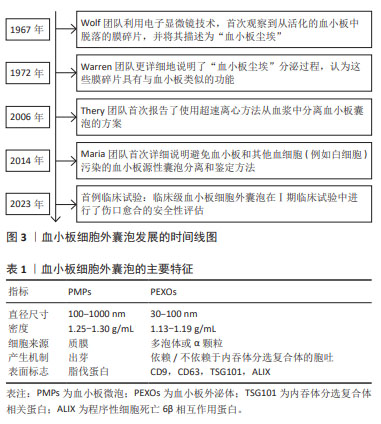
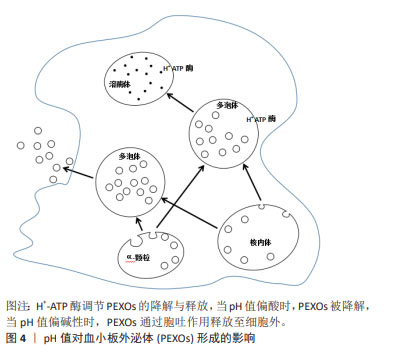
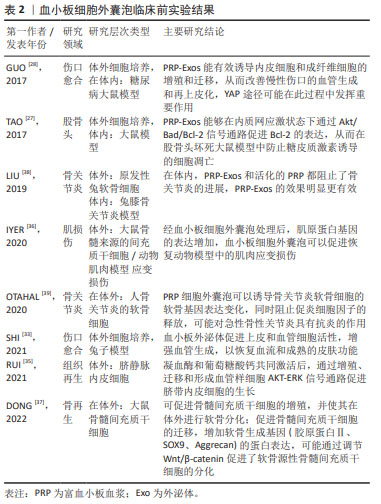
[1] VAJEN T, MAUSE SF, KOENEN RR. Microvesicles from platelets: novel drivers of vascular inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 2015;114(2): 228-236.
[2] WU J, PIAO Y, LIU Q, et al. Platelet-rich plasma-derived extracellular vesicles: a superior alternative in regenerative medicine? Cell Proliferation. 2021;54(12):e13123.
[3] SINAURIDZE EI, KIREEV DA, POPENKO NY, et al. Platelet microparticle membranes have 50-to 100-fold higher specific procoagulant activity than activated platelets. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97(3):425-434.
[4] ROSSELLO MA, GENESTRA MAF, MONJO M, et al. Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles for regenerative medicine. Preprints. 2021; 22(16):8580.
[5] ARRAUD N, LINARES R, TAN S, et al. Extracellular vesicles from blood plasma: determination of their morphology, size, phenotype and concentration. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12(5):614-627.
[6] AATONEN MT, OHMAN T, NYMAN TA, et al. Isolation and characterization of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;6:3.
[7] SPAKOVA T, JANOCKOVA J, ROSOCHA J. Characterization and therapeutic use of extracellular vesicles derived from platelets. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(18):9701.
[8] FLAUMENHAFT R, DILKS JR, RICHARDSON J, et al. Megakaryocyte-derived microparticles: direct visualization and distinction from platelet-derived microparticles. Blood. 2009;5:113.
[9] ITALIANO JE, MAIRUHU AT, FLAUMENHAFT R. Clinical relevance of microparticles from platelets and megakaryocytes. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(6):578-584.
[10] GANGALUM RK, ATANASOV IC, ZHOU ZH, et al. αB-crystallin is found in detergent-resistant membrane microdomains and is secreted via exosomes from human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(5):3261-3269.
[11] MOREL O, JESEL L, FREYSSINET JM, et al. Cellular mechanisms underlying the formation of circulating microparticles. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31(1):15-26.
[12] VEDPATHAK S, SHARMA A, PALKAR S, et al. Platelet derived exosomes disrupt endothelial cell monolayer integrity and enhance vascular inflammation in dengue patients. Front Immunol. 2024;14:1285162.
[13] TRIPISCIANO C, RENE W, EICHHORN T, et al. Different potential of extracellular vesicles to support thrombin generation: contributions of phosphatidylserine, tissue factor, and cellular origin. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):6522.
[14] EUSTES AS, DAYAL S. The role of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in immune-mediated thrombosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(14):7837.
[15] CHOEZOM D, GROSS JC. Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 controls exosome secretion by counteracting V-ATPase-mediated endosome acidification. J Cell Sci. 2022;135(5):jcs259324.
[16] COLOMBO M, MOITA C, VAN NG, et al. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 24): 5553-5565.
[17] STOORVOGEL W. Resolving sorting mechanisms into exosomes. Cell Res. 2015;25(5):531-532.
[18] COLOMBO M, RAPOSO G, THERY C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255-289.
[19] TRAJKOVIC K, HSU C, CHIANTIA S, et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science. 2008; 319(5867):1244-1247.
[20] WEI DH, ZHAN WX, GAO Y, et al. RAB31 marks and controls an ESCRT-independent exosome pathway.Cell Res. 2021;31(2):157-177.
[21] HOLLIDAY LS, FARIA LP, RODY WJ Jr. Actin and actin-associated proteins in extracellular vesicles shed by osteoclasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1):158.
[22] COLLIER ME, MARAVEYAS A, ETTELAIE C. Filamin-A is required for the incorporation of tissue factor into cell-derived microvesicles. Thromb Haemost. 2014;111(4):647-655.
[23] MOREL O, JESEL L, FREYSSINET JM, et al. Cellular mechanisms underlying the formation of circulating microparticles. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31(1): 15-26.
[24] LI X, WANG Q. Platelet-derived microparticles and autoimmune Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(12):10275.
[25] JOHNSON J, LAW SQK, SHOJAEE M, et al. First-in-human clinical trial of allogeneic, platelet-derived extracellular vesicles as a potential therapeutic for delayed wound healing. J Extracell Vesicles. 2023;12(7):e12332.
[26] SUN Y, LIU XL, ZHANG D, et al. Platelet-derived exosomes affect the proliferation and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via miR-126. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;17(4):379-387.
[27] TAO SC, YUAN T, RUI BY, et al. Exosomes derived from human platelet-rich plasma prevent apoptosis induced by glucocorticoid-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat osteonecrosis of the femoral head via the Akt/Bad/Bcl-2 signal pathway. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):733.
[28] GUO SC, TAO SC, YIN WJ, et al. Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma promote the re-epithelization of chronic cutaneous wounds via activation of YAP in a diabetic rat model. Theranostics. 2017;7(1): 81-96.
[29] HAYON Y, DASHEVSKY O, SHAI E, et al. Platelet microparticles induce angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2012;9(3):185-192.
[30] WANG Y, ZHANG S, LUO L, et al. Platelet-derived microparticles regulates thrombin generation via phophatidylserine in abdominal sepsis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(2):1051-1060.
[31] LOPEZ L, SRIVASTAVA AK, BURCHFIELD J, et al. Platelet-derived- extracellular vesicles promote hemostasis and prevent the developmentof hemorrhagic shock. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1-10.
[32] DTER MR, ALEXANDER W, HASSOUNE A, et al. Platelet‐derived extracellular vesicles released after trauma promote hemostasis and contribute to DVT in mice. J Thromb Haemost. 2019;17(10):1733-1745.
[33] SHI A, LI J, QIU X, et al. TGF-β loaded exosome enhances ischemic wound healing in vitro and in vivo. Theranostics. 2021;11(13):6616-6631.
[34] ZHU Z, SUN S, JIANG T, et al. A double-edged sword of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in tissues, injury or repair: thecurrent research overview. Tissue Cell. 2023;82:102066.
[35] RUI S, YUAN Y, DU C, et al. Comparison and investigation of exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma activated by different agonists. Cell Transpl. 2021;30:9636897211017833.
[36] IYER SR, SCHEIBER AL, YAROWSKY P, et al. Exosomes isolated from platelet-rich plasma and mesenchymal stem cells promote recovery of function after muscle injury. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48:2277-2286.
[37] DONG B, LIU X, LI J, et al. Berberine encapsulated in exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma promotes chondrogenic differentiation of the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 2022;45:1444-1451.
[38] LIU X, WANG L, MA C, et al. Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma present a novel potential in alleviating knee osteoarthritis by promoting proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis of chondrocyte via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):470.
[39] OTAHAL A, KRAMER K, KUTEN PO, et al. Characterization and chondroprotective effects of extracellular vesicles from plasma- and serum-based autologous blood-derived products for osteoarthritis therapy. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:584050.
[40] THÉRY C, AMIGORENA S, RAPOSO G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;30(1):3-22.
[41] TAMAS B, HERCZEG K, ZSOFIA O, et al. Isolation of exosomes from blood plasma: qualitative and quantitative comparison of ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography methods. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0145686.
[42] FERREIRA PM, BOZBAS E, TANNETTA SD, et al. Mode of induction of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles is a critical determinant of their phenotype and function. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):18061.
[43] OTAHAL A, KUTEN PO, KRAMER K, et al. Functional repertoire of EV-associated miRNA profiles after lipoprotein depletion via ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography from autologous blood products. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):5823.
[44] MIYAZAWA B, TRIVEDI A, TOGARRATI PP, et al. Regulation of endothelial cell permeability by platelet-derived extracellular vesicles. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019;86(6):931-942.
[45] AYON Y, DASHEVSKY O, SHAI E, et al. Platelet microparticles promote neural stem cell proliferation, survival and differentiation. J Mol Neurosci. 2012;47(3):659-665.
[46] TORREGGIANI E, PERUT F, RONCUZZI L, et al. Exosomes:novel effectors of human platelet lysate activity. Eur Cell Mater. 2014;28: 137-151.
[47] ANTICH RM, FORTEZA GMA, CALVO J, et al. Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles promote osteoinduction of mesenchymal stromal cells. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(10):667-674.
[48] LOVISOLO F, CARTON F, GINO S, et al. Platelet rich plasma-derived microvesicles increased in vitro wound healing. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(18):9658-9664.
[49] MAUSE SF, RITZEL E, LIEHN EA, et al. Platelet microparticles enhance the vasoregenerative potential of angiogenic early outgrowth cells after vascular injury. Circulation. 2010;122(5):495.
[50] KIM HK, SONG KS, JUN C, et al. Platelet microparticles induce angiogenesis in vitro. Br J Haematol. 2015;124(3)376-384.
[51] LIANG C, HUANG J, LUO P, et al. Platelet-derived microparticles mediate the intra-articular homing of mesenchymal stem cells in early-stage cartilage lesions. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(7):414-424.
[52] MOEST T, KOEHLER F, PRECHTL C, et al. Bone formation in peri-implant defects grafted with microparticles: a pilot animal experimental study. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41(10):990-998.
[53] ZHANG X, TAKRUCHI T, TAKEDA A, et al. Comparison of serum and plasma as a source of blood extracellular vesicles: increased levels of platelet-derived particles in serum extracellular vesicle fractions alter content profiles from plasma extracellular vesicle fractions. PLoS One. 2022;17(6):e0270634.
[54] LACROIX R, JUDICONE C, MOOBERR M, et al. Standardization of pre-analytical variables in plasmamicroparticle determination: results of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis SSC Collaborative workshop. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11:1190-1193.
[55] SAUMELL-ESNAOLA M, DELGADO D, GARCIA DCG, et al. Isolation of platelet-derived exosomes from human platelet-rich plasma: biochemical and morphological characterization. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(5):2861.
[56] GARDIN C, FERRONI L, LEO S, et al. Platelet-derived exosomes in atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12546.
[57] PONOMAREVA AA, NEVZOROVA TA, MORDAKHANOVA ER, et al. Intracellular origin and ultrastructure of platelet-derived microparticles. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(8):1655-1667.
[58] ANTICH RM, FORTEZA GMA, MONJO M, et al. Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles for regenerative medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(16):8580.
[59] BOUDREAU LH, CUCHEZ AC, CLOUTIER N, et al. Platelets release mitochondria serving as substrate for bactericidal group IIA-secreted phospholipase A2 to promote inflammation. Blood. 2014;124(14): 2173-2183.
[60] JOHNSON J, WU YW, BLYTHl C, et al. Prospective therapeutic applications of platelet extracellular vesicles. Trends Biotechnol. 2020; 39(6):598-612.
[61] OWENS AP, MACKMAN N. Microparticles in hemostasis and thrombosis. Circ Res. 2011;108(10):1284-1297.
[62] CLARK SR, THOMAS CP, HAMMOND VJ, et al. Characterization of platelet aminophospholipid externalization reveals fatty acids as molecular determinants that regulate coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(15):5875-5880.
|