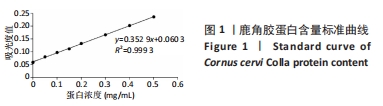
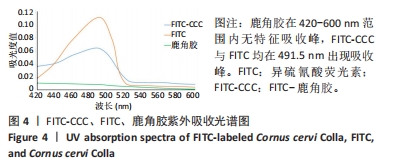
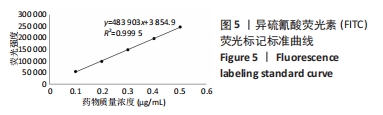
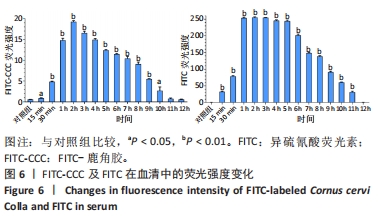
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中国药典(一部)[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社,2020.
[2] 孙铁锋, 王平. 鹿角胶-壳聚糖细胞支架修复大鼠股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中成药,2015, 37(11):2337-2341.
[3] 孙伟珊. 补肾健脾化瘀中药对绝经后骨质疏松血液流变学的改变[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学, 2014.
[4] 王平,张会敏,李刚.鹿角多肽对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2018, 33(12):5644-5647.
[5] WANG P, SUN T, LI G, et al. The Separation of Antler Polypeptide and Its Effects on the Proliferation and Osteogenetic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:1294151.
[6] FAUBERT B, TASDOGAN A, MORRISON SJ, et al. Stable isotope tracing to assess tumor metabolism in vivo. Nat Protoc. 2021;16(11):5123-5145.
[7] TRIUMBARI EKA, MORLAND D, LAUDICELLA R, et al. Clinical Applications of Immuno-PET in Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(14):3488.
[8] CAI L, LI H, YU X, et al. Green Fluorescent Protein GFP-Chromophore-Based Probe for the Detection of Mitochondrial Viscosity in Living Cells. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(3):2128-2134.
[9] LONGMIRE M, OGAWA M, HAMA Y, et al. Determination of Optimal Rhodamine Fluorophore for in Vivo Optical Imaging. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19(8):1735-1742.
[10] YANG J, WANG K, ZHENG Y, et al. Molecularly Precise, Bright, Photostable, and Biocompatible Cyanine Nanodots as Alternatives to Quantum Dots for Biomedical Applications. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022;61(36):e202202128.
[11] CAPRIFICO AE, POLYCARPOU E, FOOT PJS, et al. Biomedical and Pharmacological Uses of Fluorescein Isothiocyanate Chitosan-Based Nanocarriers. Macromol Biosci. 2021;21(1):e2000312.
[12] GREEN MR, SAMBROOK J. Spun-Column Chromatography. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2019;2019(3). doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot100594.
[13] GREEN MR, SAMBROOK J. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2020; 2020(12). doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot100412.
[14] PETIBON C, MALIK GHULAM M, CATALA M, et al. Regulation of ribosomal protein genes: An ordered anarchy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021;12(3):e1632.
[15] YANG P, NEAL SE, BUEHNE KL, et al. Complement-mediated release of fibroblast growth factor 2 from human RPE cells. Exp Eye Res. 2021;204:108471.
[16] ZHAO H, ZHANG R, YAN X, et al.Superoxide dismutase nanozymes: an emerging star for anti-oxidation. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(35):6939-6957.
[17] YILMAZ D, FURST A, MEABURN K, et al. Activation of homologous recombination in G1 preserves centromeric integrity. Nature. 2021;600(7890):748-753.
[18] DONG Y, ZHONG J, DONG L. The Role of Decorin in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. J Immunol Res. 2022;17:1283383.
[19] GARCIA MM, GOICOECHEA C, MOLINA-ÁLVAREZ M, et al. Toll-like receptor 4: A promising crossroads in the diagnosis and treatment of several pathologies. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;874:172975.
[20] 周芳妍, 李婷, 刘力, 等. 鹿角胶中氨基酸类成分的HPLC指纹图谱[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(9):47-51.
[21] 石岩, 范晓磊, 肖新月, 等. 鹿角胶中4个主要氨基酸的测定研究[J]. 药物分析杂志, 2012,32(5):783-787.
[22] 蒋梦彤, 黄潇正, 蔡朔, 等. 基于Label-free定量多肽组学的鹿角胶与鹿皮胶糖基化肽研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(14):3487-3493.
[23] 宫瑞泽, 张磊, 刘畅, 等. 《中华人民共和国药典》收载的鹿源药材中胶原蛋白对比分析[J]. 药物分析杂志,2020,40(2):373-381.
[24] 郑洁. 胶类中药蛋白质的分析及鉴定研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学,2017.
[25] KRAM V, SHAINER R, JANI P, et al. Biglycan in the skeleton. J Histochem Cytochem. 2020;68(11):747-762.
[26] LIN W, ZHU X, GAO L, et al. Osteomodulin positively regulates osteogenesis through interaction with BMP2. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(2):147.
[27] HARTEN IA, KABER G, AGARWAL KJ, et al. The synthesis and secretion of versican isoform V3 by mammalian cells: A role for N-linked glycosylation. Matrix Biol. 2020;89:27-42.
[28] DAQUINAG AC, GAO Z, FUSSELL C, et al. Glycosaminoglycan modification of decorin depends on MMP14 activity and regulates collagen assembly. Cells. 2020;9(12):2646.
[29] BERTASSONI L, SWAIN M. The contribution of proteoglycans to te mechanical behavior of mineralized tissues. Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;38(10):91-104.
[30] CHERY DR, HAN B, ZHOU Y,et al. Decorin regulates cartilage pericellular matrix micromechanobiology. Matrix Biol. 2021;96:1-17.
[31] HAN B, LI Q, WANG C, et al. Differentiated activities of decorin and biglycan in the progression of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(8):1181-1192. |