[1] WHITTAKER A, ABOUGHDIR M, MAHBUB S, et al. Myocardial protection in cardiac surgery: how limited are the options? A comprehensive literature review. Perfusion. 2021;36(4):338-351.
[2] MA YY, CAO Y, GAO H, et al. Sevoflurane Improves Ventricular Conduction by Exosomes Derived from Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts After Hypothermic Global Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023;17:1719-1732.
[3] SHARMA AK, SINGH S, BHAT M, et al. New drug discovery of cardiac anti-arrhythmic drugs: insights in animal models. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1):16420.
[4] KWEK XY, HALL AR, LIM WW, et al. Role of cardiac mitofusins in cardiac conduction following simulated ischemia-reperfusion. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):21049.
[5] UPADHYAY RK, KUMAR K, VISHWAKARMA VK, et al. Delineating the NOX-Mediated Promising Therapeutic Strategies for the Management of Various Cardiovascular Disorders: A Comprehensive Review. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2024. doi: 10.2174/0115701611308870240910115023.
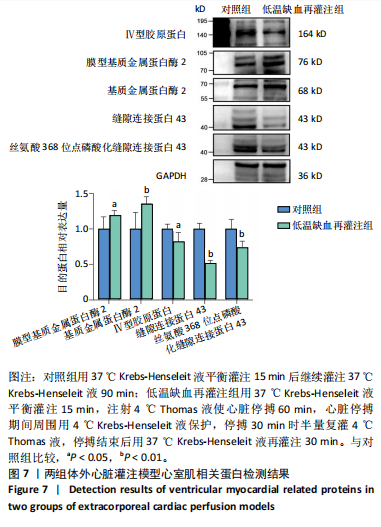
[6] YANG F, ZHANG XL, LIU HH, et al. Post translational modifications of connexin 43 in ventricular arrhythmias after myocardial infarction. Mol Biol Rep. 2024; 51(1):329.
[7] DHEIN S, SALAMEH A. Remodeling of Cardiac Gap Junctional Cell-Cell Coupling. Cells. 2021;10(9):2422.
[8] 王贵龙,糜睿,徐雄坤,等.七氟醚对低温全心缺血-再灌注心脏电传导及Cx43 Ser368磷酸化的影响[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2020,36(12):1216-1220.
[9] 任文鑫,马艺宸,高鸿,等.电针后处理对大鼠缺血再灌注心室肌电传导和缝隙连接蛋白43表达的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2023,39(2):81-85.
[10] YANG H, BORG TK, SCHMIDT LP, et al. Laser cell-micropatterned pair of cardiomyocytes: the relationship between basement membrane development and gap junction maturation. Biofabrication. 2014;6(4):45003.
[11] VO HVT, NGUYEN YT, KIM N, et al. Vitamin A, D, E, and K as Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/9 Regulators That Affect Expression and Enzymatic Activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(23):17038.
[12] ITOH Y. Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases: Their functions and regulations. Matrix Biol. 2015;44-46:207-223.
[13] IMOTO K, HIRAKAWA M, OKADA M, et al. Canstatin modulates L-type calcium channel activity in rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;499(4):954-959.
[14] OKADA M, YAMAWAKI H. A current perspective of canstatin, a fragment of type IV collagen alpha 2 chain. J Pharmacol Sci. 2019;139(2):59-64.
[15] 安丽,高鸿,刘艳秋,等.应激诱导磷蛋白1可能通过调节Cx43表达影响低温缺血再灌注后心室肌电传导[J].实用医学杂志,2023,39(1):35-40.
[16] BAARK F, WATERS E, EYKYN TR, et al. Characterization and Validation of Radiotracer Kinetics Using the Langendorff Isolated Perfused Heart. Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2729:251-267.
[17] HAN B, TREW ML, ZGIERSKI-JOHNSTON CM. Cardiac Conduction Velocity, Remodeling and Arrhythmogenesis. Cells. 2021;10(11):2923.
[18] LEYBAERT L, DE SMET MA, LISSONI A, et al. Connexin hemichannels as candidate targets for cardioprotective and anti-arrhythmic treatments. J Clin Invest. 2023; 133(6):e168117.
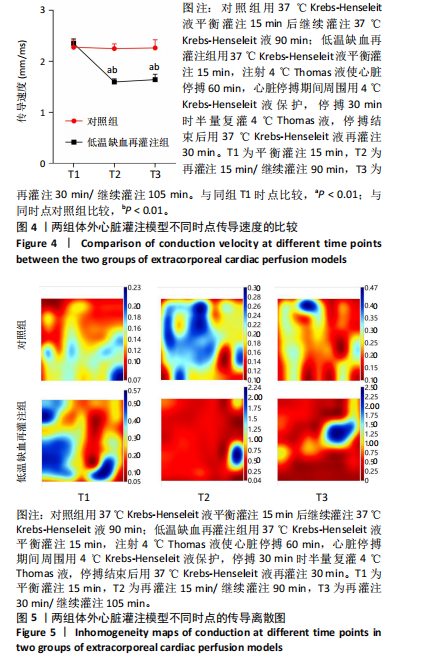
[19] CAO Y, SONG YN, WANG ZJ, et al. Effects of different dosages esketamine on cardiac conduction and heterogeneity of Cx43: the epicardial mapping in guinea pigs. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(14):772.
[20] VAN RIJEN HV, ECKARDT D, DEGEN J, et al. Slow conduction and enhanced anisotropy increase the propensity for ventricular tachyarrhythmias in adult mice with induced deletion of connexin43. Circulation. 2004;109(8):1048-1055.
[21] LIM S, MANGALA MM, HOLLIDAY M, et al. Reduced connexin-43 expression, slow conduction and repolarisation dispersion in a model of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Dis Model Mech. 2024;17(8):dmm050407.
