中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (2): 371-378.doi: 10.12307/2025.232
• 脊柱组织构建 spinal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
加味春泽汤调控内质网应激凋亡治疗脊髓损伤大鼠的尿潴留
朱博超1,李彦杰2,秦合伟2,赵楠楠1,刘昊源1,徐振华1,王煜普1
- 1河南中医药大学,河南省郑州市 450046;2河南省中医院/河南中医药大学第二附属医院,河南省郑州市 450002
Jiawei Chunze Decoction treats urinary retention after spinal cord injury in rats based on the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis
Zhu Bochao1, Li Yanjie2, Qin Hewei2, Zhao Nannan1, Liu Haoyuan1, Xu Zhenhua1, Wang Yupu1
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine/The Second Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
脊髓损伤后尿潴留:常指由于外伤导致脊髓结构或功能改变从而使骶髓初级排尿中枢受损或其周围神经(副交感和躯体神经)受损引起的以逼尿肌无反射、膀胱容量不断增大、尿液无法排出的一种膀胱功能障碍。
内质网应激:是一种新型的细胞凋亡调控通路,当出现缺血、缺氧和氧化应激等生理或病理损伤时会导致错误折叠或未折叠蛋白质在内质网腔大量聚集,从而引起内质网的稳态发生紊乱,导致内质网应激的发生。
背景:前期临床观察发现加味春泽汤是临床治疗脊髓损伤后尿潴留的有效方剂。动物实验发现磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3K/Akt)信号通路与膀胱功能障碍程度密切相关。
目的:进一步验证加味春泽汤对脊髓损伤后尿潴留大鼠膀胱功能及PI3K/Akt通路的影响。
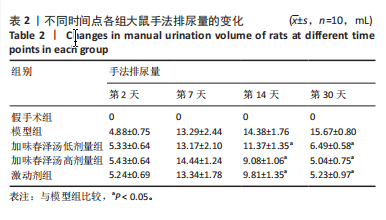
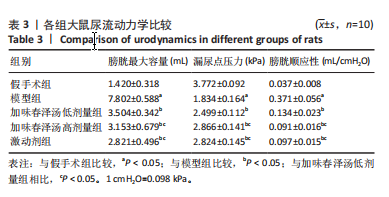
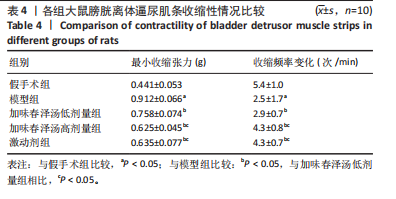
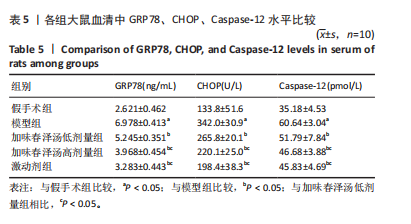
方法:将60只SD雌性大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、加味春泽汤低剂量组、加味春泽汤高剂量组、激动剂组。假手术组大鼠暴露脊髓但不切断,其余各组大鼠采用改良后的Hassan Shaker脊髓横断法建立骶髓损伤大鼠模型。造模24 h后,假手术组和模型组大鼠给予等体积生理盐水灌胃,加味春泽汤低、高剂量组大鼠分别给予含有14.4 g/kg和28.8 g/kg的加味春泽汤颗粒剂,等体积灌胃4周,激动剂组大鼠给予PI3K/Akt信号通路激动剂740Y-P腹腔注射0.02 mg/kg治疗。治疗4周后采用尿流动力学检测各组大鼠膀胱最大容量、漏尿点压力、膀胱顺应性,膀胱离体逼尿肌条收缩性检测各组大鼠膀胱最小收缩张力、收缩频率,苏木精-伊红染色观察各组大鼠膀胱病理学改变,ELISA法检测各组大鼠血清中GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12水平,RT-PCR、Western blot法检测大鼠膀胱组织PI3K、Akt、GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12 mRNA及蛋白的表达。
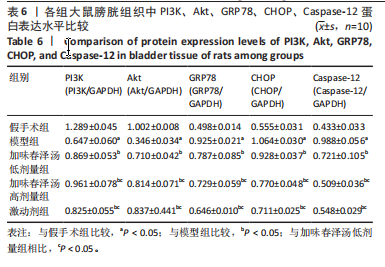
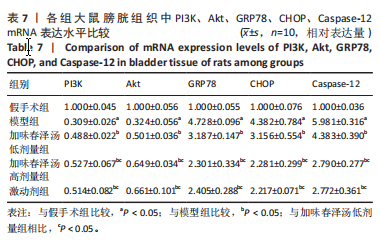
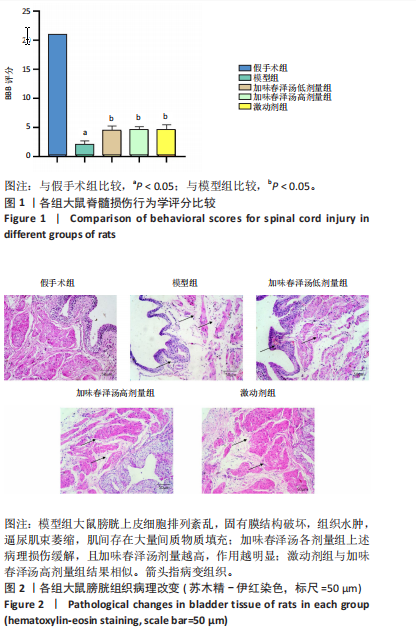
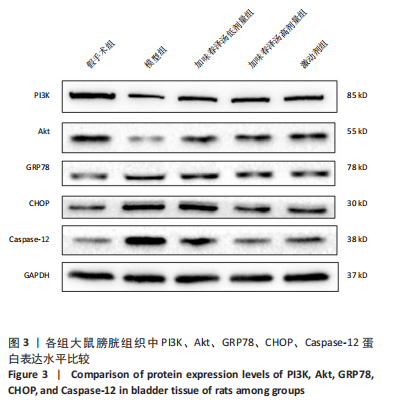
结果与结论:①与假手术组相比,模型组大鼠膀胱最大容量、膀胱顺应性、最小收缩张力升高(P < 0.05),漏尿点压力、膀胱收缩频率降低(P < 0.05);血清中GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12水平升高(P < 0.05);膀胱上皮细胞排列紊乱,细胞间存在单核细胞浸润,组织水肿,逼尿肌束萎缩;膀胱组织PI3K、Akt mRNA和蛋白表达降低,GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12 mRNA和蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05)。②与模型组相比,加味春泽汤低、高剂量组及激动剂组干预4周后,大鼠膀胱最大容量、膀胱顺应性、最小收缩张力降低(P < 0.05),漏尿点压力、膀胱收缩频率升高(P < 0.05);血清中GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12水平降低(P < 0.05);膀胱上皮细胞分布较均匀,排列较整齐,炎细胞浸润较少,逼尿肌束较饱满;膀胱组织PI3K、Akt mRNA和蛋白表达增加,GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12 mRNA和蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05)。加味春泽汤高剂量组优于低剂量组,与激动剂组结果相似。③结果说明,加味春泽汤可以改善脊髓损伤后尿潴留大鼠膀胱功能,其作用机制可能与通过PI3K/Akt信号通路减轻膀胱组织内质网应激的发生,进而减轻凋亡有关。
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-3848-0173(朱博超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: