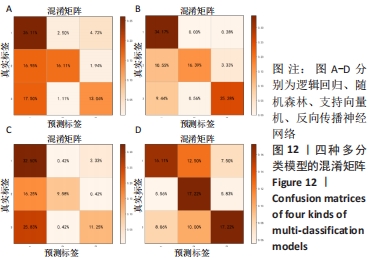
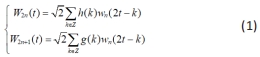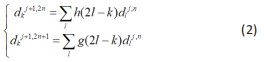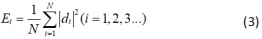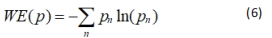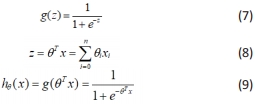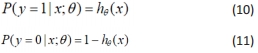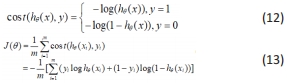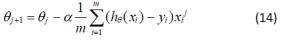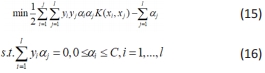1.1 设计 眩晕基于脑电信号的分类研究。
1.2 时间及地点 试验于2020年9月至2021年11月在河北工业大学电气工程学院生物医学工程系脑电信号采集与处理实验室完成。
1.3 对象 在校园内招募志愿者,选取37名在校大学生作为健康被试,其中男22名,女15名;年龄20-28岁,平均年龄24.8岁;皆为右利手。所有被试均不存在任何精神和神经类疾病,体内无植入器件。参加试验前被试应得到充足的睡眠和休息,以便集中精神配合试验。试验前已告知试验内容,并签署了知情同意书,参加试验前均未接触过类似的相关试验。被试在试验过程中闭眼,佩戴耳塞,并保持安静清醒。该研究的实施符合河北工业大学的相关伦理要求,河北工业大学伦理委员出具了伦理审查证明(HEBUThMEC2020007)。
1.4 方法
1.4.1 刺激试验 采用的前庭电刺激设备为德国Neuroconn公司生产的前庭神经电刺激仪。刺激模式选择为DC模式,淡入淡出时间设置为10 s,刺激持续时间为1 min,刺激电流的变化,见图1。选取左右乳突作为刺激点,将刺激电极阴阳两极贴片分别放置于左右乳突位置上,刺激电极位置,见图2。
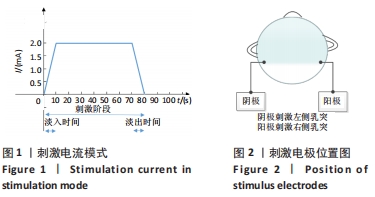
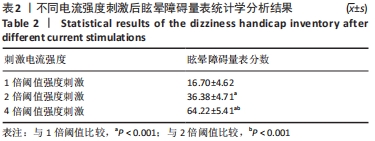
首先,进行皮肤感知阈值测试,即电流强度从20 μA开始,施加20 s电流刺激。如果被试没有报告刺痛感,电流强度就以20 μA的增量递增再进行电流刺激,以此类推。相邻2次刺激间隔至少为10 min,以防止滞后效应影响下一次测试。直到被试口头报告在刺激区域感受到轻微的局部刺痛感,测试结束。这时的刺激电流强度即为皮肤感知阈值电流强度。而后以1,2,4倍皮肤感知阈值的电流强度来进行前庭电刺激。根据目前直流电刺激的安全指导参数,最大刺激电流不超过2 mA,最长持续时间不超过20 min。在安全指导参数下将直流电应用于皮质,无论是对健康人还是有神经病学疾病患者,不良作用都很小[28],该试验刺激电流强度和持续时间严格符合安全指导参数。为防止不同阈值电流强度刺激试验的叠加效应,不同的阈值刺激试验前后间隔时间为10 min以上。
1.4.2 眩晕障碍量表评估 眩晕障碍量表共25个问题,分别评定患者的躯体、情绪和功能3方面的损害程度,分别有7,9,9个问题,对应的分值为28,36,36分,每个问题都会有3个选项供患者选择,分别是“是、有时、无”,相应计分为“4,2,0”分。总分为3方面评分之和,满分为100分,得分越高,主体症状与躯体、情绪和功能障碍越严重。依据评分的等级标准,0-30分为轻度障碍(Ⅰ级眩晕等级),31-60分为中度障碍(Ⅱ级眩晕等级),61-100分为重度障碍(Ⅲ级眩晕等级)。上述量表皆为自填问卷,测评时需向患者说明调查的目的、意义及填写要求,让被试如实、独立填写[29]。
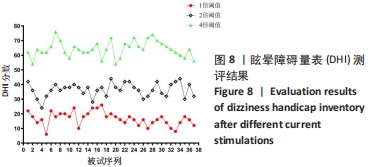
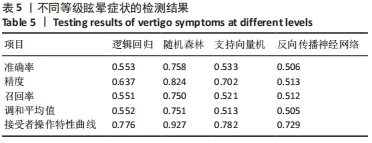
为了将前庭电刺激引起的眩晕效果进行具体量化,被试在不同强度电流刺激前后需要填写眩晕障碍量表,为确保测评结果的准确性,要求每位被试熟悉了解刺激试验流程以及量表内容填写规则,对某一强度的刺激电流重复刺激3次,取3次测评结果的平均值作为最终的测评结果。根据测评分数的统计学分析将不同眩晕症状划分为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ等级。以此作为脑电信号小波分解特征分类的有监督学习分类标签。
1.4.3 脑电试验 采用的脑电采集系统为美国Neuroscan公司生产的ESI-128脑电信号采集分析系统。试验中记录64导电极的脑电信号,采样频率为1 000 Hz,电极阻抗参考阈值为5 kΩ,左右耳垂作为参考电极。对每位被试分别在刺激前后采集60 s脑电信号。将采集到的脑电信号按眩晕障碍量表测评分数得到的眩晕等级来标记和划分,作为分类样本。
1.5 数据处理方法
1.5.1 脑电数据预处理 利用MATLAB软件工具箱EEGLAB对脑电信号进行预处理。主要包括通过PCA主成分分析法去除眼电、肌电,去除工频伪迹干扰,进行0.5-45 Hz范围的带通滤波,剔除坏导、坏段,对脑电信号进行分段和基线校正,分段提取刺激前和刺激后的试验数据。
1.5.2 小波分解 小波分析是一种时间和尺度熵的局部分析方法,它对信号具有自适应性。小波变换可以把原始信号分成不同的频段,进而获得有效的时频信息。小波变换的双尺度方程为:
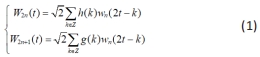
其中,h(k),g(k)是尺度函数与小波函数的滤波器系数,也是多分辨分析中的滤波系数。当n=0时。w0(t)=φ(t),w1=(t)=Ψ(t)。其中,w0(t)=φ(t)为尺度函数,w1(t)=Ψ(t)为小波函数。{wn=(t),n∈z}为由w0(t)=φ(t)所确定的小波包。根据小波包变换的性质,可以得到小波包系数的递推公式为:
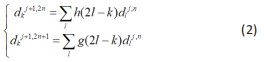
小波包的节律能量均值定义为:
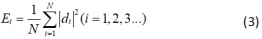
其中,N为采样点个数,d1-d6为各个节律的小波系数,Ei为第i个节律波的平均能量。对其值进行归一化处理,信号的总能量E为各个频带能量之和。

Pn为相对小波能量,计算公式如下:

小波熵WE(p)的公式如下:
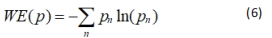
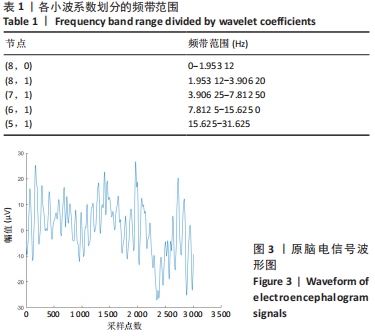
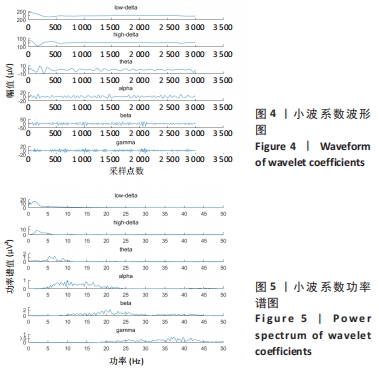
采用小波基为db4,用8层小波包分解,提取能近似反映不同的脑电节律low-δ(0.5-2 Hz),high-δ(2-4 Hz),θ(4-8 Hz),α(8-13 Hz),β(13-30 Hz),γ(30-45 Hz)的小波系数。其中,各个小波系数划分的频带范围,见表1。这里将此次试验采集的一段3 s的脑电信号进行小波分解,原始脑电信号,见图3,小波系数波形以及对应的频谱,见图4和图5。
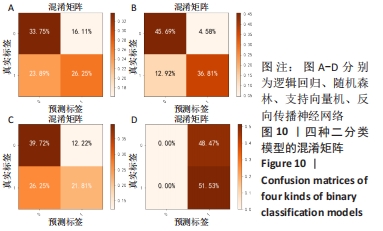
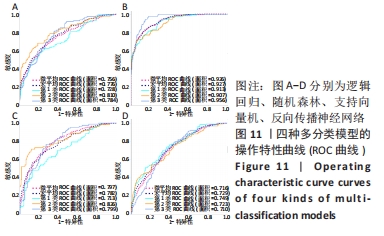
1.5.3 脑电信号分类特征的提取 为提取脑电信号的分类特征,取代表不同脑区的9个典型电极(FP1,FP2,P1,P2,T7,T8,CZ,O1,O2)。设1.5 s为小波变换的单位,取其小波系数能量以及小波熵作为样本特征,得到了8 880行63列的数据集。训练集与测试集的划分比例为7∶3,为保证模型对样本特征的适应性,在划分数据集前均进行归一化和交叉验证处理。由于健康被试刺激前无眩晕症状而且刺激后会引起健康被试明显的眩晕症状,因此将无眩晕症状的数据特征标签设定为0类,对存在眩晕症状的数据特征标签设定为1类,对有无眩晕症状的样本特征进行二分类研究。根据眩晕障碍量表的评测结果将刺激后引起的眩晕症状划分为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ这3个等级,为了对存在眩晕症状的样本特征进行检测分类,依次将眩晕等级为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ级的样本特征的标签设定为1,2,3类,对这3种不同等级的眩晕样本特征进行多分类研究。
1.5.4 分类算法
(1)逻辑回归分类:逻辑回归是一种比较有效和实用的分类算法,逻辑回归算法是基于多元线性回归的算法,而多分类逻辑回归是逻辑回归的扩展延伸,可以进行多类别预测。与其他分类器相比,多分类逻辑回归有一定的优势,算法对高维数据有更好的计算能力,逻辑回归算法如下:
①构造逻辑回归的预测函数hθ(x):
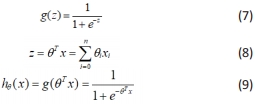
其中,x为输入特征,θ为估计量,当Logistic回归用来分类标签0和1问题时,就转化为预测标签概率问题。
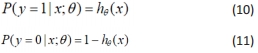
其中,x为输入特征,y为标签,θ为估计量。
②构造损失函数cos t(hθ,y)和j(θ),假设存在有m个样本且每个样本有n个特征。
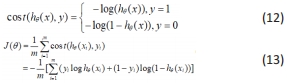
③为使得损失j(θ)最小,采用梯度下降法更新迭代θ,求解最优参数θ,进而得出预测结果。
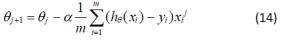
其中,j=0,1,2,…,n;α为更新步长。
(2)支持向量机:支持向量机通过将低维度的信号映射到高维度的特征空间,实现将样本特征进行更好地分离[30],从而用于模式分类和非线性回归。支持向量机的主要思想是建立一个分类超平面作为决策曲面,使得正例和反例之间的隔离边缘最大化。支持向量机最终决策函数只是由少数的支持向量所决定,计算的复杂性取决于支持向量的数目,而不是样本空间的维数,这在某种意义上避免了“维数灾难”。这里以二分类模型为例介绍其基本原理,其中,C-SVC模型是比较常见的二分类支持向量机模型,其具体形式如下:
①设已知训练集:
 其中,X为特征向量,Y为标签。
其中,X为特征向量,Y为标签。
②选取适当的核函数K(x,x’)和适当的参数C,构造并求解最优化问题:
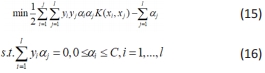
得到最优解:α*={α1*,…,αl*}T
③选取α*的一个正分量,0<αj*<C并据此计算阈值:

④构造决策函数:

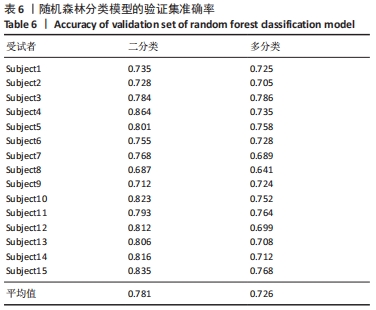
(3)随机森林分类:随机森林算法实质是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,这些决策树的形成采用了随机方法,随机森林中的树之间是没有关联的。当测试数据进入随机森林时,其实就是让每一棵决策树进行分类,其输出的类别是由个别决策树输出的类别的众数而定,最后取所有决策树中分类结果最多的那类为最终结果,随机森林算法的结构示意图,见图6。随机森林算法在构建决策树的时候,采用了随机选取分类属性集的方法。详细的随机森林算法如下所示(设样本的属性个数为M,m为大于0且小于M的整数):
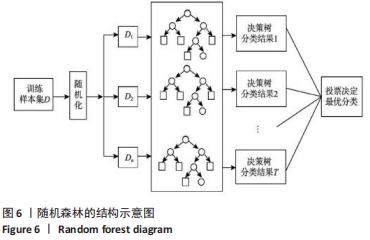
①利用Bootstrap方法重采样,随机产生T个训练集S1,S2,S3,…,ST。
②利用每个训练集,生成对应的决策树D1,D2,…,DT;在每个非叶子节点(内部节点)上选择属性前,从M个属性中随机抽取m个属性作为当前节点的分类属性集,并以这m个属性中最好的分裂方式对该节点进行分裂(一般而言,在整个森林的成长过程中,m的值维持不变)。
③每棵树都完整成长,而不进行剪枝。
④对于测试集样本X,利用每个决策数进行测试,得到对应的类别D1(X),D2(X),…,DT(X)。
⑤利用投票的方法,将T个决策树中输出最多的类别作为测试集样本X所属的类别。
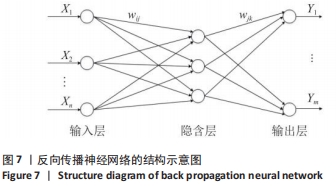
(4)反向传播神经网络(BP神经网络)分类:反向传播神经网络是一种多层前馈神经网络,该网络的主要特点是信号前向传递,误差反向传播。在前向传递中,输入信号从输入层经隐含层处理,直至输出层。每一层的神经元状态只影响下一层神经元状态。如果输出层得不到期望输出,则转入误差反向传播,根据预测误差调整网络权值和阈值,从而使反向传播神经网络预测输出不断逼近期望输出。反向传播神经网络的拓扑结构,见图7。
反向传播神经网络的训练过程包括以下几个步骤:
①网络初始化。根据系统输入输出序列(X,Y)确定网络输入层节点数n、隐含层节点数l,输出层节点数m,初始化输入层、隐含层和输出层神经元之间的连接权值wij,wjk。初始化隐含层阈值a,输出层阈值b,给定学习速率和神经元激励函数。
②隐含层输出计算。根据输入变量X,输入层和隐含层间连接权值wij以及隐含层阈值a,计算隐含层输出H。

式中,l为隐含层接点数;f为隐含层激励函数,该函数有多种表达形式,文中所选函数为:

③输出层输出计算。根据隐含层输出H,连接权值wjk和阈值b,计算反向传播神经网络预测输出O。

④误差计算。根据网络预测输出和期望输出Y,计算网络预测误差e。

⑤权值更新。根据网络预测误差e更新网络连接权值wij,wjk。

其中,i=1,2,…,n,j=1,2,…,l。

其中,j=1,2,…,l,k=1,2,…,m,式中η为学习速率。
⑥阈值更新。根据网络预测误差更新网络节点阈值a,b。

其中,j=1,2,…,l,k=1,2,…,m。
⑦判断算法迭代是否结束,若没有结束,返回步骤②。
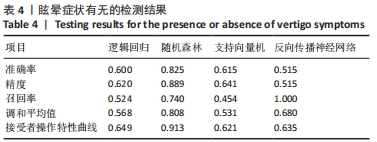
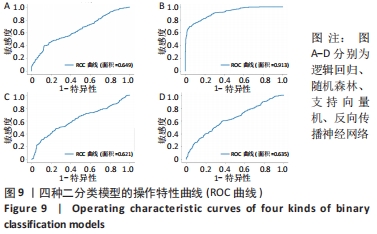
1.6 主要观察指标 为了更好地评估机器学习模型的分类性能,采用准确率、精确率、召回率、调和平均值、接受者操作特性曲线(ROC)以及操作特性曲线下面积(AUC)这6个评价指标来综合评估不同模型的分类效果。定义TP、TN、FP、FN分别为真阳性、真阴性、假阳性、假阴性。其中,准确率、精确率、召回率、调和平均值的计算公式如下:

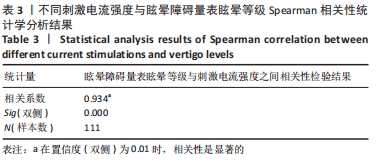
1.7 统计学分析 利用SPSS 21.0软件将1,2,4倍阈值刺激的眩晕障碍量表评分两两进行配对样本t检验,分析其显著性差异。不同刺激电流强度与眩晕障碍量表眩晕等级两者之间的关系采用Spearman相关性方法进行分析,观察并分析刺激电流强度与眩晕等级之间的相关性。