中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2738-2743.doi: 10.12307/2022.544
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
构建大肠埃希菌pgaABCD基因缺失株和互补株的生物被膜形成能力
宫海燕1,程 倩2,赵智龙1,施 洋3
- 1新疆医科大学第五附属医院检验科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000;2中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所,北京市 102206;3新疆医科大学,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
Construction of pgaABCD gene deletion and complementation strains and properties of biofilm formation ability for Escherichia coli
Gong Haiyan1, Cheng Qian2, Zhao Zhilong1, Shi Yang3
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 102206, China; 3Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
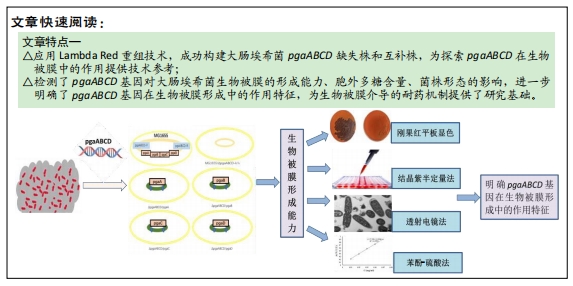
Lambda Red重组技术:该技术能使外源同源线性DNA片段快速与基因组DNA相应基因同源重组,主要包括pKD46、pKD3、pCP20三个协助质粒。该方法广泛用于细菌的基因重组,稳定性较好,方法成熟。此次研究采用质粒pKD46、pCP20、pBR322,成功构建大肠埃希菌pgaABCD基因的缺失株和互补株,稳定性较好,适合该基因的敲除和回补。
生物被膜:生物被膜细菌对抗生素和杀菌消毒剂的抵抗力比浮游的非生物膜细菌高100-1 000倍,抗生素的应用不仅不能有效清除生物被膜,甚至还可以诱导细菌耐药性的产生,即生物被膜是造成细菌耐药性的首要因素。
背景:大肠埃希菌形成生物被膜引发难治性的慢性感染,严重威胁了人类的健康。pgaABCD操纵子是生物被膜形成的重要调节基因之一。
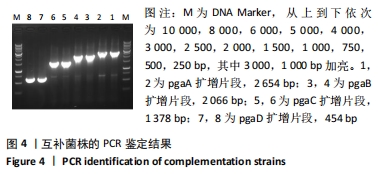
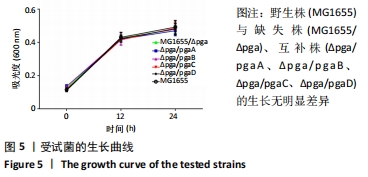
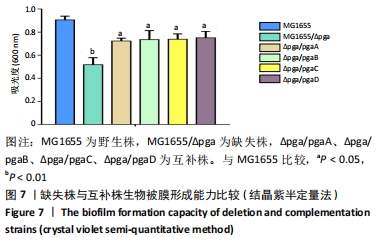
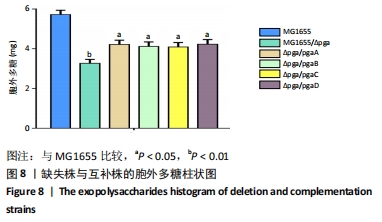
目的:构建大肠埃希菌缺失菌株MG1655/Δpga,并分别回补pgaA、pgaB、pgaC、pgaD,构建互补株Δpga/pgaA、Δpga/pgaB、Δpga/pgaC、Δpga/pgaD,观察缺失株、互补株的生物被膜形成能力、胞外多糖含量及菌株形态学特征,分析pga基因对生物被膜的调节作用。
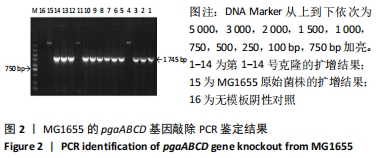
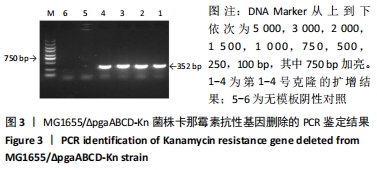
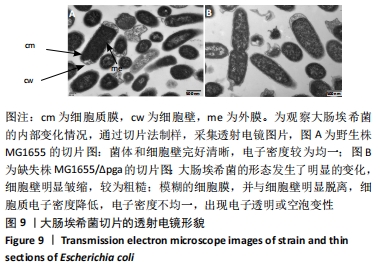
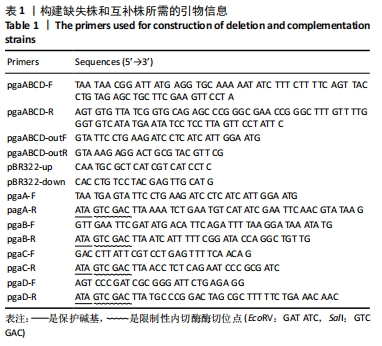
方法:在Lambda Red重组系统基础上,将pKD46辅助质粒转化入MG1655感受态细胞,获得MG1655/pKD46单克隆。pgaABCD打靶片段转入感受态细胞MG1655/pKD46,利用辅助质粒pCP20构建缺失株MG1655/ΔG16。以质粒pBR322作为回补载体,构建pBR322-pgaA、pgaB、pgaC、pgaD四个质粒,通过电转化的方式分别转入MG1655/ΔG16,获得相应的互补株。应用刚果红平板、结晶紫半定量法、透射电镜检测构建菌株生物被膜形成能力特性的变化,苯酚-硫酸法检测其胞外多糖的含量。
结果与结论:①缺失株生物被膜形成能力和胞外多糖含量显著降低(P < 0.05),有细胞溃烂溶解现象,切片发现菌内空泡变性;②提示大肠埃希菌pgaABCD基因的缺失会影响生物被膜的特性,且pgaA、pgaB、pgaC、pgaD均参与生物被膜的形成,但不是唯一调控基因。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9698-7644 (宫海燕)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: