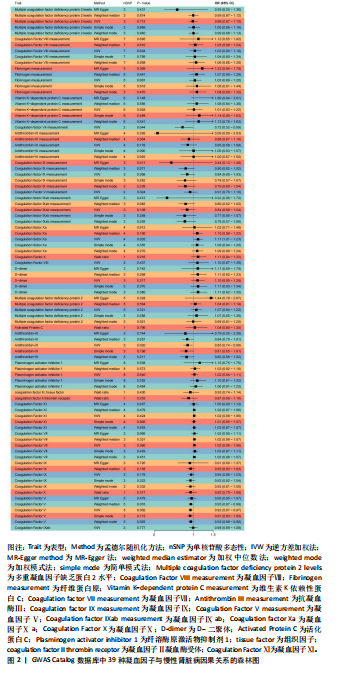
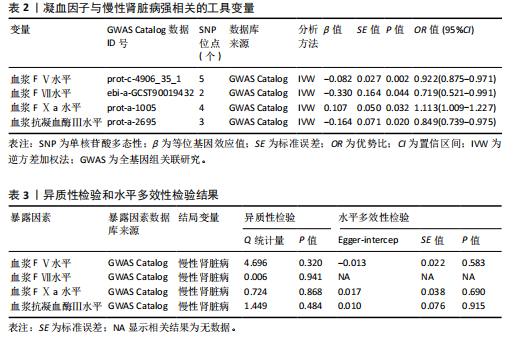
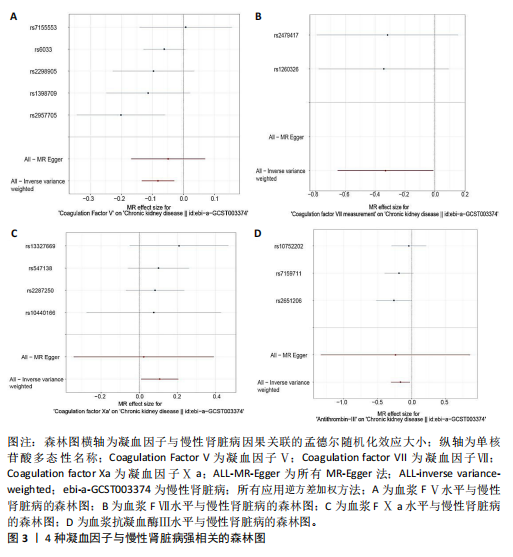
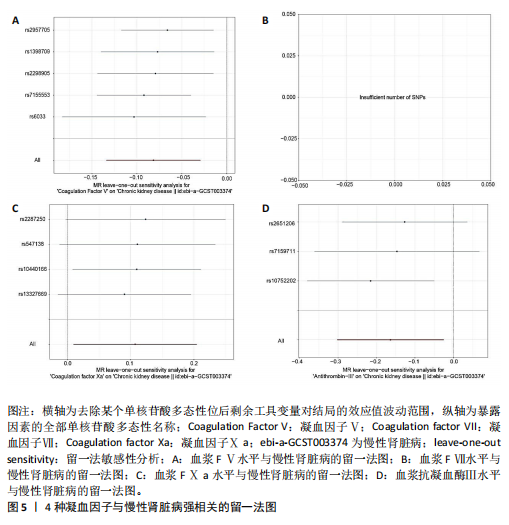
[1] AMMIRATI AL. Chronic kidney disease. rev assoc med bras (1992). 2020;66Suppl 1 (Suppl 1):s03-s09.
[2] KIDNEY DISEASE: IMPROVING GLOBAL OUTCOMES (KDIGO) CKD WORK GROUP. KDIGO 2024. Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2024; 105(4S):S117-S314.
[3] CHEN TK, KNICELY DH, GRAMS ME. Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: a review. JAMA. 2019;322(13):1294-1304.
[4] ADDI T, DOU L, BURTEY S. Tryptophan-derived uremic toxins and thrombosis in chronic kidney disease. Toxins (Basel). 2018;10(10):412.
[5] PARIKH AM, SPENCER FA, LESSARD D, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients with reduced estimated GFR: a population-based perspective. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011; 58(5):746-755.
[6] PAVORD S, MYERS B. Bleeding and thrombotic complications of kidney disease. Blood Rev. 2011;25(6):271-278.
[7] JALAL DI, CHONCHOL M, TARGHER G. Disorders of hemostasis associated with chronic kidney disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2010;36(1):34-40.
[8] WEINER DE, TIGHIOUART H, ELSAYED EF, et al. The relationship between nontraditional risk factors and outcomes in individuals with stage 3 to 4 CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51(2):212-223.
[9] ZHAO J, ZHOU SQ, CHEN YX, et al. Causal relationship between mitochondrial-associated proteins and sepsis in ICU patients: a mendelian randomization study. ACS Omega. 2024;9(7):8457-8463.
[10] ZHANG T, CHEN H, SHI Y, et al. Mitochondrial biological function and risk of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter: a 2-sample Mendelian randomization study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(27):e38631.
[11] LAWLOR DA, HARBORD RM, STERNE JA, et al. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med. 2008;27(8):1133-1163.
[12] LIU H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Effect of plasma vitamin C levels on Parkinson’s disease and age at onset: a Mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2021; 19(1):221.
[13] YANG H, SHI P, LI M, et al. Mendelian-randomization study reveals causal relationships between nitrogen dioxide and gut microbiota. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023;267:115660.
[14] DUNBAR JK, CAMPBELL H. Genetic epidemiology. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42(2):139-141; quiz 142.
[15] WALSH R, JURGENS SJ, ERDMANN J, et al. Genome-wide association studies of cardiovascular disease. Physiol Rev. 2023; 103(3):2039-2055.
[16] ARDISSINO M, MORLEY AP, SLOB E, et al. Birth weight influences cardiac structure, function, and disease risk: evidence of a causal association. Eur Heart J. 2024; 45(6):443-454.
[17] FENG R, LU M, XU J, et al. Pulmonary embolism and 529 human blood metabolites: genetic correlation and two-sample Mendelian randomization study. BMC Genom Data. 2022;23(1):69.
[18] NGUYEN K, MITCHELL BD. A guide to understanding mendelian randomization studies. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024; 76(11):1451-1460.
[19] XU R, LIU S, LI LY, et al. Causal effects of gut microbiota on the risk of erectile dysfunction: a Mendelian randomization study. Int J Impot Res. 2024. doi: 10.1038/s41443-024-00824-7.
[20] JING S, LIN L, LI J, et al. Causal relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and IgA nephropathy: a bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization study. Ren Fail. 2024;46(2):2371055.
[21] LIU X, QI X, HAN R, et al. Gut microbiota causally affects cholelithiasis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:1253447.
[22] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377-389.
[23] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-698.
[24] LIU G, ZHAO Y, JIN S, et al. Circulating vitamin E levels and Alzheimer’s disease: a Mendelian randomization study. Neurobiol Aging. 2018;72:189.e1-189.e9.
[25] WANG S, WANG J, NIU Z, et al. Causal relationship between mitochondrial-associated proteins and cerebral aneurysms: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1405086.
[26] YUAN S, MASON AM, TITOVA OE, et al. Morning chronotype and digestive tract cancers: Mendelian randomization study. Int J Cancer. 2023;152(4):697-704.
[27] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF B, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621.
[28] WU F, HUANG Y, HU J, et al. Mendelian randomization study of inflammatory bowel disease and bone mineral density. BMC Med. 2020;18(1):312.
[29] NABER T, PUROHIT S. Chronic kidney disease: role of diet for a reduction in the severity of the disease. Nutrients. 2021; 13(9):3277.
[30] JONES A, SWAN D, LISMAN T, et al. Anticoagulation in chronic kidney disease: current status and future perspectives. J Thromb Haemost. 2024;22(2):323-336.
[31] MUSLIMOVIC A, RASIC S, TULUMOVIC D, et al. Inflammatory markers and procoagulants in chronic renal disease stages 1-4. Med Arch. 2015;69(5):307-310.
[32] HUANG MJ, WEI RB, WANG Y, et al. Blood coagulation system in patients with chronic kidney disease: a prospective observational study. BMJ Open. 2017;7(5):e014294.
[33] PANOUTSOPOULOU K, WHEELER E. Key concepts in genetic epidemiology. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1793:7-24.
[34] DAVEY SMITH G, HEMANI G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-R98.
[35] WATTANAKIT K, CUSHMAN M, STEHMAN-BREEN C, et al. Chronic kidney disease increases risk for venous thromboembolism. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19(1):135-140.
[36] MAST AE, RUF W. Regulation of coagulation by tissue factor pathway inhibitor: Implications for hemophilia therapy. J Thromb Haemost. 2022;20(6):1290-1300.
[37] YAU JW, TEOH H, VERMA S. Endothelial cell control of thrombosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015;15:130.
[38] JOURDE-CHICHE N, DOU L, SABATIER F, et al. Levels of circulating endothelial progenitor cells are related to uremic toxins and vascular injury in hemodialysis patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7(9):1576-1584.
[39] CHEN TY, LIN TT, HSIEH MY, et al. Circulating progenitor cells affect thrombosis of dialysis arteriovenous fistulas. Am J Nephrol. 2016; 44(6):428-438.
[40] YISIREYILI M, SAITO S, ABUDUREYIMU S, et al. Indoxyl sulfate-induced activation of (pro)renin receptor promotes cell proliferation and tissue factor expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109268.
[41] ONO T. Roles of coagulation pathway and factor Xa in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012;132(4):449-453.
[42] AHNSTRöM J. FV/FVa revealed. Blood. 2021;137(22):3011-3013.
[43] LI Y, LIU H, YE S, et al. The effects of coagulation factors on the risk of endometriosis: a Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):195.
[44] YUAN S, BRUZELIUS M, DAMRAUER SM, et al. Cardiometabolic, lifestyle, and nutritional factors in relation to varicose veins: a mendelian randomization study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(21):e022286.
[45] HOU Y, XIAO Z, ZHU Y, et al. Blood metabolites and chronic kidney disease: a Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med Genomics. 2024;17(1):147.
[46] ZHAO Y, HU Y, SMITH JP, et al. Cohort profile: the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43(1):61-68.
[47] CNCB-NGDC MEMBERS AND PARTNERS. Database resources of the national genomics data center, china national center for bioinformation in 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52(D1):D18-D32. |