[22] QU Z, WEISS JN. Cardiac Alternans: From Bedside to Bench and Back. Circ Res. 2023;132(1):127-149.
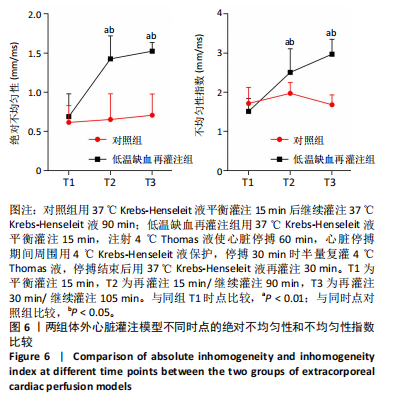
[23] DONG X, TSE G, HAO G, et al. Heterogeneities in Ventricular Conduction Following Treatment with Heptanol: A Multi-Electrode Array Study in Langendorff-Perfused Mouse Hearts. Life (Basel). 2022;12(7):996.
[24] GUO YH, YANG YQ. Atrial Fibrillation: Focus on Myocardial Connexins and Gap Junctions. Biology (Basel). 2022;11(4):489.
[25] WANG YJ, LI QH, TAO B, et al. Fibroblasts in heart scar tissue directly regulate cardiac excitability and arrhythmogenesis. Science. 2023; 381(6665):1480-1487.
[26] JI J, REN X, ZORLUTUNA P. Cardiac Cell Patterning on Customized Microelectrode Arrays for Electrophysiological Recordings. Micromachines (Basel). 2021;12(11): 1351.
[27] LEIVADITIS V, MULITA F, DAHM M, et al. History of the development of isolated heart perfusion experimental model and its pioneering role in understanding heart physiology. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2024;9(1):109-121.
[28] BOSE A, TRUONG QA, SINGH JP. Biomarkers in electrophysiology: role in arrhythmias and resynchronization therapy. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015; 43(1):31-44.
[29] PLAISIER E, GRIBOUVAL O, ALAMOWITCH S, et al. COL4A1 mutations and hereditary angiopathy, nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(26):2687-2695.
[30] SUGIYAMA A, SHIMIZU Y, OKADA M, et al. Preventive Effect of Canstatin against Ventricular Arrhythmia Induced by Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: A Pilot Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1004.
[31] FANA XZ, ZHU HJ, WU X, et al. Effects of doxycycline on cx43 distribution and cardiac arrhythmia susceptibility of rats after myocardial infarction. Iran J Pharm Res. 2014;13(2):613-621.
[32] LI JF, LEVIN MD, XIONG YM, et al. N-cadherin haploinsufficiency affects cardiac gap junctions and arrhythmic susceptibility. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44(3):597-606.
[33] CAO J, GAO Q, CHEN H, et al. Desmin Correlated with Cx43 May Facilitate Intercellular Electrical Coupling during Chronic Heart Failure. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021(1):6621132.
[34] PRUNSKAITE-HYYRYLAINEN R, SHAN JD, RAILO A, et al. Wnt4, a pleiotropic signal for controlling cell polarity, basement membrane integrity, and antimullerian hormone expression during oocyte maturation in the female follicle. FASEB J. 2014;28(4):1568-1581.
[35] ZHOU P, YANG XL, YANG DZ, et al. Integrin-Linked Kinase Activation Prevents Ventricular Arrhythmias Induced by Ischemia/Reperfusion Via Inhibition of Connexin 43 Remodeling. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021;14(4):610-618.
[36] LV JY, FU ZY, ZHENG HR, et al. Global research trends and emerging opportunities for integrin adhesion complexes in cardiac repair: a scientometric analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024;11:1308763.
[37] MIAO LJ, LU YY, NUSRAT A, et al. beta1 integrins regulate cellular behavior and cardiomyocyte organization during ventricular wall formation. Cardiovasc Res. 2024;120(11):1279-1294.
[38] PANG XC, HE X, QIU ZW, et al. Targeting integrin pathways: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):1.
[39] AI X, YAN JJ, POGWIZD SM. Serine-threonine protein phosphatase regulation of Cx43 dephosphorylation in arrhythmogenic disorders. Cell Signal. 2021;86:110070.
[40] NERGER BA, SINHA S, LEE NN, et al. 3D Hydrogel Encapsulation Regulates Nephrogenesis in Kidney Organoids. Adv Mater. 2024;36(14):e2308325.
[41] LEWIS-ISRAELI YR, WASSERMAN AH, GABALSKI MA, et al. Self-assembling human heart organoids for the modeling of cardiac development and congenital heart disease. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):5142.
[42] BAI L, LI MM, SU JC. 432A perspective on light-based bioprinting of DNA hydrogels for advanced bone regeneration: Implication for bone organoids. Int J Bioprint. 2023;9(2):688.
[43] LI WX, ZHOU ZH, ZHOU XY, et al. 3D Biomimetic Models to Reconstitute Tumor Microenvironment In Vitro: Spheroids, Organoids, and Tumor-on-a-Chip. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(18):e2202609.
[44] ZHANG LH, LI T, YU Y, et al. An injectable conductive hydrogel restores electrical transmission at myocardial infarct site to preserve cardiac function and enhance repair. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:339-354.
[45] IOAKEIMIDIS NS, PITSIS A, ZEGKOS T, et al. Periostin is overexpressed, correlated with fibrosis and differs among grades of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in myectomy tissue of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. PLoS One. 2023; 18(11):e293427.
[46] ZHAO S, HULSURKAR MM, LAHIRI SK, et al. Atrial proteomic profiling reveals a switch towards profibrotic gene expression program in CREM-IbDeltaC-X mice with persistent atrial fibrillation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024;190:1-12. |