中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (24): 3875-3879.doi: 10.12307/2022.569
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
沈阳地区血小板输注无效患者的抗体检测与交叉配型结果分析
王宏阳,李晓丰,周助人,李函频,丛日娇,李剑平
- 辽宁省血液中心输血医学研究所,辽宁省沈阳市 110044
Antibody detection and cross-matching results in patients with ineffective platelet transfusion in Shenyang region
Wang Hongyang, Li Xiaofeng, Zhou Zhuren, Li Hanpin, Cong Rijiao, Li Jianping
- Liaoning Blood Center Institute of Transfusion Medicine, Shenyang 110044, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
血小板输注无效:是指患者在连续2次输注ABO血型相合且足够剂量的血小板悬液后仍处于无反应状态,即血小板计数未见显著升高,临床出血倾向未见减轻。
血小板抗原系统:分为两类,一类是血小板非特异性抗原,即血小板与其他细胞或组织共有的抗原,包括HLA-1抗原、ABH抗原、Le及P抗原等;另一类是血小板特异性抗原(human platelet antigen,HPA)。
背景:随着血小板输注的广泛应用,血小板输注无效患者呈逐年增多的趋势。
目的:通过对血小板输注无效患者的血小板抗体和交叉配型情况进行检测分析,为血小板输注无效患者提高输注效果提供参考依据。
方法:选取2020年4-12月期间112例血小板输注无效患者,使用血小板抗体检测试剂盒(固相凝集法)进行血小板抗体检测及交叉配型实验。
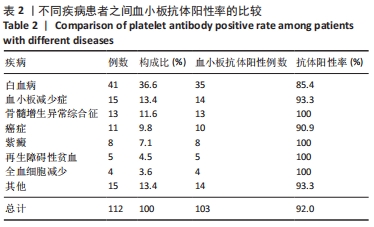
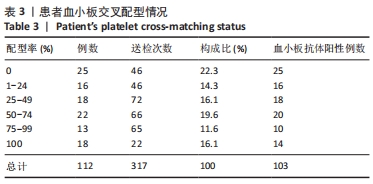
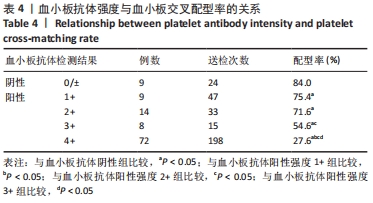
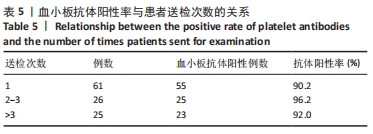
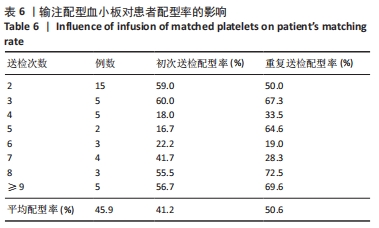
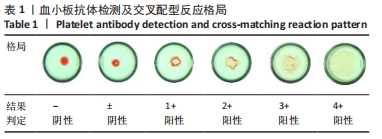
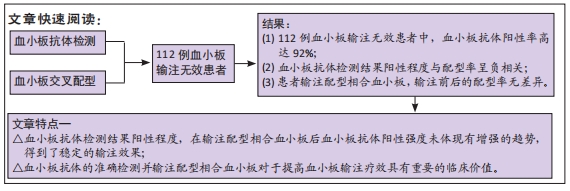
结果与结论:①血小板抗体检测结果:112例患者中有103例血小板抗体检测结果为阳性,阳性率高达92%;②血小板交叉配型结果:有25例患者在交叉配型实验中与供者的血小板均不相合,有18例患者与所有供者的血小板均相合;③血小板抗体检测结果与配型率的关系:血小板抗体检测结果为阴性的血小板配型率为84%、血小板抗体检测结果为1+,2+,3+,4+的血小板配型率分别为75.4%,71.6%,54.6%,27.6%,各组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④血小板抗体阳性率与患者多次送检的关系:血小板输注次数<2次和≥2次的血小板抗体阳性率分别为90.2%和94.2%,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤输注配型血小板对患者配型率的影响:在送检次数相同的各组中,初次送检配型率与重复送检配型率差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);在所有重复送检的患者中,初次送检与重复送检的平均配型率分别为41.2%和50.6%,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑥结果表明,血小板抗体检测结果阳性程度越高其配型率越低,患者在输注配型相合血小板后血小板抗体阳性强度未体现有增强的趋势,得到了稳定的输注效果,血小板抗体的准确检测以及输注配型相合血小板对于提高血小板输注疗效具有重要的临床价值。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5392-0471 (李剑平);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3888-6359 (李晓丰)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: