracy of Bone Resection in MAKO Total Knee Robotic-Assisted Surgery. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(7):745-748.
[18] SHEN TS, UPPSTROM TJ, WALKER PJ, et al. High Degree of Alignment Precision Associated With Total Knee Arthroplasty Performed Using a Surgical Robot or Handheld Navigation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(11):4735-4740.
[19] BATAILLER C, FERNANDEZ A, SWAN J, et al. MAKO CT-Based Robotic Arm-Assisted System Is a Reliable Procedure for Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(11):3585-3598.
[20] MARCHAND RC, SODHI N, KHLOPAS A, et al. Patient Satisfaction Outcomes After Robotic Arm-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Short-Term Evaluation. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(9):849-853.
[21] MARCHAND RC, SODHI N, ANIS HK, et al. One-Year Patient Outcomes for Robotic-Arm-Assisted Versus Manual Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(11):1063-1068.
[22] WONG WK, ABU BAKAR SAJAK A, CHUA HS. Real-World Accuracy of Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty and Its Impact on Expedited Recovery. J Robot Surg. 2024;18(1):309.
[23] COTTER EJ, WANG J, ILLGEN RL. Comparative Cost Analysis of Robotic-Assisted and Jig-Based Manual Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2022;35(2):176-184.
[24] KAYANI B, KONAN S, TAHMASSEBI J, et al. Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Is Associated With Improved Early Functional Recovery and Reduced Time to Hospital Discharge Compared With Conventional Jig-Based Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Cohort Study. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(7):930-937.
[25] KARUMURI K, DESAI KB, HIPPALGAONKAR K, et al. Is It Worth the Risk? Frailty Transition and Complications Following Robotic Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Observational Study. Knee. 2023;44: 72-78.
[26] KAYANI B, KONAN S, HUQ SS, et al. Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Has a Learning Curve of Seven Cases for Integration Into the Surgical Workflow But No Learning Curve Effect for Accuracy of Implant Positioning. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019; 27(4):1132-1141.
[27] SULTAN AA, SAMUEL LT, KHLOPAS A, et al. Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty More Accurately Restored the Posterior Condylar Offset Ratio and the Insall-Salvati Index Compared to the Manual Technique; A Cohort-Matched Study. Surg Technol Int. 2019;34: 409-413.
[28] LEE JH, KWON SC, HWANG JH, et al. Functional Alignment Maximises Advantages of Robotic Arm-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty With Better Patient-Reported Outcomes Compared to Mechanical Alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024;32(4):896-906.
[29] MANARA JR, GOONATILLAKE M, MARLEY M, et al. Virtual Assessment of Coronal Balance Prior to Bone Resection With the MAKO Robotic-Assisted System Accurately Predicts Final Balance in TKA. J Robot Surg. 2023;17(6):2849-2854.
[30] MUKARTIHAL R, BHAT VK, DAS R, et al. Relationship Between Femoral Component Placement and Patient-Specific Anatomical Rotational Landmarks in Robotic Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty- A Multicentric Study. J Orthop. 2023;45:87-90.
[31] GU Y, HOWELL SM, HULL ML. Simulation of Total Knee Arthroplasty in 5° or 7° Valgus: A Study of Gap Imbalances and Changes in Limb and Knee Alignments From Native. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(9):2031-2039.
[32] MASILAMANI ABS, JAYAKUMAR T, MULPUR P, et al. Functional Alignment Is Associated With Increased Incidence of Pre-Balance, Reduced Soft-Tissue Release, and Post-Operative Pain Compared to Mechanical Alignment in Patients Undergoing Simultaneous Bilateral Robotic-Assisted TKA. J Robot Surg. 2023;17(6):2919-2927.
[33] SELVANATHAN N, AYENI FE, SORIAL R. Incidence of Soft Tissue Releases in Robotic Assisted Cementless TKA With Mechanical Alignment and Flexion Gap Balancing. Arthroplasty. 2023;5(1):28.
[34] VIGDORCHIK JM, WAKELIN EA, KOENIG JA, et al. Impact of Component Alignment and Soft Tissue Release on 2-Year Outcomes in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(10):2035-2040.
[35] CHUNG BJ, KANG YG, CHANG CB, et al. Differences Between Sagittal Femoral Mechanical and Distal Reference Axes Should Be Considered in Navigated TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(9):2403-2413.
[36] SHAWEN SB, BELMONT PJ, KLEMME WR, et al. Osteoporosis and Anterior Femoral Notching in Periprosthetic Supracondylar Femoral Fractures: A Biomechanical Analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(1):115-121.
[37] MOON YW, HA CW, DO KH, et al. Comparison of Robot-Assisted and Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Controlled Cadaver Study Using Multiparameter Quantitative Three-Dimensional CT Assessment of Alignment. Comput Aided Surg. 2012;17(2):86-95.
[38] SONG EK, SEON JK, YIM JH, et al. Robotic-Assisted TKA Reduces Postoperative Alignment Outliers and Improves Gap Balance Compared to Conventional TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):118-126.
