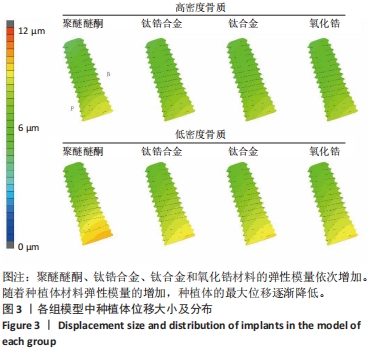
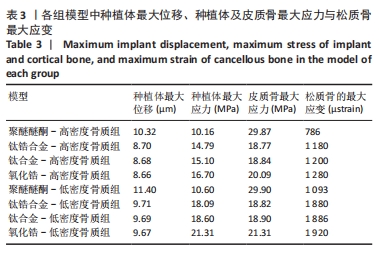
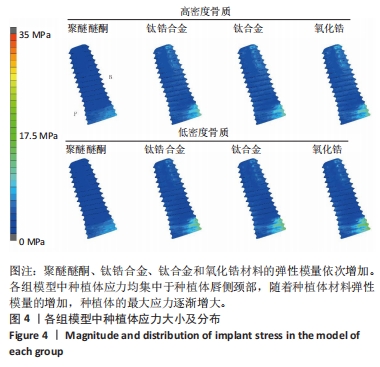
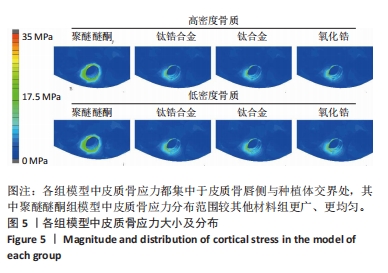
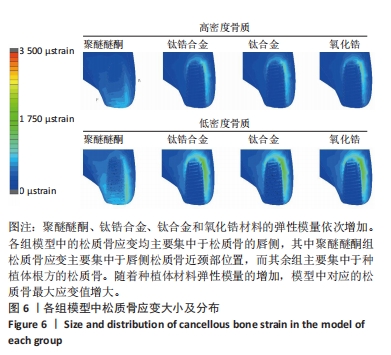
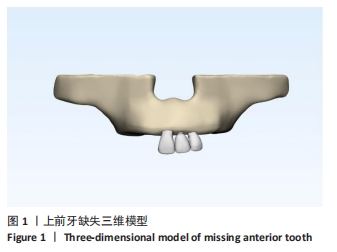
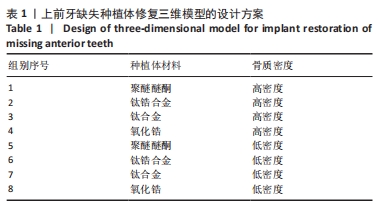
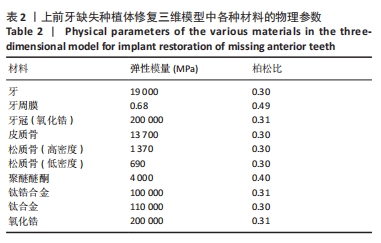
[1] LIU X, LV H, CHEN M, et al. Case report and literature review: autonomous robotic system assisted palatal implantation at an anterior teeth site compromised by periapical cyst. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1335043.
[2] ALAMOUDI R, KANAVAKIS G, OESCHGER ES, et al. Occlusal characteristics in modern humans with tooth agenesis. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):5840.
[3] JOHANSSON L, LATORRE JL, LIVERSAIN M, et al. Three-Dimensional Printed Patient-Specific Vestibular Augmentation: A Case Report. J Clin Med. 2024;13(8). doi: 10.3390/jcm13082408.
[4] GOLMAYO P, BARALLAT L, LOSADA M, et al. Keratinized tissue gain after free gingival graft augmentation procedures around teeth and dental implants: A prospective observational study. J Clin Periodontol. 2021;48(2):302-314.
[5] 沈洁,陈俊良,赵田琦,等.鹿角可再生动物模型建立与即刻加载对种植体及其周围骨改建的作用[J]. 西南医科大学学报,2022, 45(1):34-38.
[6] ZHENG HM, ZHANG SJ, JIAO Y, et al. Fabrication and evaluation of porous coatings doped with bioactive elements on titanium surfaces. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024;28(9):3391-3402.
[7] ZHENG HM, ZHANG SJ, JIAO Y, et al. Fabrication and evaluation of porous coatings doped with bioactive elements on titanium surfaces. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024;28(9):3391-3402.
[8] DOLGOLEV A, RESHETOV I, SVYATOSLAVOV D, et al. Experimental Biointegration of a Titanium Implant in Delayed Mandibular Reconstruction. Pers Med. 2020;10(1):6.
[9] XIONG J, MILLER CM, SHARMA D. Effect of Bergenin on Human Gingival Fibroblast Response on Zirconia Implant Surfaces: An In Vitro Stud. Funct Biomater. 2023;14(9):474.
[10] BOLLEN C, HAKOBAYAN G, JÖRGENS M. One-piece versus two-piece ceramic dental implants. Br Dent J. 2024;236(5):383-387.
[11] DUA R, SHARUFA O, TERRY J, et al. Surface modification of Polyether-ether-ketone for enhanced cell response: a chemical etching approach. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1202499.
[12] TRIBST JPM, DE JAGER N, DAL PIVA AMO, et al. Effect of crown retention systems and loading direction on the stress magnitude of posterior implant-supported restorations: A 3D-FEA. Heliyon. 2024;10(6):e28129.
[13] SHAW RB JR, KATZEL EB, KOLTZ PF, et al. Facial bone density: effects of aging and impact on facial rejuvenation. Aesthet Surg J. 2012;32(8): 937-942.
[14] RAVIDÀ A, SERRONI M, BORGNAKKE WS, et al. Short (≤6 mm) compared with ≥10-mm dental implants in different clinical scenarios: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials with meta-analysis, trial sequential analysis and quality of evidence grading. J Clin Periodontol. 2024;51(7):936-965.
[15] ALVAREZ-ARENAL A, BRIZUELA-VELASCO A, DELLANOS-LANCHARES H, et al. Should oral implants be splinted in a mandibular implant-supported fixed complete denture? A 3-dimensional-model finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2014;112(3):508-514.
[16] BACCHI A, CONSANI RL, MESQUITA MF, et al. Stress distribution in fixed-partial prosthesis and peri-implant bone tissue with different framework materials and vertical misfit levels: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Sci. 2013;55(3):239-244.
[17] 郝永明,赵伟,邢一栋,等.牙种植区骨密度的CBCT评价[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2014,24(3):204-207.
[18] XIE B, CHEN J, ZHAO T, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior fixed partial denture supported by implants with different materials.Ann Anat. 2022;243:151943.
[19] HOUDAIFA R, ALZOUBI H, JAMOUS I. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Worn Molars With Prosthetic Crowns and Onlays Made of Various Materials. Cureus. 2022;14(10):e30240.
[20] PENTEADO MM, MENDES TRIBST JP, DAL PIVA AMO, et al. Influence of different restorative material and cement on the stress distribution of ceramic veneer in upper central incisor. Indian J Dent Res. 2020; 31(2):236-240.
[21] WU B, TANG Y, YAO K, et al. Ion-incorporated titanium implants for staged regulation of antibacterial activity and immunoregulation-mediated osteogenesis. Nanoscale. 2024;16(14):7167-7184.
[22] SILVA-HENAO JD, SCHOBER S, PAHR DH, et al. Critical loss of primary implant stability in osteosynthesis locking screws under cyclic overloading. Med Eng Phys. 2024;126:104143.
[23] COZZOLINO F, APICELLA D, WANG G, et al. Implant-to-bone force transmission: a pilot study for in vivo strain gauge measurement technique. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;90:173-181.
[24] MAO B, TIAN Y, LI J, et al. Expansion rebound deformation of clear aligners and its biomechanical influence: a three-dimensional morphologic analysis and finite element analysis study. Angle Orthod. 2023;93(5):572-579.
[25] HUANG Y, WANG J, ZHU L, et al. The optimal design and three-dimensional finite element analysis of CAD/CAM integrated roach attachment. Heliyon. 2023;10(1):e23283.
[26] CHAND Y B, MAHENDRA J, JIGEESH N, et al. Comparison of stress distribution and deformation of four prosthetic materials in full-mouth rehabilitation with implants: A three-dimensional finite element study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2020;21(11):1210-1217.
[27] WOŹNIAK A, SMOK W, SZEWCZENKO J, et al. Influence of Hybrid Surface Modification on Biocompatibility and Physicochemical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI Titanium. J Funct Biomater. 2024;15(3):52.
[28] SHAH SD, ZHENG F, SEGHI RR, et al. Strength of titanium-zirconium alloy implants with a conical connection after implantoplasty. J Prosthet Dent. 2022:S0022-3913(22)00511-X. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2022.08.015.
[29] SCARANO A, KHATER AGA, GEHRKE SA, et al. Animal Models for Investigating Osseointegration: An Overview of Implant Research over the Last Three Decades. J Funct Biomater. 2024;15(4). doi: 10.3390/jfb15040083.
[30] HAIMOV E, SARIKOV R, HAIMOV H, et al. Differences in Titanium, Titanium-Zirconium, Zirconia Implants Treatment Outcomes: a Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2023;14(3):e1.
[31] ALGHAULI M, ALQUTAIBI AY, WILLE S, et al. 3D-printed versus conventionally milled zirconia for dental clinical applications: Trueness, precision, accuracy, biological and esthetic aspects. J Dent. 2024:144: 104925.
[32] LINZHI J, TIEYAN C, GUIXIANG Z, et al. Effects of machining gap on the surface integrity in CBN spherical magnetic abrasives grinding of ZrO2 ceramic. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2023;129(1-2):825-835.
[33] ZHENG W, WU D, ZHANG Y, et al. Multifunctional modifications of polyetheretherketone implants for bone repair: A comprehensive review. Biomater Adv. 2023;154:213607.
[34] AN J, SHI X, ZHANG J, et al. Dual aldehyde cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogels loaded with PRP and NGF biofunctionalized PEEK interfaces to enhance osteogenesis and vascularization. Mater Today Bio. 2023; 24:100928.
[35] DENG Y, MA R, HE Y, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the maxillary sinus floor membrane during internal sinus floor elevation with implants at different angles of the maxillary sinus angles. Int J Implant Dent. 2024;10(1):11.
[36] NICOLIELO LFP, VAN DESSEL J, JACOBS R, et al. Relationship between trabecular bone architecture and early dental implant failure in the posterior region of the mandible. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020;31(2): 153-161.
[37] DUA R, SHARUFA O, TERRY J, et al. Surface modification of Polyether-ether-ketone for enhanced cell response: a chemical etching approach. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1202499.
[38] TALMAZOV G, VEILLEUX N, ABDULMAJEED A, et al. Finite element analysis of a one-piece zirconia implant in anterior single tooth implant applications. PLoS One. 2020;15(2):e0229360.
[39] AJAJ AL-KORDY NMT, AL-SAADI MH. Finite Element Study of Stress Distribution with Tooth-Supported Mandibular Overdenture Retained by Ball Attachments or Resilient Telescopic Crowns. Eur J Dent. 2023; 17(2):539-547.
[40] CHENG R, WANG H, JIANG Z, et al. The Femoral Tunnel Drilling Angle at 45° Coronal and 45° Sagittal Provided the Lowest Peak Stress and Strain on the Bone Tunnels and Anterior Cruciate Ligament Graft. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:797389.
[41] BATAINEH K, AL JANAIDEH M. Effect of different biocompatible implant materials on the mechanical stability of dental implants under excessive oblique load. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(6): 1206-1217.
[42] PANMEI G, KUMAR A, BASAK S, et al. Evaluation and Comparison of Stress in Divergent and Convergent Collar Designs of Implants With Different Bone Densities: A Finite Element Study. Cureus. 2023;15(3): e36550. |