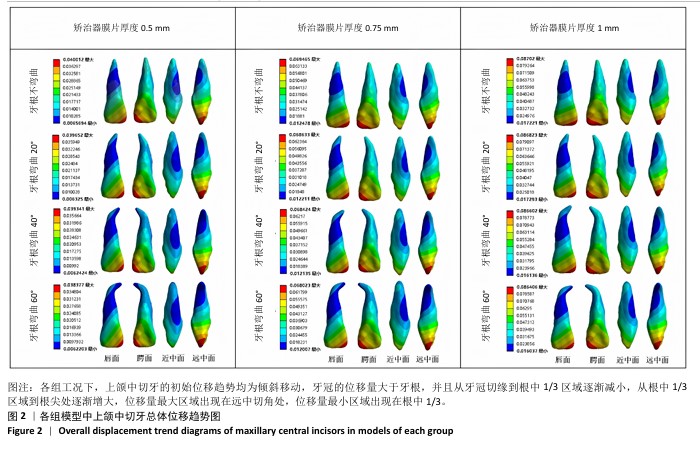
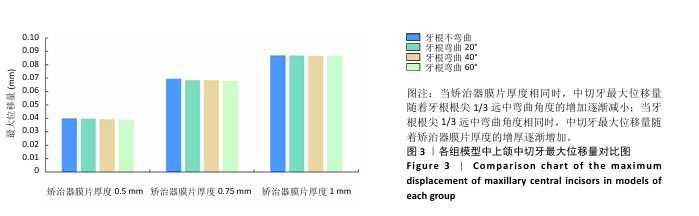
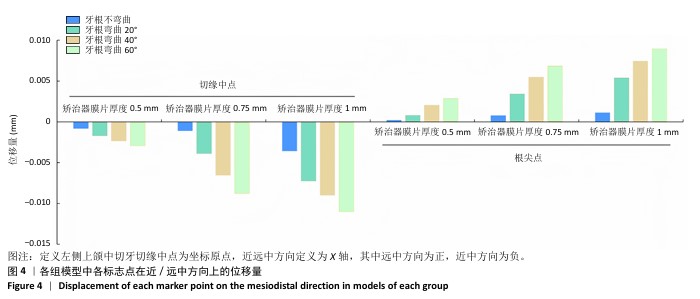
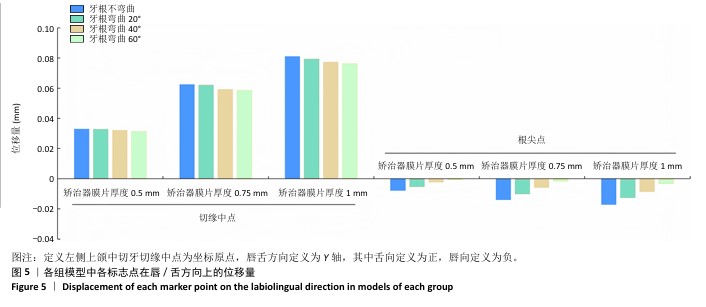
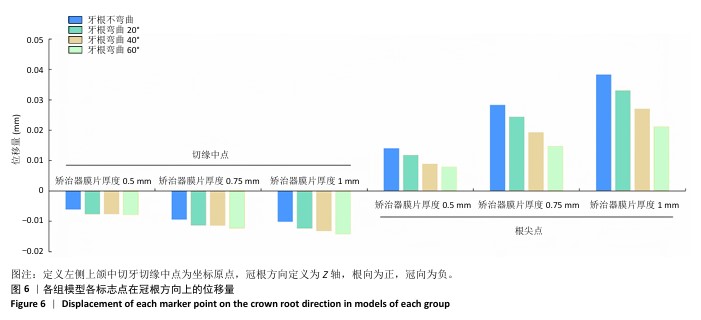
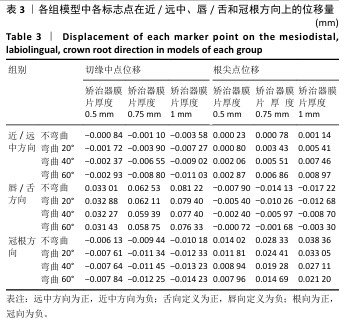
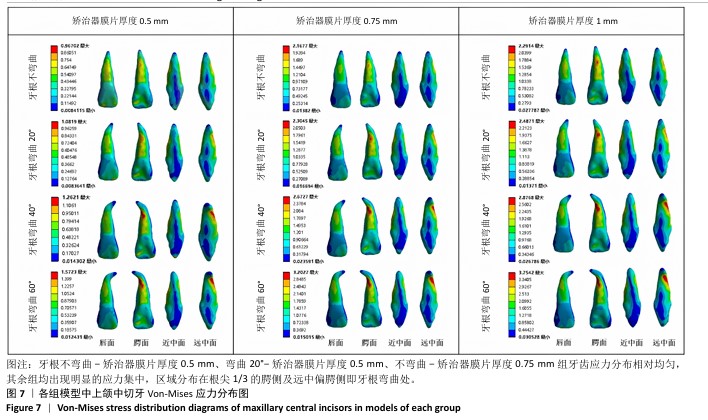
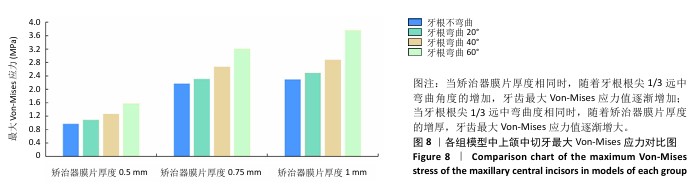
[1] SHRIVASTAVA A, MOHANTY P, DASH BP, et al. Proficiency of Clear Aligner Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus. 2023;15(9):e45072.
[2] LU HF, MAI ZH, CHEN Q, et al. Initial stress distribution of the maxillary anterior teeth, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone by different intruding loadings. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res. 2011;15(48): 8964-8967.
[3] 李煌,武秀萍,黄兰,等.正畸根尖区牙根外吸收的风险因素及其临床处理建议的专家共识[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2022,40(6): 629-637.
[4] 李亦方,汤秀春,张佳男,等.正畸患者上颌前牙区牙根吸收易感因素的研究进展[J].现代实用医学,2023,35(9):1257-1260.
[5] 叶泽林,刘璐,龙虎,等.弯曲前牙的影像评价及治疗的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2022,49(2):173-181.
[6] GUPTA M, MADHOK K, KULSHRESTHA R. Determination of stress distribution on periodontal ligament and alveolar bone by various tooth movements-A 3D FEM study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2020;10(4): 758-763.
[7] LI JY, PARADA C, CHAI Y. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of tooth root development. Development. 2017;144(3):374-384.
[8] SAVIGNANO R, VIECILLI RF, OYOYO U. Three-dimensional nonlinear prediction of tooth movement from the force system and root morphology. Angle Orthod. 2020;90(6):811-822.
[9] 刘展,钱英莉,樊瑜波.正畸中牙根形态对牙根应力分布的影响[J].工程科学与技术, 2009,41(6):71-75.
[10] SAHEBI S, RAZAVIAN A, MADDAHI N, et al. Evaluation of Root Dilaceration in Permanent Anterior and Canine Teeth in the Southern Subpopulation of Iran Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. J Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci. 2023;24(3):320-327.
[11] JIA L, WANG C, WANG C, et al. Efficacy of various multi-layers of orthodontic clear aligners: a simulated study. Comput Method Biomec. 2022;25(15):1710-1721.
[12] WANG DC, AKBARI A, JIANG FF. The effects of different types of periodontal ligament material models on stresses computed using Finite Element Models. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022;162(6): 328-336.
[13] PALONE M, LONGO M, ARVEDA N, et al. Micro-computed tomography evaluation of general trends in aligner thickness and gap width after thermoforming procedures involving six commercial clear aligners: an in vitro study. Korean J Orthod. 2021;51(2):135-141.
[14] GAO HY, LUO LY, LIU J. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of maxillary molar distalization treated with clear aligners combined with different traction methods. Prog Orthod. 2024; 25(1):1-11.
[15] CHENG YX, LIU X, CHEN X, et al. The three-dimensional displacement tendency of teeth depending on incisor torque compensation with clear aligners of different thicknesses in cases of extraction: a finite element study. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):1-12.
[16] 康芙嘉,吴聿淼,刘心雨,等.不同前牙唇倾度及内收压低步距下隐形矫治器作用的比较:三维有限元研究[J].口腔医学研究,2023, 39(4):345-349.
[17] SCHWERTNER A, DE ALMEIDA-PEDRIN RR, POLETI TMFF. Biomechanical analysis of total arch maxillary distalization using infrazygomatic crest miniscrews: a finite element analysis study. Prog Orthod. 2024;25(10):1-8.
[18] GHANNAM M, KAMILOLU B. Effects of Skeletally Supported Anterior en Masse Retraction with Varied Lever Arm Lengths and Locations in Lingual Orthodontic Treatment: A 3D Finite Element Study. Biomed Res Int. 2021;13(2):9975428.
[19] ELSHAZLY TM, BOURAUEL C, ALDESOKI M, et al. Effect of attachment configuration and trim line design on the force system of orthodontic aligners: A finite element study on the upper central incisor. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2024;20(1):1-10.
[20] PEDE K, SHETTY P, RANJAN A, et al. Evaluation of effects of different sizes and shapes of attachments during rotation, tipping, and torquing in clear aligner therapy-A finite element study. J Orthodont Sci. 2024; 5(12):13-30.
[21] ROMANYK DL, VAFAEIAN B, ADDISON OAS. The use of finite element analysis in dentistry and orthodontics: Critical points for model development and interpreting results. Semin Orthod. 2020;26(3): 162-173.
[22] 王碧琦,张苗苗.无托槽隐形矫治器压低上颌伸长第一磨牙的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(25):4051-4056.
[23] HONG K, KIM WH, EGHAN AE, et al. Efficient Design of a Clear Aligner Attachment to Induce Bodily Tooth Movement in Orthodontic Treatment Using Finite Element Analysis. Materials. 2021;14(17):10-18.
[24] AHMED HMA, WOLF TG, NAGENDRABABU V, et al. Controversial Terminology In Root and Canal Anatomy: A Comprehensive Review. Eur Endod J. 2024;9(4):308-334.
[25] RENUGALAKSHMI A, VINOTHKUMAR TS, BOKHARI AM, et al. Prevalence of Dental Anomalies and Its Role in Sex Estimation among Children of Jazan Region, Saudi Arabia. Children. 2023;10(2):759-764.
[26] MANTRI A, PANDIAR D, KRISHNAN RP, et al. Prevalence and morphometric evaluation of dilaceration in Indian Tamils: an analysis of 10,089 permanent teeth. Oral Radiol. 2024;12(3):190-196.
[27] WANG JM, GUO LF, MA LQ, et al. Labial inverse dilaceration of bilateral maxillary central incisors: A case report. World J Clin Cases. 2024; 12(1):180-187.
[28] 王京楠,邓淑丽.牙根发育异常疾病概述[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2023,50(6):639-645.
[29] ELHADDAOUI R, BENYAHIA H, AZEROUAL MF, et al. Resorption of maxillary incisors after orthodontic treatment-clinical study of risk factors. Int Orthod. 2016;14(1):48-64.
[30] 徐科峰.异常牙根形态对正畸治疗前后前牙根吸收的影响[J].口腔医学,2011,31(11):689-691.
[31] LIU WK, LI S, PARK HS. Eighty Years of the Finite Element Method: Birth, Evolution, and Future. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022;29(3): 4431-4453.
[32] UPADHYAY M, ARQUB SA. Biomechanics of clear aligners: hidden truths & first principles. J World Fed Orthod. 2022;11(2):12-21.
[33] OYAMA K, MOTOYOSHI M, HIRABAYASHI M, et al. Effects of root morphology on stress distribution at the root apex. Eur J Orthod. 2007;29(2):113-117.
[34] ALHASYIMI AA, AYUB A, FARMASYANTI CA. Effectiveness of the Attachment Design and Thickness of Clear Aligners during Orthodontic Anterior Retraction: Finite Element Analysis. Eur J Dent. 2023;18(1):174-181.
[35] TARTAGLIA GM, MAPELLI A, MASPERO C, et al. Direct 3D Printing of Clear Orthodontic Aligners: Current State and Future Possibilities. Materials. 2021;14(7):1-11.
[36] LI JW, SI JR, XUE CR, et al. Seeking orderness out of the orderless movements: an up-to-date review of the biomechanics in clear aligners. Prog Orthod. 2024;25(1):1-17.
[37] GANDHI V, MEHTA S, GAUTHIER M, et al. Comparison of external apical root resorption with clear aligners and pre-adjusted edgewise appliances in non-extraction cases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthod. 2020;43(1):1-10.
[38] OZKALAYCI N, KARADENIZ EI, ELEKDAG-TURK S, et al. Effect of continuous versus intermittent orthodontic forces on root resorption: A microcomputed tomography study. Angle Orthod. 2018;88(6):733-739.
[39] JAGTAP SB, BHOSALE VI, PATIL AS. Comparative evaluation of interrupted and intermittent forces on canine retraction: an in vivo study. Folia Med. 2021;63(5):686-691.
[40] GHALEB S, TAMISH N, ELKENANY W, et al. The effect of two different types of forces on possible root resorption in relation to dentin phosphoprotein levels: a single-blind, split-mouth, randomized controlled trial. Prog Orthod. 2021;22(44):1-12.
[41] BI S, SHI G. The crucial role of periodontal ligament’s Poisson’s ratio and tension-compression asymmetric moduli on the evaluation of tooth displacement and stress state of periodontal ligament. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2023;148(3):1-8.
[42] JAIN A, PRASANTHA GS, MATHEW S, et al. Analysis of stress in periodontium associated with orthodontic tooth movement: a three dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Method Biomec. 2021;21(2):1-11.
[43] SCHWARZ AM. Tissue changes incidental to orthodontic tooth movement. Int J Orthod Oral Surg Radiol. 1932;18(4):331-352.
[44] LYU XW, CAO X, YAN RTJ. Biomechanical effects of clear aligners with different thicknesses and gingival-margin morphology for appliance design optimization. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023;164(2): 239-252.
[45] SUN HF, FENG Y, TU SQ, et al. Dopamine promotes osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs by activating DRD1 and DRD2 during orthodontic tooth movement via ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Regen Ther. 2024;27(1):268-278.
[46] DANZ JZ, DEGEN M. Selective modulation of the bone remodeling regulatory system through orthodontic tooth movement-a review. Front Oral Health. 2025;6(1):1-16.
[47] WANG Q, WANG X, CHEN YZ, et al. Dual role of Sfrp4 in bone remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2025;28(1):175-186.
[48] ANDREA C. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular round-shaped teeth: A finite element study. Angle Orthod. 2020; 90(2):247-254.
[49] DIAN F, HAO L, CHANG YY. Effectiveness of the attachment position in molar intrusion with clear aligners: a finite element study. BMC Oral Health, 2022;22(1):474.
[50] SOSLY R, MOHAMMED H, RIZK MZ, et al. Effectiveness of miniscrew-supported maxillary incisor intrusion in deep-bite correction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Angle Orthod. 2020;90(2): 291-304.
[51] 程兰欣,刘钧.打开咬合的三维有限元分析的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,202,30(11):827-831.
[52] KHOSRAVI R, COHANIM B, HUJOEL F, et al. Management of overbite with the Invisalign appliance. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2017; 151(4):691-699.
[53] GUPTA M, MADHOK K, KULSHRESTHA R, et al. Determination of stress distribution on periodontal ligament and alveolar bone by various tooth movements-A 3D FEM study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2020;10(4): 758-763.
[54] 张羽彤,陈颖,熊国平.无托槽隐形矫治器不同设计对伴牙槽骨吸收中切牙压低效能的有限元分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022, 38(10):604-607. |