[39] SIRES JD, WILSON CJ. CT Validation of Intraoperative Implant Position and Knee Alignment as Determined by the MAKO Total Knee Arthroplasty System. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(10):1133-1137.
[40] SCHOLL LY, HAMPP EL, DE SOUZA KM, et al. How Does Robotic-Arm Assisted Technology Influence Total Knee Arthroplasty Implant Placement for Surgeons in Fellowship Training? J Knee Surg. 2022; 35(2):198-203.
[41] DECKEY DG, VERHEY JT, ROSENOW CS, et al. Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Allows for Trainee Involvement and Teaching Without Lengthening Operative Time. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(6S):S201-S206.
[42] JUNG HJ, KANG MW, LEE JH, et al. Learning Curve of Robot-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty and Its Effects on Implant Position in Asian Patients: A Prospective Study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):332.
[43] MURPHY GT, SHATROV J, DUONG J, et al. How Does the Use of Quantified Gap-Balancing Affect Component Positioning and Limb Alignment in Robotic Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Functional Alignment Philosophy? A Comparison of Two Robotic Platforms. Int Orthop. 2023;47(5):1221-1232.
[44] PATIL S, D’LIMA DD, FAIT JM, et al. Improving Tibial Component Coronal Alignment During Total Knee Arthroplasty With Use of a Tibial Planing Device. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(2):381-387.
[45] JENNY JY, CLEMENS U, KOHLER S, et al. Consistency of Implantation of a Total Knee Arthroplasty With a Non-Image-Based Navigation System: A Case-Control Study of 235 Cases Compared With 235 Conventionally Implanted Prostheses. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(7):832-839.
[46] AGARWAL N, TO K, MCDONNELL S, et al. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes in Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(11):3393-3409.
[47] BECKER R, BONNIN M, HOFMANN S. The Painful Knee After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(9): 1409-1410.
[48] CHIN BZ, TAN SSH, CHUA KCX, et al. Robot-Assisted Versus Conventional Total and Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis of Radiological and Functional Outcomes. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(10): 1064-1075.
[49] ONGGO JR, ONGGO JD, DE STEIGER R, et al. Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Is Comparable to Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(10):1533-1549.
[50] ZHANG J, NDOU WS, NG N, et al. Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Is Associated With Improved Accuracy and Patient Reported Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(8):2677-2695.
[51] CHANG JS, KAYANI B, WALLACE C, et al. Functional Alignment Achieves Soft-Tissue Balance in Total Knee Arthroplasty as Measured With Quantitative Sensor-Guided Technology. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(3): 507-514.
[52] YOUNG SW, ZENG N, TAY ML, et al. A Prospective Randomised Controlled Trial of Mechanical Axis With Soft Tissue Release Balancing vs Functional Alignment With Bony Resection Balancing in Total Knee Replacement-A Study Using Stryker Mako Robotic Arm-Assisted Technology. Trials. 2022;23(1):580.
[53] DIQUATTRO E, PRILL R, SALZMANN M, et al. High Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Component Placement and Lower Limb Alignment Using a Robotic Arm-Assisted System and Gap-Balancing Instrument in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024;32(3):685-692.
[54] GLOWALLA C, LANGER S, LENZE U, et al. Postoperative Full Leg Radiographs Exhibit Less Residual Coronal Varus Deformity Compared to Intraoperative Measurements in Robotic Arm-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty With the MAKO™ System. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(9):3912-3918.
[55] SONG EK, SEON JK, PARK SJ, et al. Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty With Robotic and Conventional Techniques: A Prospective, Randomized Study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(7):1069-1076.
[56] STIMSON LN, STEELMAN KR, HAMILTON DA, et al. Evaluation of Blood Loss in Conventional vs MAKOplasty Total Knee Arthroplasty. Arthroplast Today. 2022;16:224-228.
[57] KAYANI B, KONAN S, PIETRZAK JRT, et al. Iatrogenic Bone and Soft Tissue Trauma in Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Compared With Conventional Jig-Based Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Cohort Study and Validation of a New Classification System. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8):2496-2501.
[58] PARRATTE S, VAN OVERSCHELDE P, BANDI M, et al. An Anatomo-Functional Implant Positioning Technique With Robotic Assistance for Primary TKA Allows the Restoration of the Native Knee Alignment and a Natural Functional Ligament Pattern, With a Faster Recovery at 6 Months Compared to an Adjusted Mechanical Technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(4):1334-1346.
[59] MCEWEN P, BALENDRA G, DOMA K. Medial and Lateral Gap Laxity Differential in Computer-Assisted Kinematic Total Knee Arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(3):331-339.
[60] NAKAMURA S, TIAN Y, TANAKA Y, et al. The Effects of Kinematically Aligned Total Knee Arthroplasty on Stress at the Medial Tibia: A Case Study for Varus Knee. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(1):43-51.
[61] TIAN R, DUAN X, KONG N, et al. Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Is More Advantageous for Knees With Severe Deformity: A Randomized Controlled Trial Study Design. Int J Surg. 2023;109(3): 287-296.
|